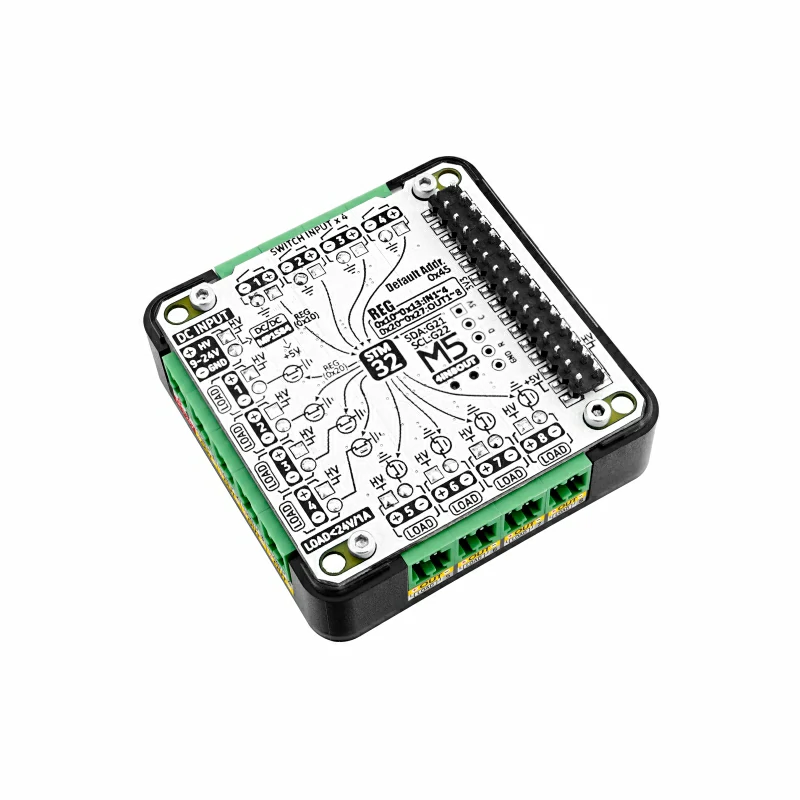
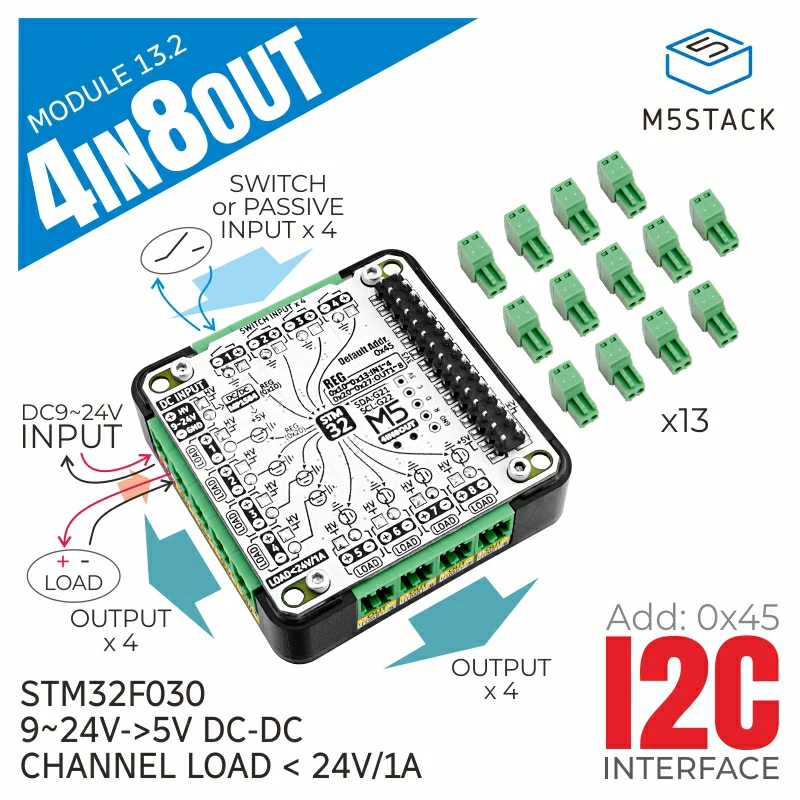
Module13.2 4In8Out
SKU:M122













描述
Module13.2 4In8Out 是一款8 路 MOS 驱动输出 + 4 路无源接点输入的 IO 扩展模块。它采用 STM32F030 作为 I2C 的 IO 扩展芯片,支持 9 ~ 24V 电源输入,内置转 5V DC-DC 电路。
产品特性
- 适用于 Basic/Fire/Core2/CoreS3 等主机
- 采用 STM32F030 作为 IO 扩展芯片,采用 I2C 与主机通信,I2C 地址能通过写入寄存器修改
- 8 路共电源正极 MOS 管驱动电路 (A3400), 能直接驱动负载,每路最大通断电流 1A
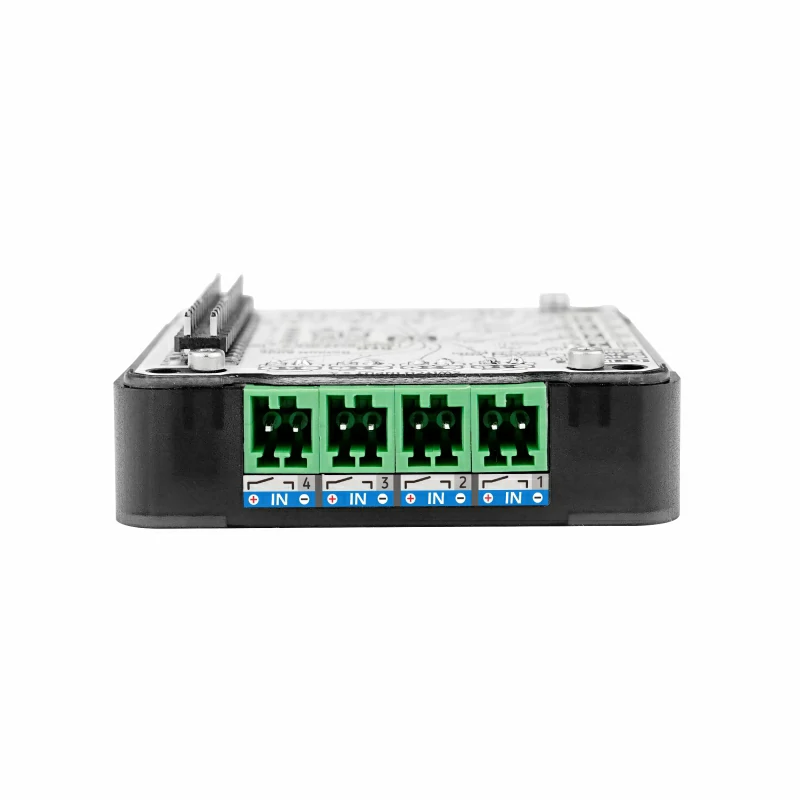
- 4 路共地无源接点输入,不能接入有源信号 或 大于5V的信号
- 内置 MP1584 9~24V -> 5V DC-DC 电路
包装内容
- 1 x Module13.2 4In8Out
- 13 x 2P 端子
应用场景
- 多通道负载驱动 (继电器、气阀、单向电机、信号指示灯等)
- 限位开关、按键检测
规格参数
| 规格 | 参数 |
|---|---|
| MCU | STM32F030F4P6 |
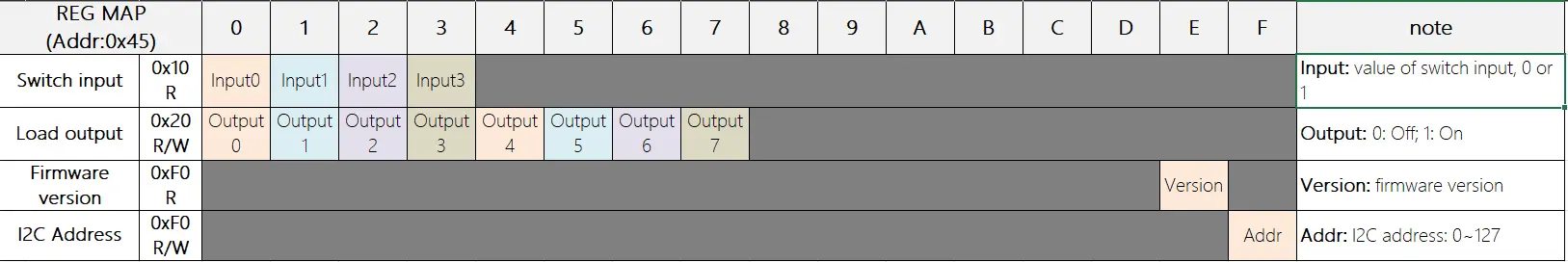
| 通信接口 | I2C 通信 @ 0x45 |
| 供电电压 | 9~24V |
| 输出通道 | 8 |
| 输入通道 | 4 |
| 输出电流 | 每路 1A, 总电流不大于 8A |
| 通讯接口 | I2C |
| I2C 地址 | 默认 0x45, 可通过写入寄存器 0xFF 修改 |
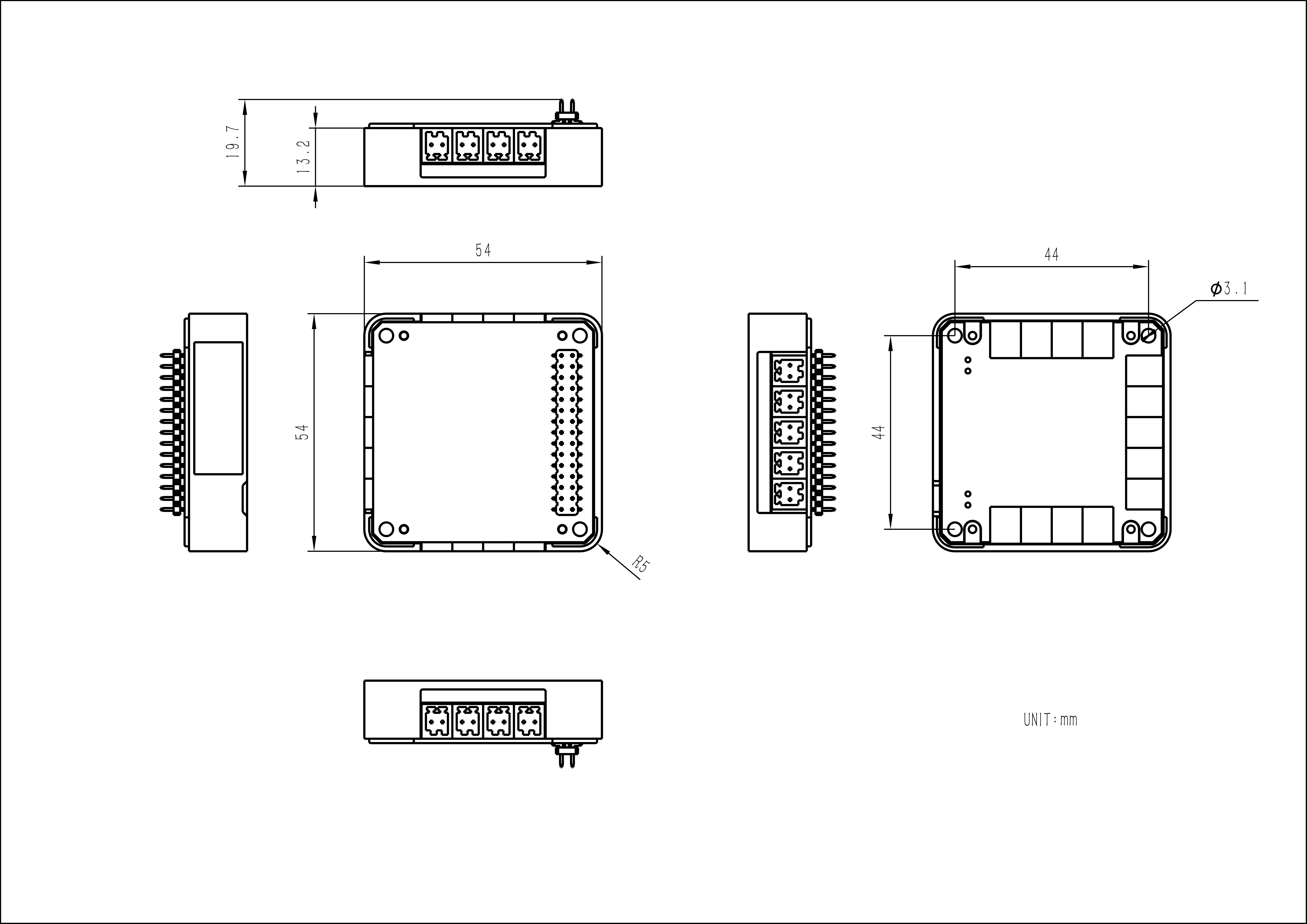
| 产品尺寸 | 54.0 x 54.0 x 19.7mm |
| 产品重量 | 21.9g |
| 包装尺寸 | 80.0 x 55.0 x 28.0mm |
| 毛重 | 52.5g |
操作说明
板载拨动开关的作用
下图红色框内是 boot0 的控制拨动开关,拨到 1 端拉高是刷写固件模式。拨到 0 端拉低是从闪存开始读取用户程序,即正常使用模式
.png)
原理图
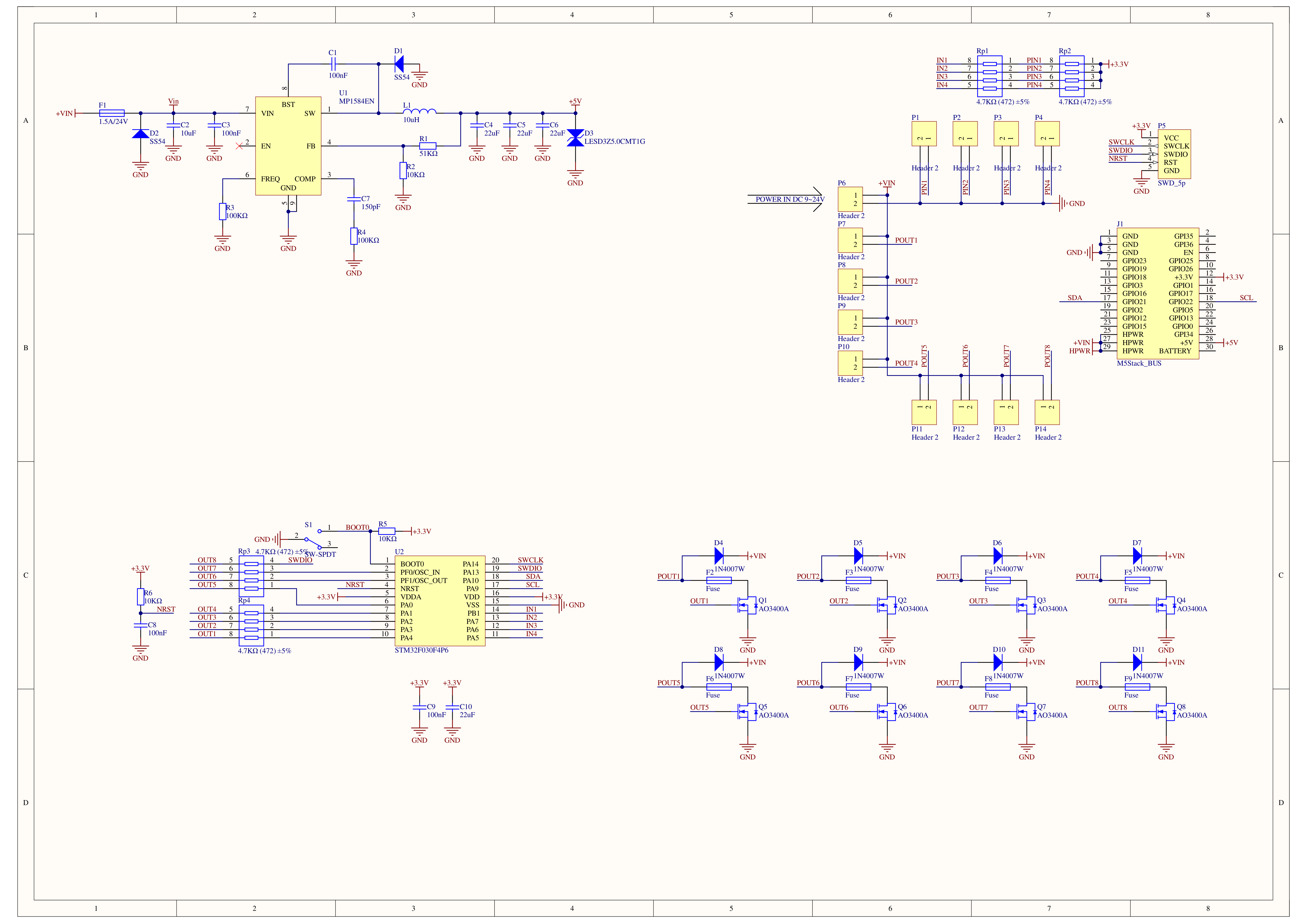
1/1

管脚映射
M5-Bus
| PIN | LEFT | RIGHT | PIN |
|---|---|---|---|
| GND | 1 | 2 | |
| GND | 3 | 4 | |
| GND | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | ||
| 9 | 10 | ||
| 11 | 12 | 3V3 | |
| 13 | 14 | ||
| 15 | 16 | ||
| SDA | 17 | 18 | SCL |
| 19 | 20 | ||
| 21 | 22 | ||
| 23 | 24 | ||
| HPWR | 25 | 26 | |
| HPWR | 27 | 28 | 5V |
| HPWR | 29 | 30 |
尺寸图
软件开发
Arduino
#include <M5Stack.h>
#include "MODULE_4IN8OUT.h"
MODULE_4IN8OUT module;
int _I2C_dev_scan();
void setup() {
M5.begin(1,1,1,1); // Init M5Stack. 初始化M5Stack
// while (1) {
// _I2C_dev_scan();
// delay(1000);
// }
while (!module.begin(&Wire, 21, 22, MODULE_4IN8OUT_ADDR)) {
Serial.println("4IN8OUT INIT ERROR");
M5.Lcd.println("4IN8OUT INIT ERROR");
_I2C_dev_scan();
delay(1000);
};
Serial.println("4IN8OUT INIT SUCCESS");
}
// void loop() {
// }
long interval = 0;
bool level = false;
void loop() {
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if (module.getInput(i) != 1) {
// M5.Lcd.fillRect(60 + 60 * i, 0, 25, 25, TFT_BLACK);
M5.Lcd.fillRect(60 + 60 * i, 0, 25, 25, TFT_GREEN);
} else {
// M5.Lcd.fillRect(60 + 60 * i, 0, 25, 25, TFT_BLACK);
// M5.Lcd.drawRect(60 + 60 * i, 0, 25, 25, TFT_GREEN);
M5.Lcd.fillRect(60 + 60 * i, 0, 25, 25, TFT_RED);
}
M5.Lcd.drawString("IN" + String(i), 40 + 60 * i, 5);
}
M5.Lcd.drawString("4IN8OUT MODULE", 60, 80, 4);
// M5.Lcd.drawString("FW VERSION:" + String(module.getVersion()), 70, 120, 4);
if (millis() - interval > 1000) {
interval = millis();
level = !level;
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
module.setOutput(i, level);
if (level) {
M5.Lcd.fillRect(20 + 35 * i, 200, 25, 25, TFT_BLACK);
M5.Lcd.fillRect(20 + 35 * i, 200, 25, 25, TFT_BLUE);
} else {
M5.Lcd.fillRect(20 + 35 * i, 200, 25, 25, TFT_BLACK);
M5.Lcd.drawRect(20 + 35 * i, 200, 25, 25, TFT_BLUE);
}
M5.Lcd.drawString("OUT" + String(i), 18 + 35 * i, 180);
// delay(50);
}
}
// if (M5.BtnB.wasPressed()) {
// if (module.setDeviceAddr(0x66)) {
// Serial.println("Update Addr: 0x66");
// }
// }
// M5.update();
delay(500);
}
int _I2C_dev_scan() {
uint8_t error, address;
int nDevices;
Serial.println("[I2C_SCAN] device scanning...");
nDevices = 0;
for (address = 1; address < 127; address++ ) {
// The i2c_scanner uses the return value of
// the Write.endTransmisstion to see if
// a device did acknowledge to the address.
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
error = Wire.endTransmission();
if (error == 0) {
Serial.print("[I2C_SCAN]: device found at address 0x");
if (address < 16)
Serial.print("0");
Serial.print(address, HEX);
Serial.println(" !");
nDevices++;
}
else if (error == 4) {
Serial.print("[I2C_SCAN]: unknow error at address 0x");
if (address < 16)
Serial.print("0");
Serial.println(address, HEX);
}
}
Serial.print("[I2C_SCAN]:");
Serial.printf(" %d devices was foundrn", nDevices);
return nDevices;
}UiFlow1
UiFlow2
通信协议