AI Pyramid - Home Assistant
Home Assistant is an open-source smart home platform that supports local device management and automation control, featuring privacy protection, high security, reliability, and extensive customization capabilities.
1. Preparation
2. Install Image
Refer to the Home Assistant Official Documentation or follow the steps below to deploy the Docker container.
- Pull the Home Assistant Docker image
- /PATH_TO_YOUR_CONFIG points to the folder where you want to store the configuration and run Home Assistant. Please make sure to keep the
:/configpart. - MY_TIME_ZONE is a tz database name, for example
TZ=America/Los_Angeles.
docker run -d \
--name homeassistant \
--privileged \
--restart=unless-stopped \
-e TZ=MY_TIME_ZONE \
-v /PATH_TO_YOUR_CONFIG:/config \
-v /run/dbus:/run/dbus:ro \
--network=host \
ghcr.io/home-assistant/home-assistant:stable3. HAOS Initialization
- Access the Home Assistant Web UI via a browser:
Local access:http://homeassistant.local:8123/
Remote access:http://DEVICE_IP:8123/
- Follow the on-screen instructions to create an administrator account and complete system initialization.
4. Device Firmware Compilation
- Refer to the ESPHome Official Installation Guide to deploy the ESPHome development environment on the development host.
This document is written based on ESPHome version 2026.2.1. There are significant differences between versions, so please select the appropriate version according to your project YAML configuration file.
pip install esphome==2026.2.1- Clone the M5Stack ESPHome Configuration Repository
git clone https://github.com/m5stack/esphome-yaml.git- Start the ESPHome Dashboard service
esphome dashboard esphome-yaml/- Access 127.0.0.1:6052 via a browser
- Configure Wi-Fi connection parameters
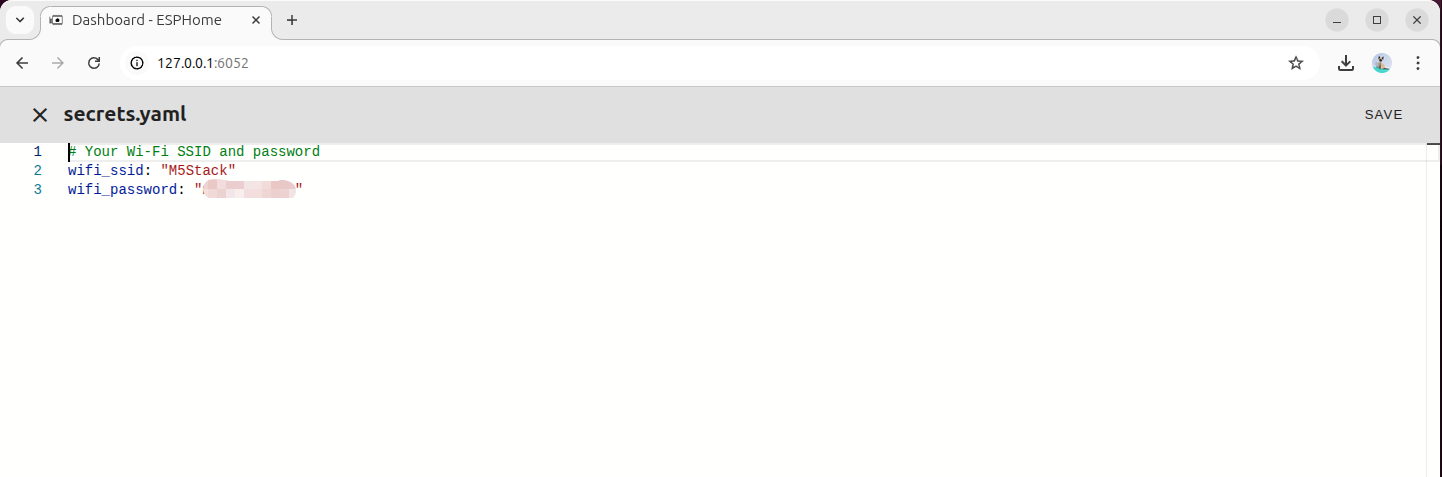
# Your Wi-Fi SSID and password
wifi_ssid: "your_wifi_name"
wifi_password: "your_wifi_password"- Generate an encryption key using OpenSSL
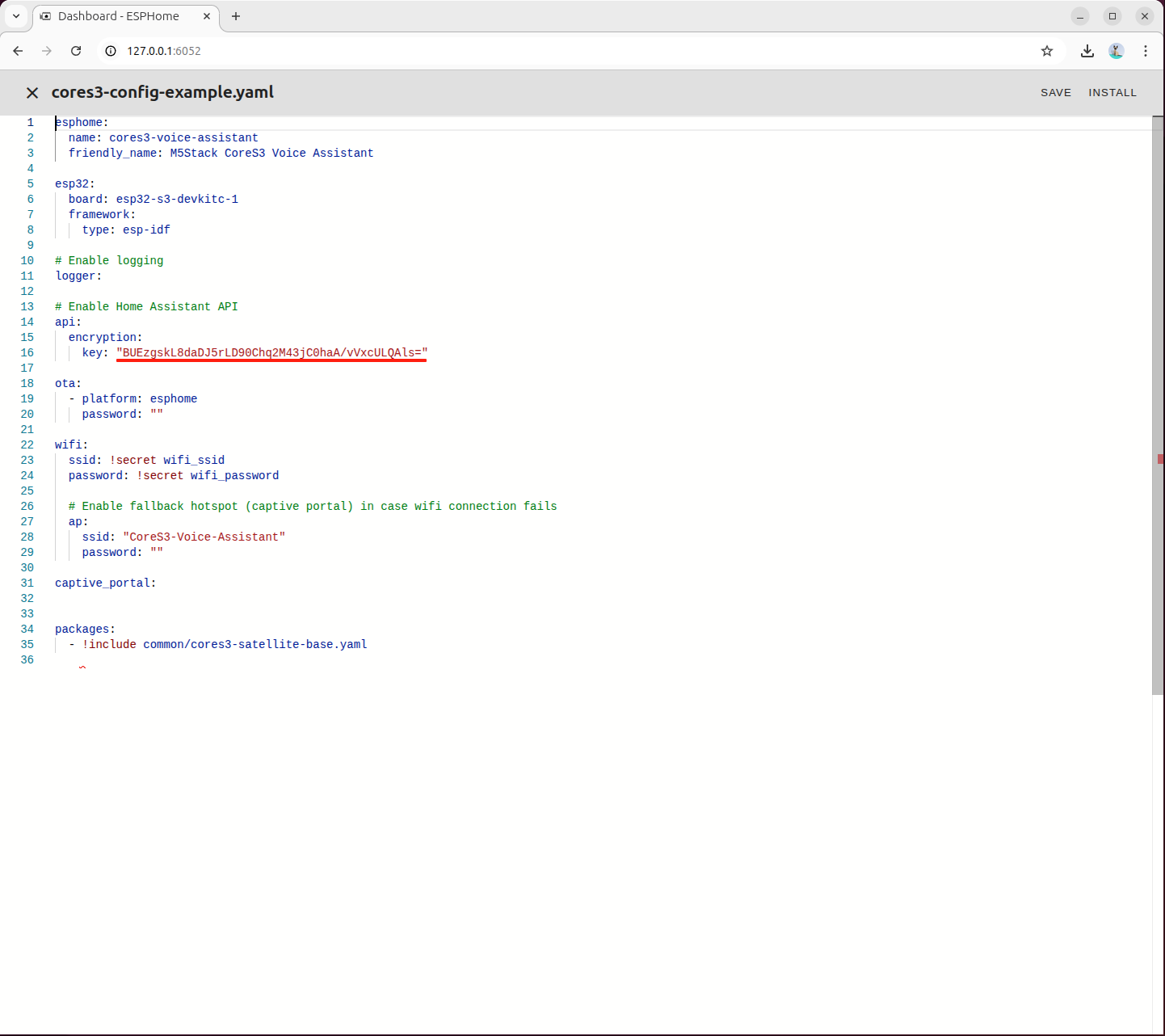
openssl rand -base64 32Example output:
(base) m5stack@MS-7E06:~$ openssl rand -base64 32
BUEzgskL8daDJ5rLD90Chq2M43jC0haA/vVxcULQAls=- Edit the
cores3-config-example.yamlconfiguration file and fill in the generated encryption key in the corresponding field
Click the INSTALL button in the upper-left corner to start compilation
Select the third option to view real-time compilation output via the terminal
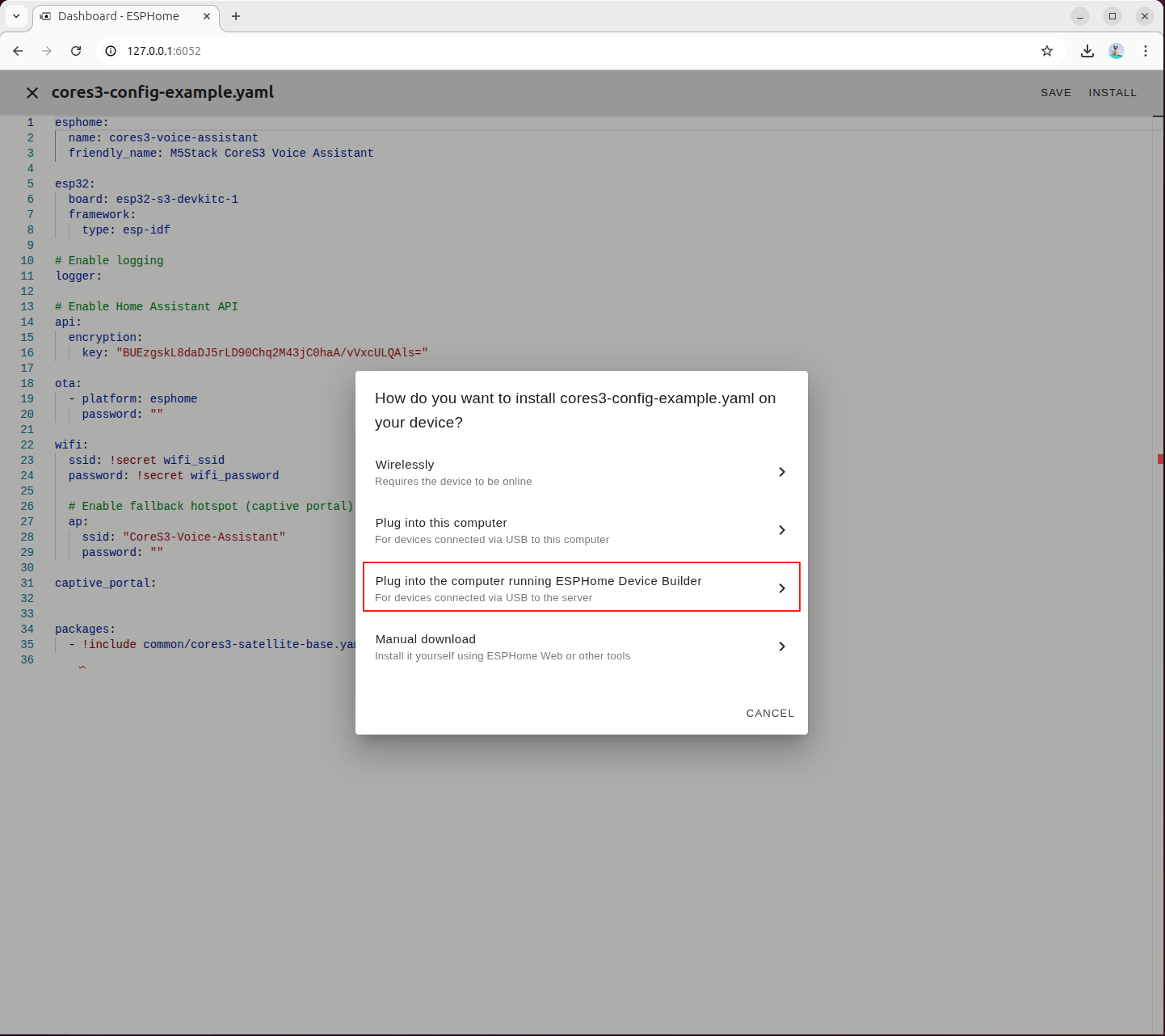
Select the serial port device corresponding to CoreS3
Required dependencies will be downloaded automatically during the first compilation
Wait for the firmware compilation and flashing process to complete
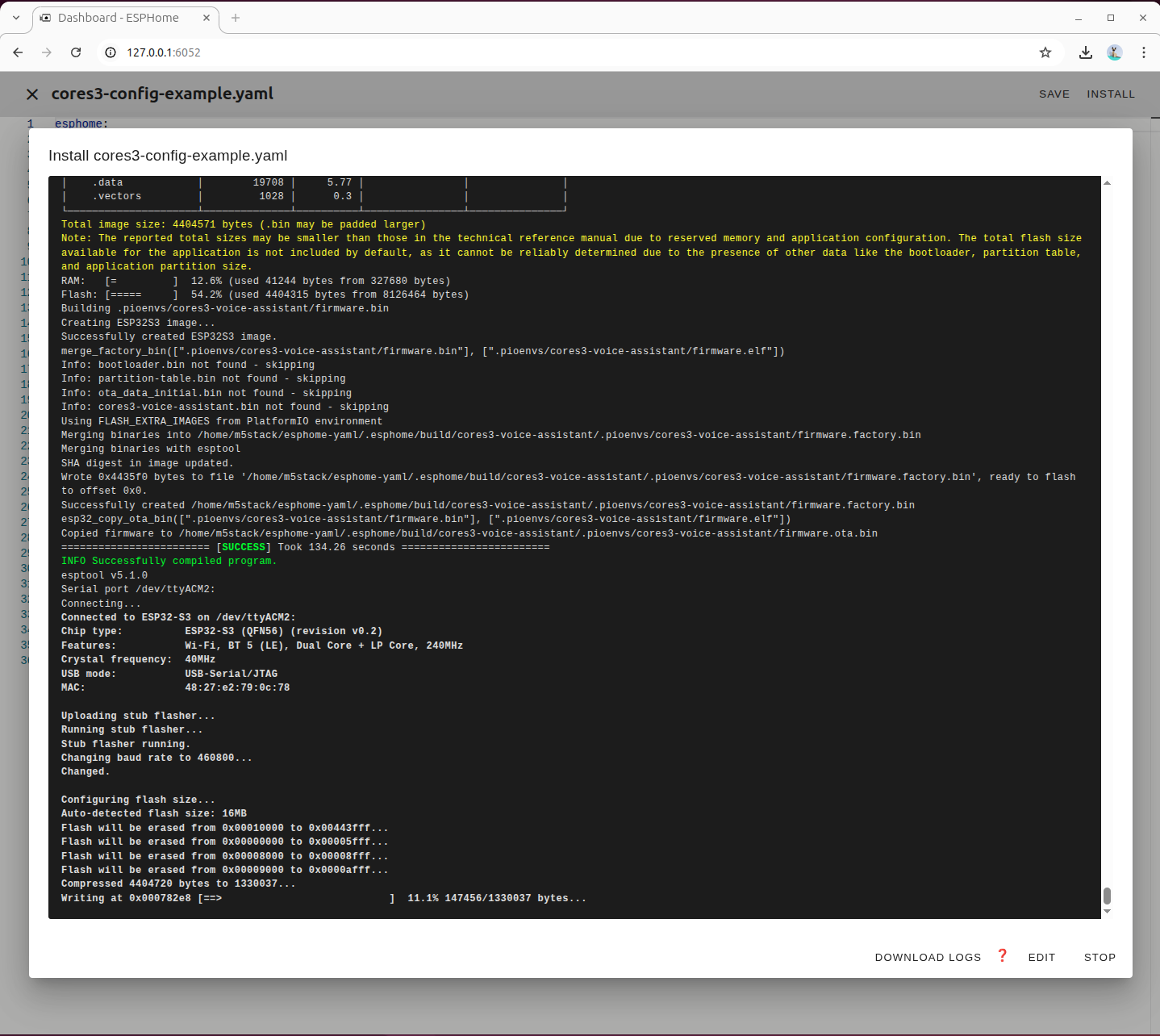
After the device restarts, record the IP address it obtains. This will be needed later when integrating the device into Home Assistant.
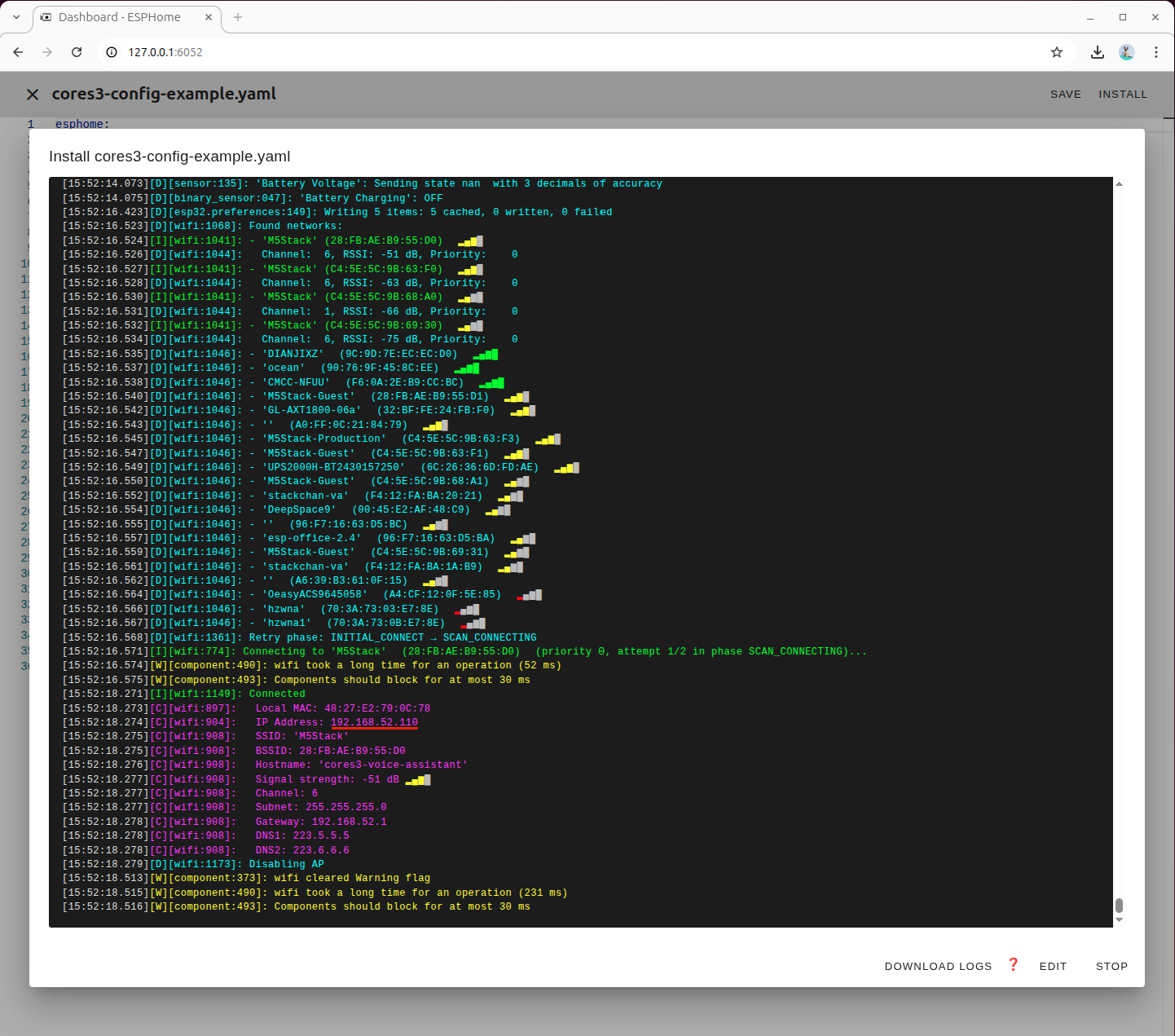
5. Add Device
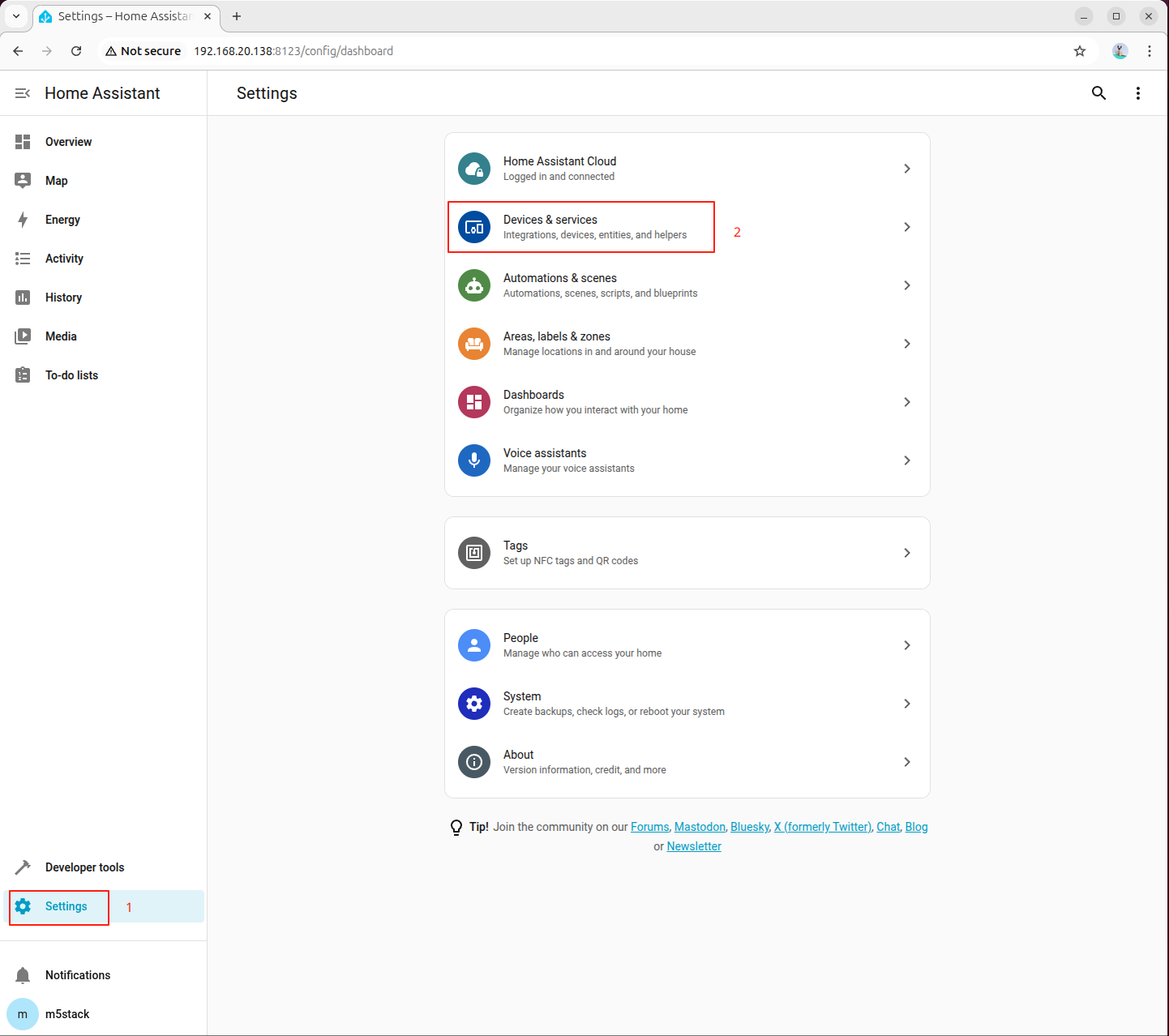
- Enter the Home Assistant settings page and select Add Device
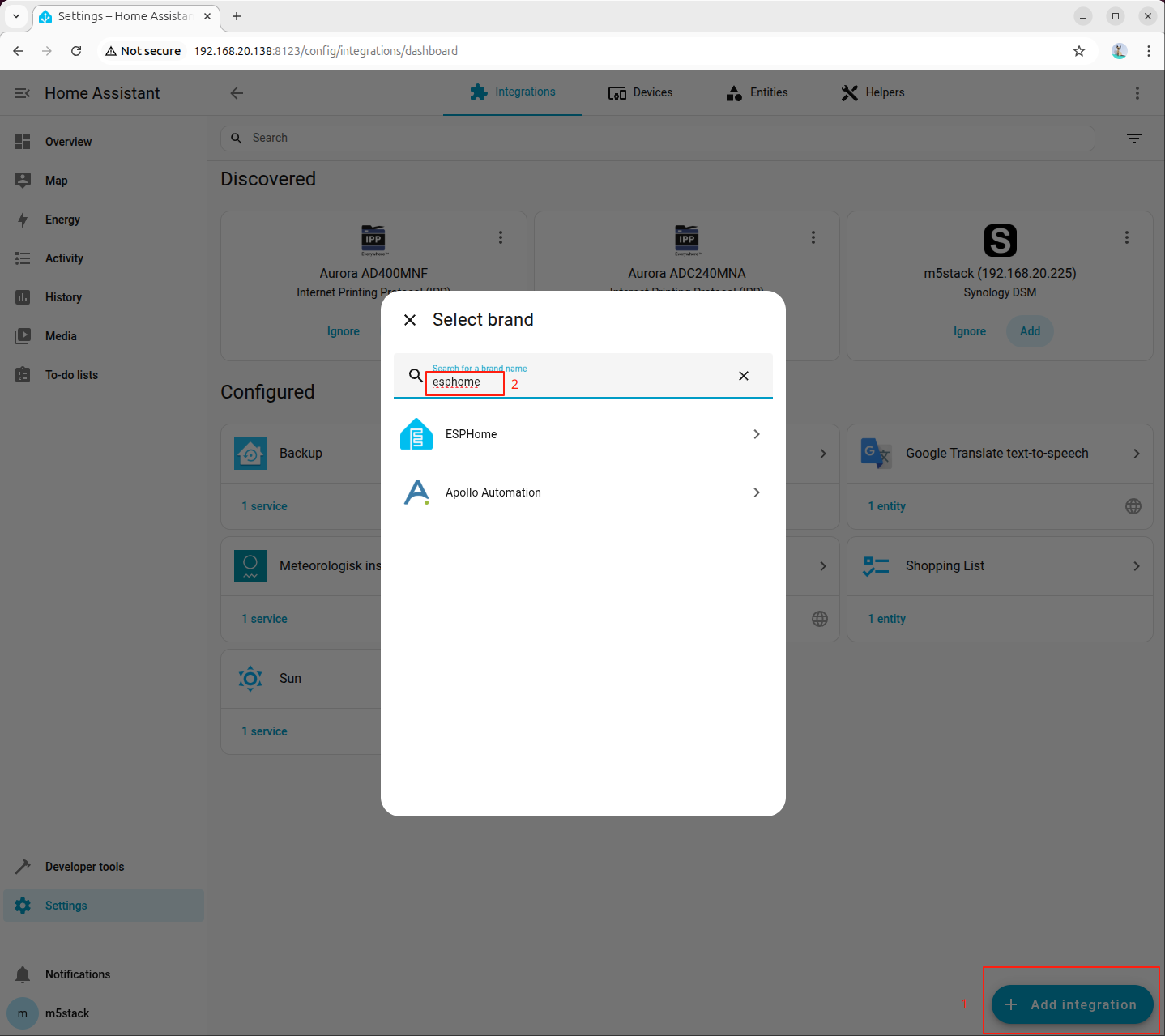
- Search for ESPHome in the integration list
- Enter the device IP address in the Host field, and the port number defined in the YAML configuration file in the Port field
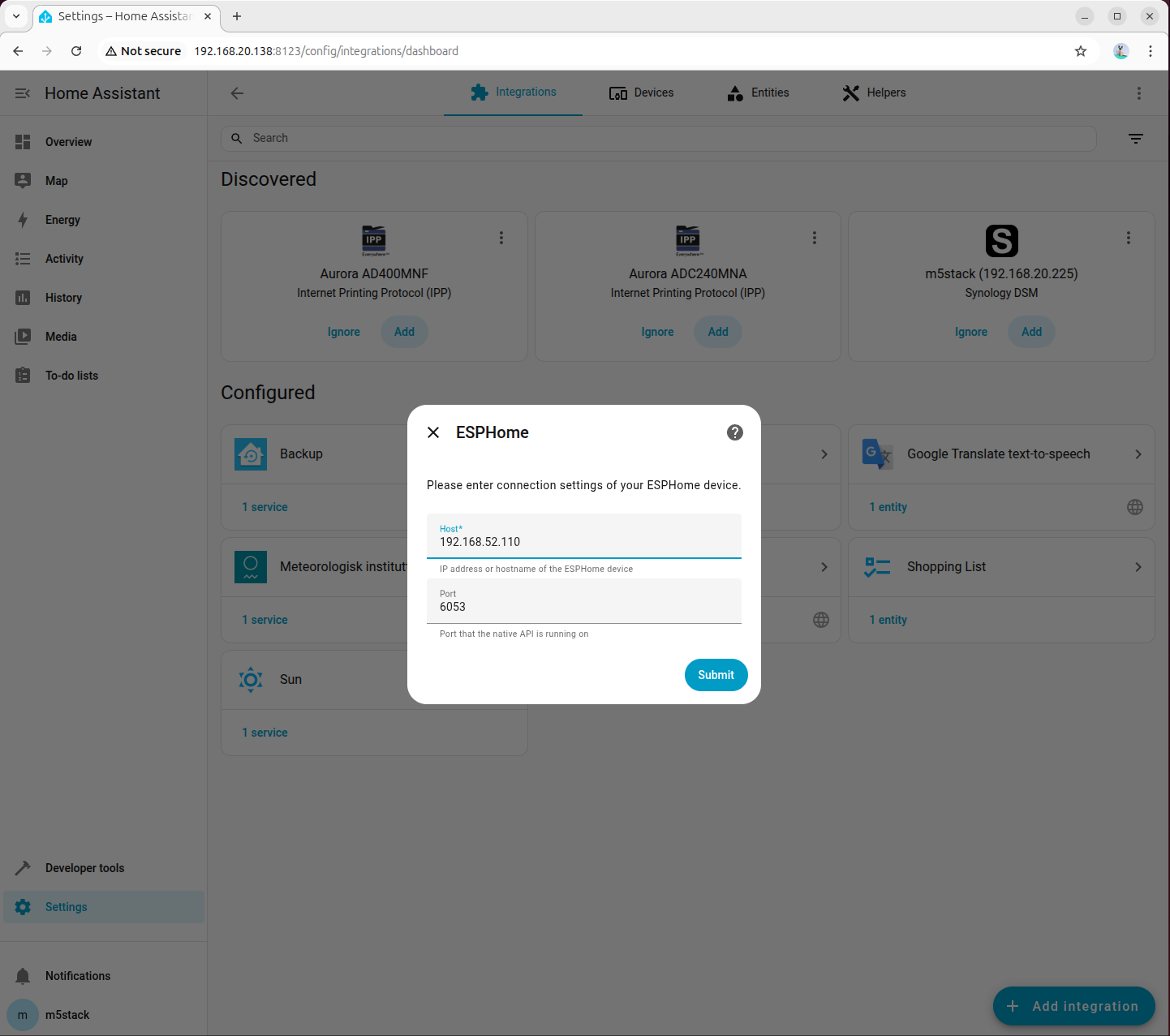
- Enter the encryption key defined in the YAML configuration file
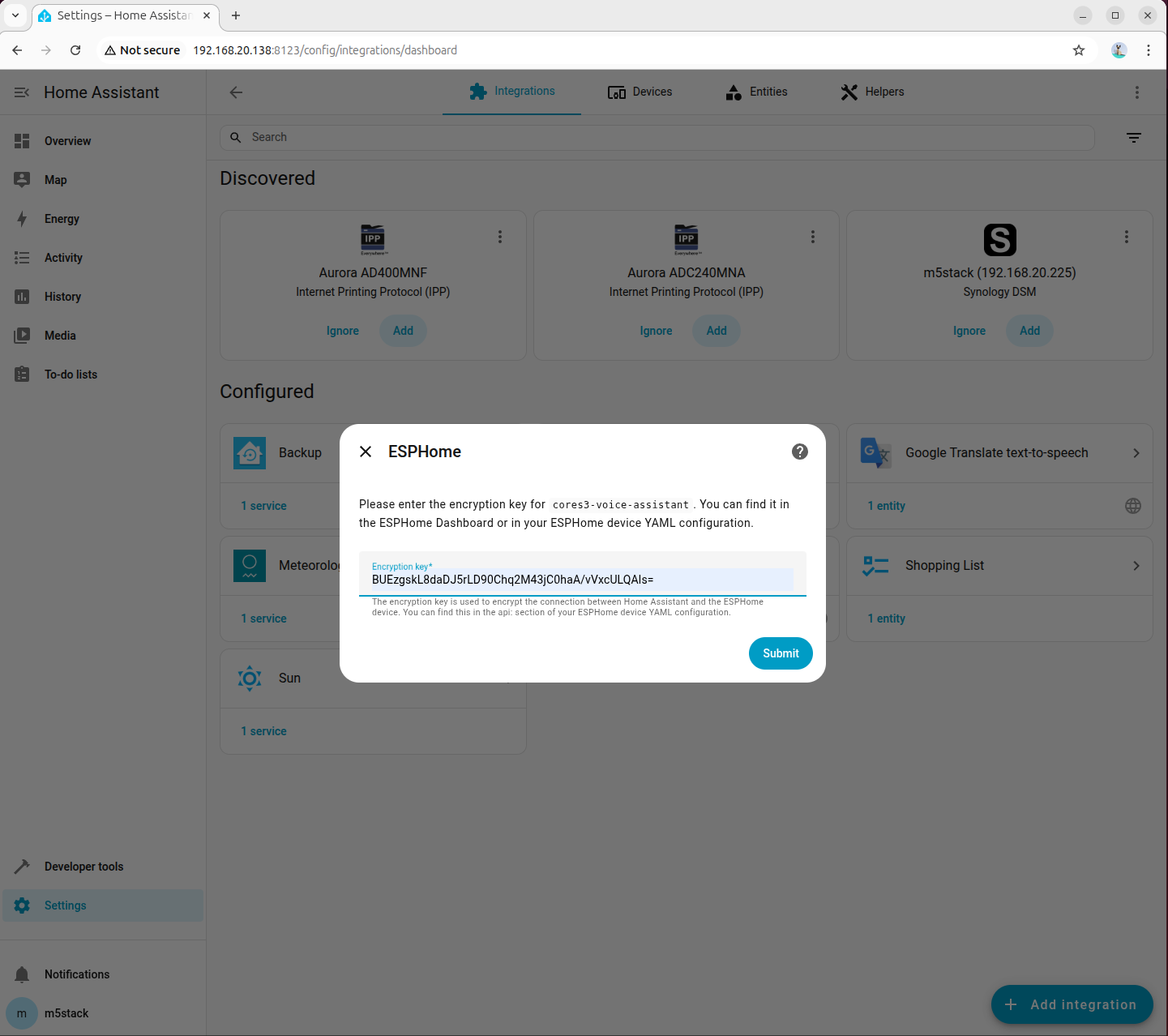
- Temporarily select cloud processing for the voice processing mode
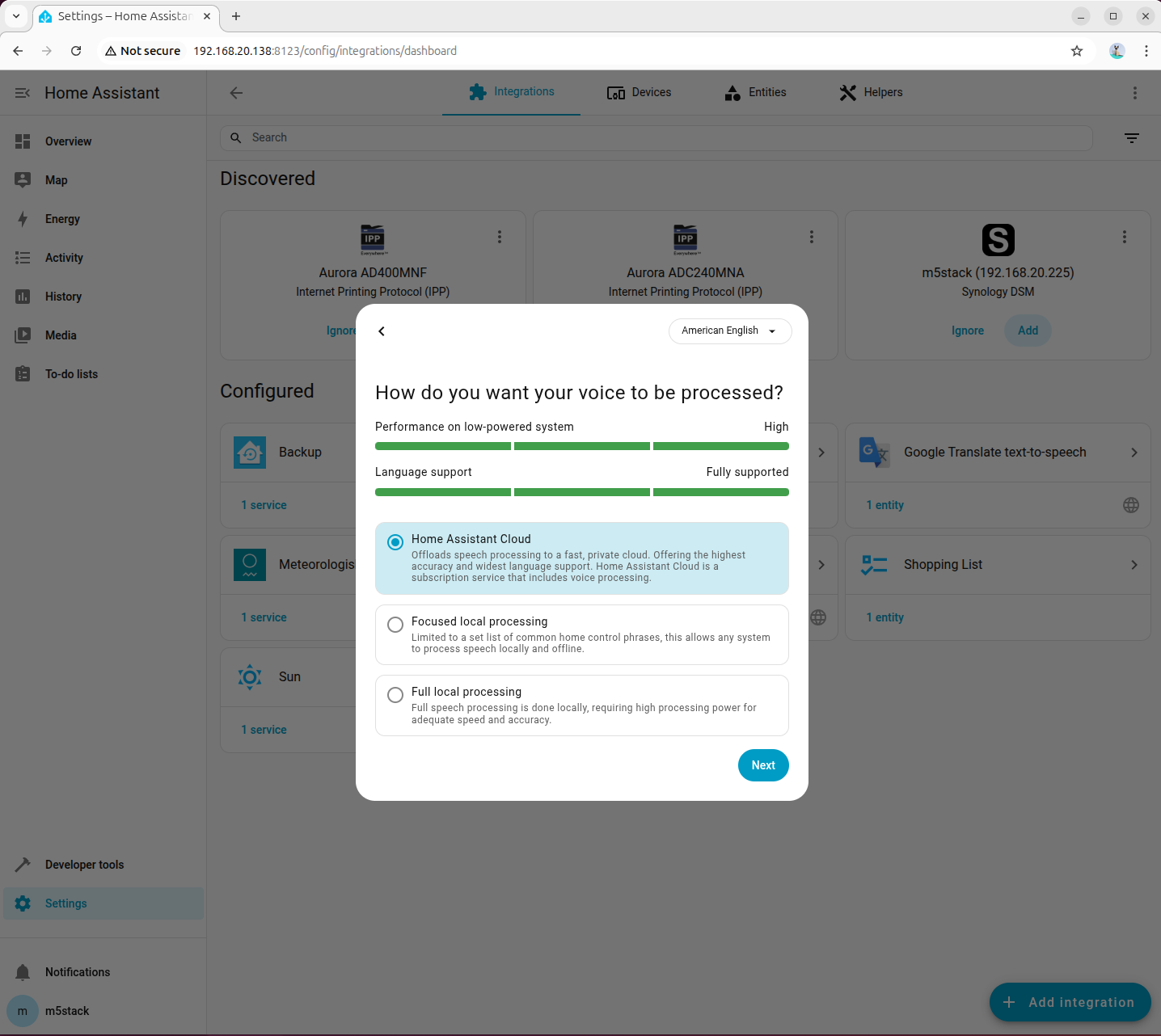
- Configure the voice wake word and TTS engine parameters
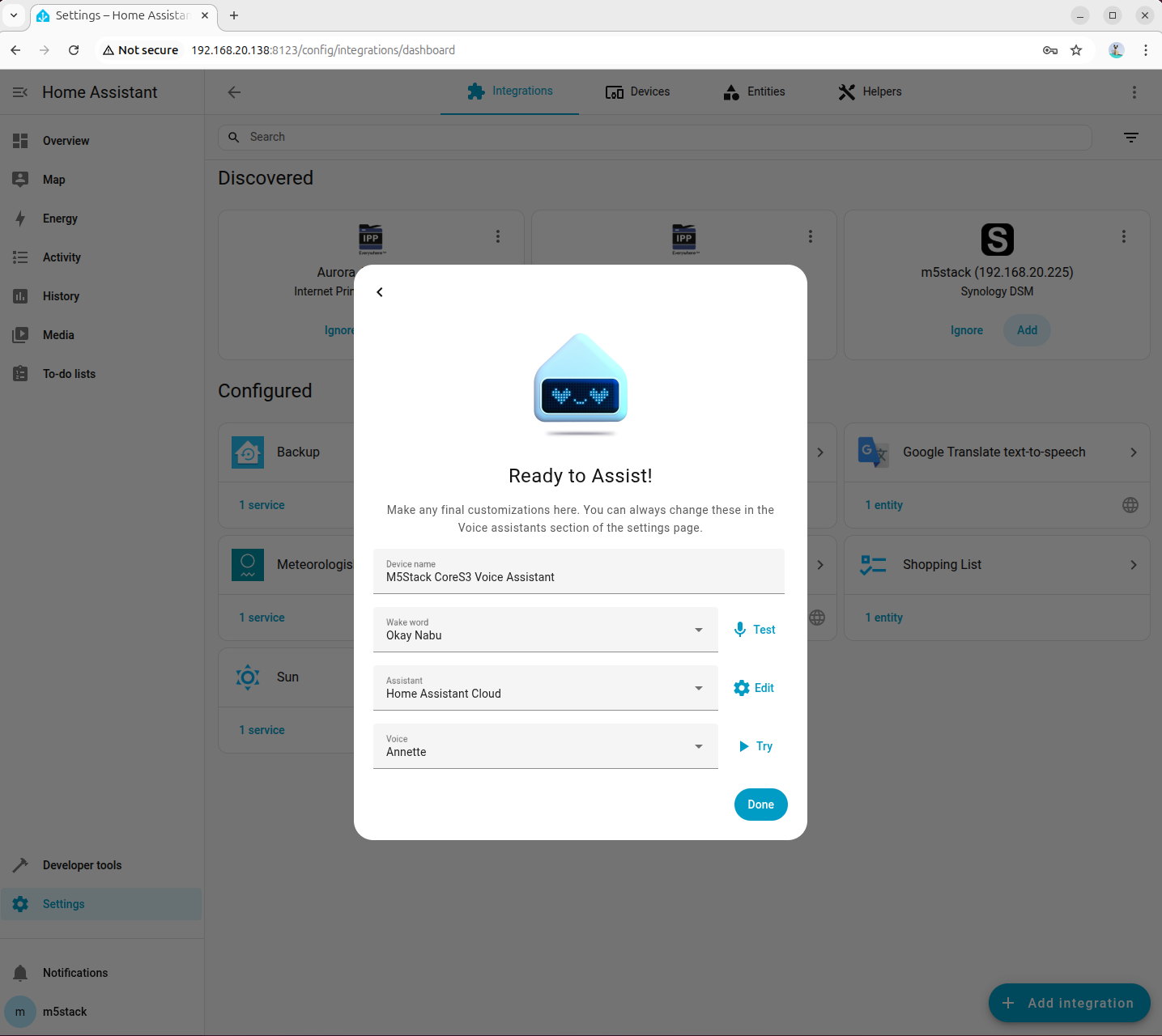
- After configuration is complete, the device will appear on the Home Assistant overview page
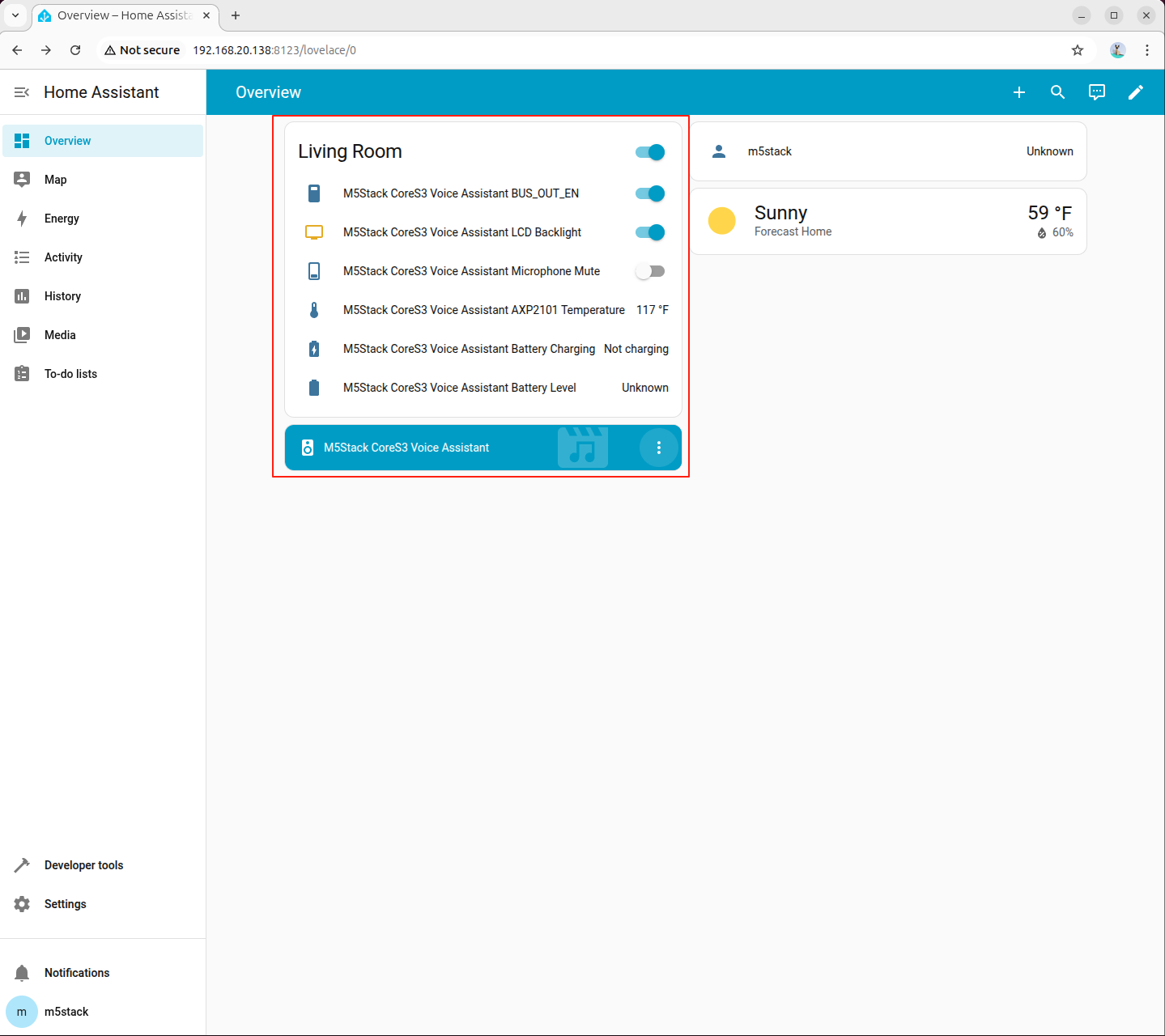
6. Configure Local Voice Assistant
Using the Wyoming Protocol, you can integrate local speech recognition and synthesis into Home Assistant to achieve a fully offline voice assistant experience.
6.1 Configure Speech-to-Text (ASR)
Step 1: Install Dependencies and Models
Ensure that the system has installed the required packages and models for speech recognition:
apt install lib-llm llm-sys llm-asr llm-openai-api llm-model-sense-voice-small-10s-ax650pip install openai wyomingStep 2: Create a Wyoming Speech-to-Text Service
Create a new file wyoming_whisper_service.py on AI Pyramid and copy the following code:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2026 M5Stack Technology CO LTD
#
# SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
"""
Wyoming protocol server for an OpenAI-compatible SenseVoice API.
Compatible with Wyoming protocol 1.8.0 for SenseVoice transcription.
"""
import argparse
import asyncio
import io
import logging
import wave
from functools import partial
from typing import Optional
from openai import OpenAI
from wyoming.asr import Transcribe, Transcript
from wyoming.audio import AudioChunk, AudioStart, AudioStop
from wyoming.event import Event
from wyoming.info import AsrModel, AsrProgram, Attribution, Info
from wyoming.server import AsyncServer, AsyncEventHandler
_LOGGER = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class SenseVoiceEventHandler(AsyncEventHandler):
"""Handle Wyoming protocol audio transcription requests."""
def __init__(
self,
wyoming_info: Info,
client: OpenAI,
model: str,
language: Optional[str] = None,
*args,
**kwargs,
) -> None:
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.client = client
self.wyoming_info_event = wyoming_info.event()
self.model = model
self.language = language
# Audio buffer state for a single transcription request.
self.audio_buffer: Optional[io.BytesIO] = None
self.wav_file: Optional[wave.Wave_write] = None
_LOGGER.info("Handler initialized with model: %s", model)
async def handle_event(self, event: Event) -> bool:
"""Handle Wyoming protocol events."""
# Service info request.
if event.type == "describe":
_LOGGER.debug("Received describe request")
await self.write_event(self.wyoming_info_event)
_LOGGER.info("Sent info response")
return True
# Transcription request.
if Transcribe.is_type(event.type):
transcribe = Transcribe.from_event(event)
_LOGGER.info("Transcribe request: language=%s", transcribe.language)
# Reset audio buffers for the new request.
self.audio_buffer = None
self.wav_file = None
return True
# Audio stream starts.
if AudioStart.is_type(event.type):
_LOGGER.debug("Audio start")
return True
# Audio stream chunk.
if AudioChunk.is_type(event.type):
chunk = AudioChunk.from_event(event)
# Initialize WAV writer on the first chunk.
if self.wav_file is None:
_LOGGER.debug("Creating WAV buffer")
self.audio_buffer = io.BytesIO()
self.wav_file = wave.open(self.audio_buffer, "wb")
self.wav_file.setframerate(chunk.rate)
self.wav_file.setsampwidth(chunk.width)
self.wav_file.setnchannels(chunk.channels)
# Append raw audio frames.
self.wav_file.writeframes(chunk.audio)
return True
# Audio stream ends; perform transcription.
if AudioStop.is_type(event.type):
_LOGGER.info("Audio stop - starting transcription")
if self.wav_file is None:
_LOGGER.warning("No audio data received")
return False
try:
# Finalize WAV payload.
self.wav_file.close()
# Extract audio bytes.
self.audio_buffer.seek(0)
audio_data = self.audio_buffer.getvalue()
# Build in-memory file for the API client.
audio_file = io.BytesIO(audio_data)
audio_file.name = "audio.wav"
# Call the transcription API.
_LOGGER.info("Calling transcription API")
transcription_params = {
"model": self.model,
"file": audio_file,
}
# Add language if explicitly set.
if self.language:
transcription_params["language"] = self.language
result = self.client.audio.transcriptions.create(**transcription_params)
# Extract transcript text.
if hasattr(result, "text"):
transcript_text = result.text
else:
transcript_text = str(result)
_LOGGER.info("Transcription result: %s", transcript_text)
# Send transcript back to the client.
await self.write_event(Transcript(text=transcript_text).event())
_LOGGER.info("Sent transcript")
except Exception as e:
_LOGGER.error("Transcription error: %s", e, exc_info=True)
# Send empty transcript on error to keep protocol flow.
await self.write_event(Transcript(text="").event())
finally:
# Release buffers for the next request.
self.audio_buffer = None
self.wav_file = None
return True
return True
async def main() -> None:
"""Program entrypoint."""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description="Wyoming protocol server for OpenAI-compatible SenseVoice API"
)
parser.add_argument(
"--uri",
default="tcp://0.0.0.0:10300",
help="URI to listen on (default: tcp://0.0.0.0:10300)",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--api-key",
default="sk-",
help="OpenAI API key (default: sk-)",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--base-url",
default="http://127.0.0.1:8000/v1",
help="API base URL (default: http://127.0.0.1:8000/v1)",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--model",
default="sense-voice-small-10s-ax650",
help="Model name (default: sense-voice-small-10s-ax650)",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--language",
help="Language code (e.g., en, zh, auto)",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--debug",
action="store_true",
help="Enable debug logging",
)
args = parser.parse_args()
# Configure logging.
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.DEBUG if args.debug else logging.INFO,
format="%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s",
)
_LOGGER.info("Starting Wyoming SenseVoice service")
_LOGGER.info("API Base URL: %s", args.base_url)
_LOGGER.info("Model: %s", args.model)
_LOGGER.info("Language: %s", args.language or "auto")
# Initialize OpenAI client.
client = OpenAI(
api_key=args.api_key,
base_url=args.base_url,
)
# Build Wyoming service metadata (protocol 1.8.0 compatible).
wyoming_info = Info(
asr=[
AsrProgram(
name=args.model,
description=f"OpenAI-compatible SenseVoice API ({args.model})",
attribution=Attribution(
name="SenseVoice",
url="https://github.com/FunAudioLLM/SenseVoice",
),
version="1.0.0",
installed=True,
models=[
AsrModel(
name=args.model,
description=f"SenseVoice model: {args.model}",
attribution=Attribution(
name="SenseVoice",
url="https://github.com/FunAudioLLM/SenseVoice",
),
installed=True,
languages=(
["zh", "en", "yue", "ja", "ko"]
if not args.language
else [args.language]
),
version="1.0.0",
)
],
)
],
)
_LOGGER.info("Service info created")
# Create server.
server = AsyncServer.from_uri(args.uri)
_LOGGER.info("Server listening on %s", args.uri)
# Run server loop.
try:
await server.run(
partial(
SenseVoiceEventHandler,
wyoming_info,
client,
args.model,
args.language,
)
)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
_LOGGER.info("Server stopped by user")
except Exception as e:
_LOGGER.error("Server error: %s", e, exc_info=True)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())Step 3: Start the Speech-to-Text Service
Run the following command to start the service (replace the IP address with the actual AI Pyramid address):
python wyoming_whisper_service.py --base-url http://192.168.20.138:8000/v1192.168.20.138 with the actual IP address of your AI Pyramid device.Example output after successful startup:
root@m5stack-AI-Pyramid:~/wyoming-openai-stt# python wyoming_whisper_service.py --base-url http://192.168.20.138:8000/v1
2026-02-04 16:29:45,121 - __main__ - INFO - Starting Wyoming Whisper service
2026-02-04 16:29:45,122 - __main__ - INFO - API Base URL: http://192.168.20.138:8000/v1
2026-02-04 16:29:45,122 - __main__ - INFO - Model: sense-voice-small-10s-ax650
2026-02-04 16:29:45,123 - __main__ - INFO - Language: auto
2026-02-04 16:29:46,098 - __main__ - INFO - Service info created
2026-02-04 16:29:46,099 - __main__ - INFO - Server listening on tcp://0.0.0.0:10300Step 4: Add Wyoming Protocol in Home Assistant
Go to the Home Assistant settings page, search for and add the "Wyoming Protocol" integration:
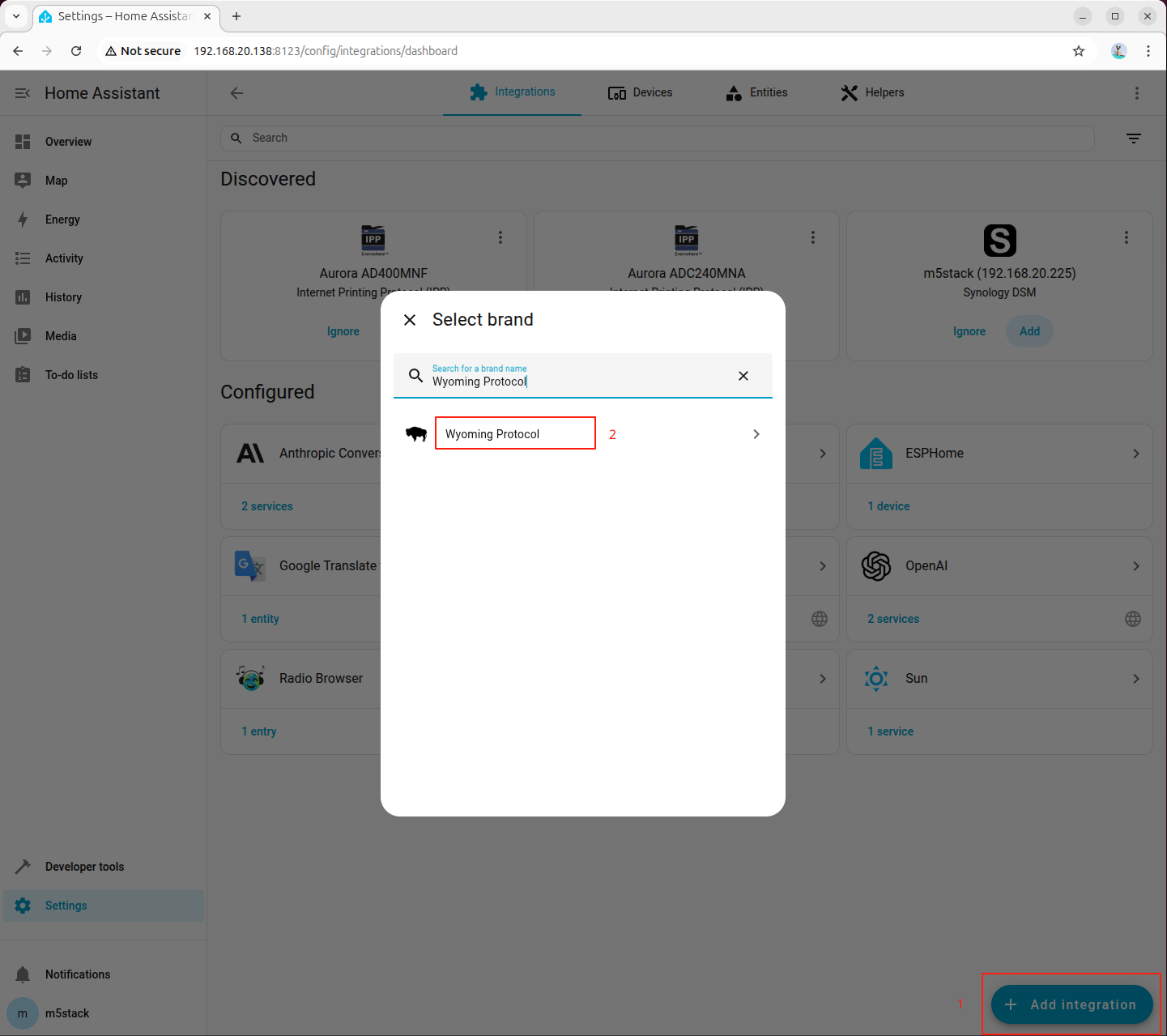
Step 5: Configure Connection Parameters
- Host: 127.0.0.1
- Port: 10300
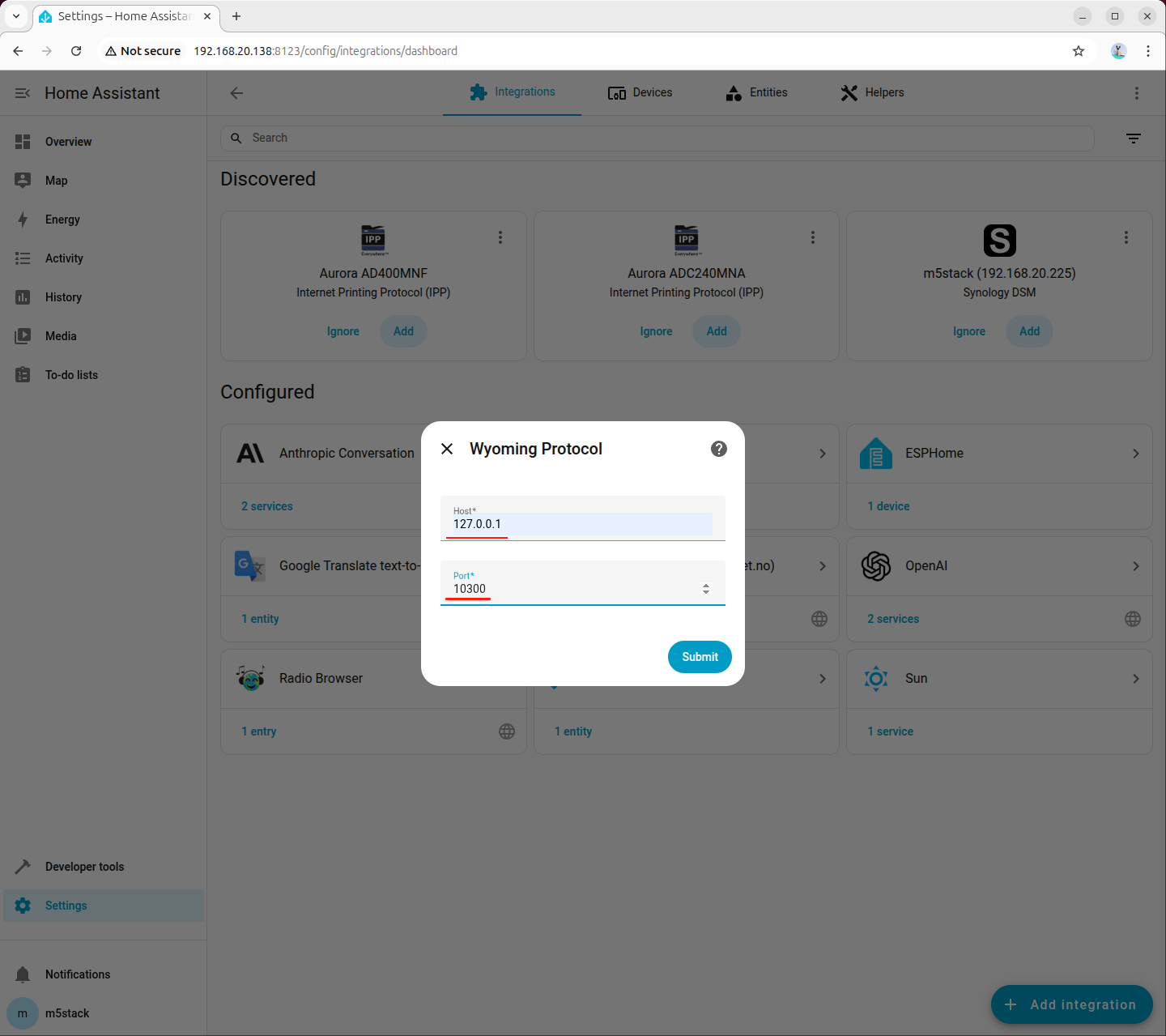
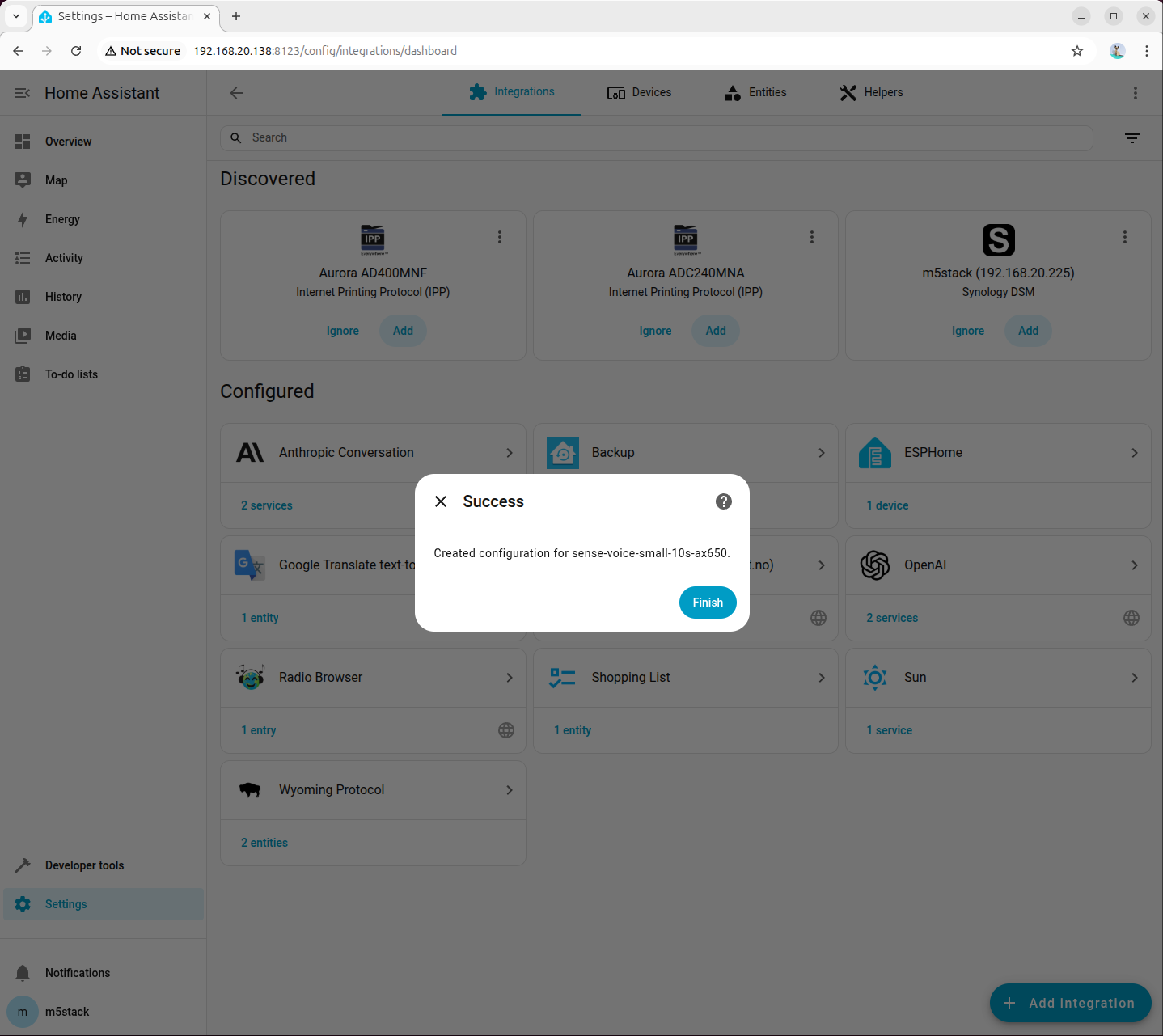
Step 6: Create a Voice Assistant
In Home Assistant settings, go to the "Voice Assistants" module and click to create a new voice assistant:
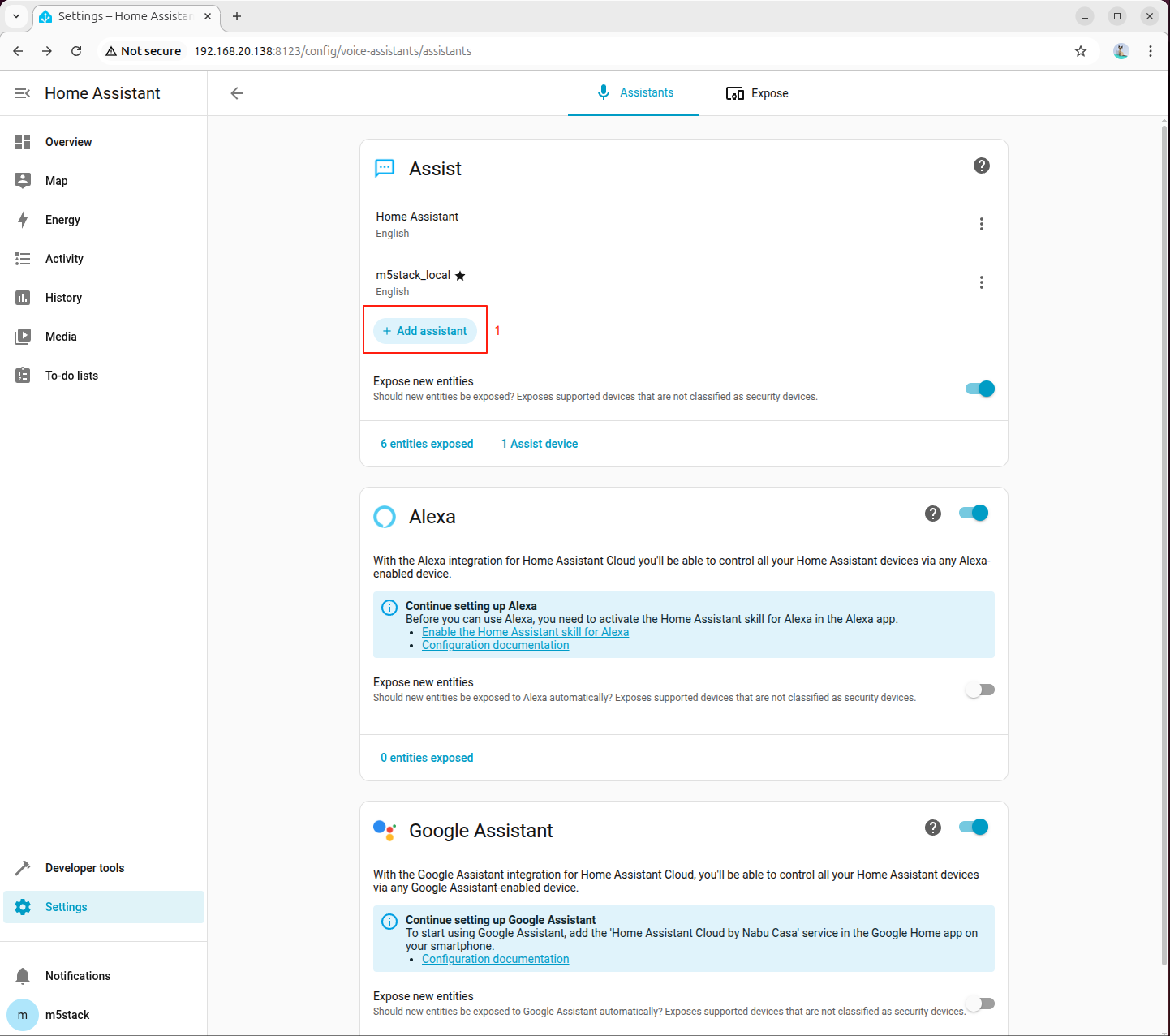
Step 7: Configure the ASR Model
Select the speech recognition model sense-voice-small-10s-ax650 that was just added. Keep the language setting as default.
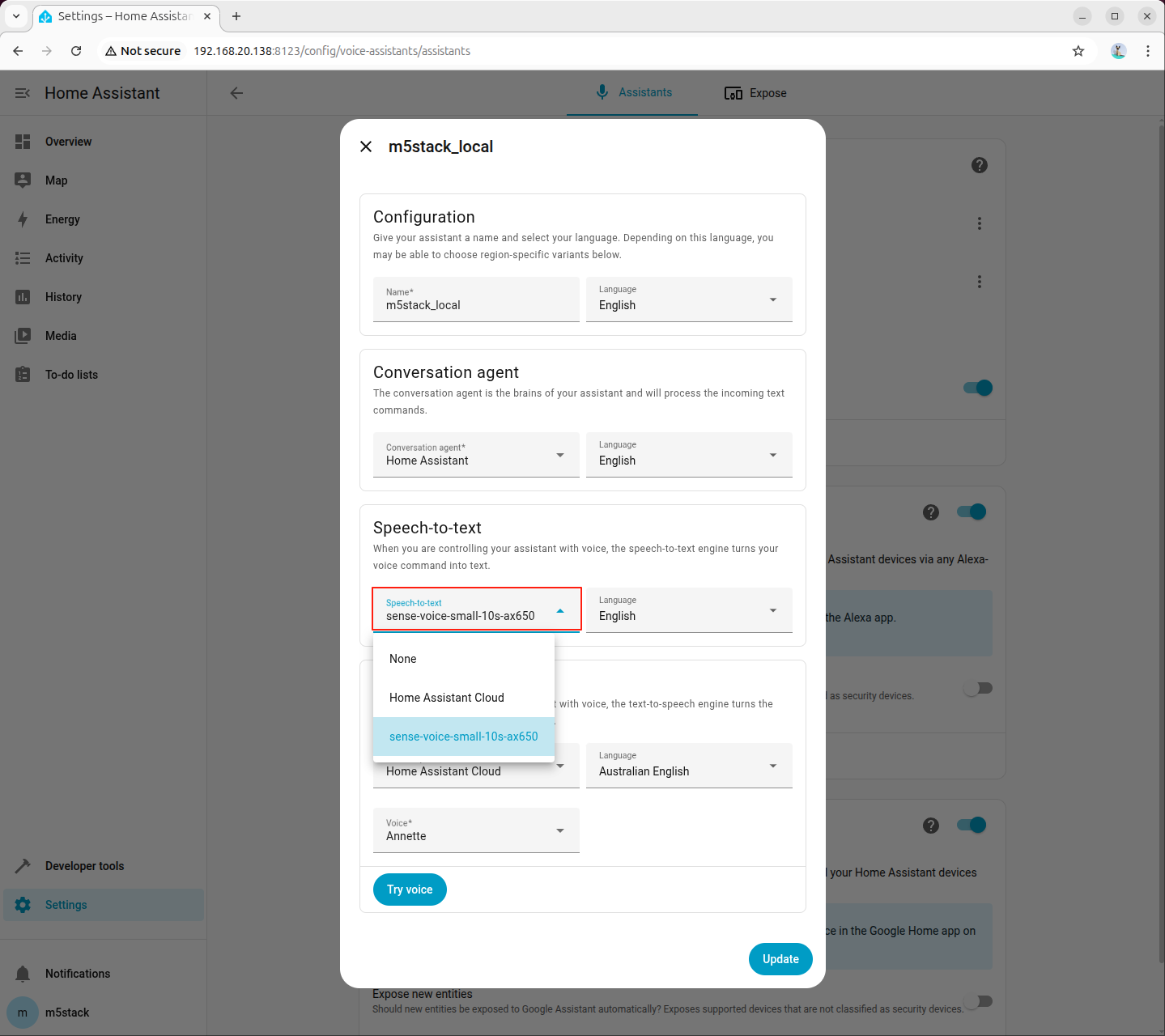
6.2 Configure Text-to-Speech (TTS)
Step 1: Install Dependencies and Models
Ensure that the system has installed the required packages and models for speech synthesis:
apt install lib-llm llm-sys llm-melotts llm-openai-api llm-model-melotts-en-us-ax650pip install openai wyomingllm-model-melotts-zh-cn-ax650, llm-model-melotts-ja-jp-ax650, etc. Install them as needed.Step 2: Create a Wyoming Text-to-Speech Service
Create a new file wyoming_openai_tts.py on AI Pyramid and copy the following code:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2024 M5Stack Technology CO LTD
#
# SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
"""
Wyoming protocol server for OpenAI API TTS service.
Connects local OpenAI-compatible TTS API to Home Assistant.
"""
import argparse
import asyncio
import logging
import wave
import io
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Optional
from openai import OpenAI
from wyoming.audio import AudioChunk, AudioStart, AudioStop
from wyoming.event import Event
from wyoming.info import Attribution, Info, TtsProgram, TtsVoice
from wyoming.server import AsyncEventHandler, AsyncServer
from wyoming.tts import Synthesize
_LOGGER = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# Default configuration
DEFAULT_HOST = "0.0.0.0"
DEFAULT_PORT = 10200
DEFAULT_API_BASE_URL = "http://192.168.20.138:8000/v1"
DEFAULT_MODEL = "melotts-zh-cn-ax650"
DEFAULT_VOICE = "melotts-zh-cn-ax650"
DEFAULT_RESPONSE_FORMAT = "wav"
# Available voices for Wyoming protocol
AVAILABLE_VOICES = [
TtsVoice(
name="melotts-en-au-ax650",
description="MeloTTS English (AU)",
attribution=Attribution(
name="MeloTTS",
url="https://huggingface.co/myshell-ai/MeloTTS-English",
),
version="1.0.0",
installed=True,
languages=["en-au"],
),
TtsVoice(
name="melotts-en-default-ax650",
description="MeloTTS English (Default)",
attribution=Attribution(
name="MeloTTS",
url="https://huggingface.co/myshell-ai/MeloTTS-English",
),
version="1.0.0",
installed=True,
languages=["en"],
),
TtsVoice(
name="melotts-en-us-ax650",
description="MeloTTS English (US)",
attribution=Attribution(
name="MeloTTS",
url="https://huggingface.co/myshell-ai/MeloTTS-English",
),
version="1.0.0",
installed=True,
languages=["en-us"],
),
TtsVoice(
name="melotts-en-br-ax650",
description="MeloTTS English (BR)",
attribution=Attribution(
name="MeloTTS",
url="https://huggingface.co/myshell-ai/MeloTTS-English",
),
version="1.0.0",
installed=True,
languages=["en-br"],
),
TtsVoice(
name="melotts-en-india-ax650",
description="MeloTTS English (India)",
attribution=Attribution(
name="MeloTTS",
url="https://huggingface.co/myshell-ai/MeloTTS-English",
),
version="1.0.0",
installed=True,
languages=["en-in"],
),
TtsVoice(
name="melotts-ja-jp-ax650",
description="MeloTTS Japanese (JP)",
attribution=Attribution(
name="MeloTTS",
url="https://huggingface.co/myshell-ai/MeloTTS-Japanese",
),
version="1.0.0",
installed=True,
languages=["ja-jp"],
),
TtsVoice(
name="melotts-es-es-ax650",
description="MeloTTS Spanish (ES)",
attribution=Attribution(
name="MeloTTS",
url="https://huggingface.co/myshell-ai/MeloTTS-Spanish",
),
version="1.0.0",
installed=True,
languages=["es-es"],
),
TtsVoice(
name="melotts-zh-cn-ax650",
description="MeloTTS Chinese (CN)",
attribution=Attribution(
name="MeloTTS",
url="https://huggingface.co/myshell-ai/MeloTTS-Chinese",
),
version="1.0.0",
installed=True,
languages=["zh-cn"],
),
]
# Map voice name -> model name for automatic switching
VOICE_MODEL_MAP = {voice.name: voice.name for voice in AVAILABLE_VOICES}
class OpenAITTSEventHandler:
"""Event handler for Wyoming protocol with OpenAI TTS."""
def __init__(
self,
api_key: str,
base_url: str,
model: str,
default_voice: str,
response_format: str,
):
"""Initialize the event handler."""
self.api_key = api_key
self.base_url = base_url
self.model = model
self.default_voice = default_voice
self.response_format = response_format
self.voice_model_map = VOICE_MODEL_MAP
# Initialize OpenAI client
self.client = OpenAI(
api_key=api_key,
base_url=base_url,
)
_LOGGER.info(
"Initialized OpenAI TTS handler with base_url=%s, model=%s",
base_url,
model,
)
async def handle_event(self, event: Event) -> Optional[Event]:
"""Handle a Wyoming protocol event."""
if Synthesize.is_type(event.type):
synthesize = Synthesize.from_event(event)
_LOGGER.info("Synthesizing text: %s", synthesize.text)
# Use specified voice or default
voice = synthesize.voice.name if synthesize.voice else self.default_voice
model = self.voice_model_map.get(voice, self.model)
try:
# Generate speech using OpenAI API
audio_data = await asyncio.to_thread(
self._synthesize_speech,
synthesize.text,
voice,
model,
)
# Read WAV file properties
with wave.open(io.BytesIO(audio_data), "rb") as wav_file:
sample_rate = wav_file.getframerate()
sample_width = wav_file.getsampwidth()
channels = wav_file.getnchannels()
audio_bytes = wav_file.readframes(wav_file.getnframes())
_LOGGER.info(
"Generated audio: %d bytes, %d Hz, %d channels",
len(audio_bytes),
sample_rate,
channels,
)
# Send audio start event
yield AudioStart(
rate=sample_rate,
width=sample_width,
channels=channels,
).event()
# Send audio in chunks
chunk_size = 8192
for i in range(0, len(audio_bytes), chunk_size):
chunk = audio_bytes[i:i + chunk_size]
yield AudioChunk(
audio=chunk,
rate=sample_rate,
width=sample_width,
channels=channels,
).event()
# Send audio stop event
yield AudioStop().event()
except Exception as err:
_LOGGER.exception("Error during synthesis: %s", err)
raise
def _synthesize_speech(self, text: str, voice: str, model: str) -> bytes:
"""Synthesize speech using OpenAI API (blocking call)."""
with self.client.audio.speech.with_streaming_response.create(
model=model,
voice=voice,
response_format=self.response_format,
input=text,
) as response:
# Read all audio data
audio_data = b""
for chunk in response.iter_bytes(chunk_size=8192):
audio_data += chunk
return audio_data
async def main():
"""Run the Wyoming protocol server."""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Wyoming OpenAI TTS Server")
parser.add_argument(
"--uri",
default=f"tcp://{DEFAULT_HOST}:{DEFAULT_PORT}",
help="URI to bind the server (default: tcp://0.0.0.0:10200)",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--api-key",
default="sk-your-key",
help="OpenAI API key (default: sk-your-key)",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--base-url",
default=DEFAULT_API_BASE_URL,
help=f"OpenAI API base URL (default: {DEFAULT_API_BASE_URL})",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--model",
default=DEFAULT_MODEL,
help=f"TTS model name (default: {DEFAULT_MODEL})",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--voice",
default=DEFAULT_VOICE,
help=f"Default voice name (default: {DEFAULT_VOICE})",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--response-format",
default=DEFAULT_RESPONSE_FORMAT,
choices=["mp3", "opus", "aac", "flac", "wav", "pcm"],
help=f"Audio response format (default: {DEFAULT_RESPONSE_FORMAT})",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--debug",
action="store_true",
help="Enable debug logging",
)
args = parser.parse_args()
# Setup logging
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.DEBUG if args.debug else logging.INFO,
format="%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s",
)
_LOGGER.info("Starting Wyoming OpenAI TTS Server")
_LOGGER.info("URI: %s", args.uri)
_LOGGER.info("Model: %s", args.model)
_LOGGER.info("Default voice: %s", args.voice)
# Create Wyoming info
wyoming_info = Info(
tts=[
TtsProgram(
name="MeloTTS",
description="OpenAI compatible TTS service",
attribution=Attribution(
name="MeloTTS",
url="https://huggingface.co/myshell-ai/MeloTTS-English",
),
version="1.0.0",
installed=True,
voices=AVAILABLE_VOICES,
)
],
)
# Create event handler
event_handler = OpenAITTSEventHandler(
api_key=args.api_key,
base_url=args.base_url,
model=args.model,
default_voice=args.voice,
response_format=args.response_format,
)
# Start server
server = AsyncServer.from_uri(args.uri)
_LOGGER.info("Server started, waiting for connections...")
await server.run(
partial(
OpenAITtsHandler,
wyoming_info=wyoming_info,
event_handler=event_handler,
)
)
class OpenAITtsHandler(AsyncEventHandler):
"""Wyoming async event handler for OpenAI TTS."""
def __init__(
self,
reader: asyncio.StreamReader,
writer: asyncio.StreamWriter,
wyoming_info: Info,
event_handler: OpenAITTSEventHandler,
) -> None:
super().__init__(reader, writer)
self._wyoming_info = wyoming_info
self._event_handler = event_handler
self._sent_info = False
async def handle_event(self, event: Event) -> bool:
if not self._sent_info:
await self.write_event(self._wyoming_info.event())
self._sent_info = True
_LOGGER.info("Client connected")
_LOGGER.debug("Received event: %s", event.type)
try:
async for response_event in self._event_handler.handle_event(event):
await self.write_event(response_event)
except Exception as err:
_LOGGER.exception("Error handling connection: %s", err)
return False
return True
async def disconnect(self) -> None:
_LOGGER.info("Client disconnected")
if __name__ == "__main__":
from functools import partial
asyncio.run(main())Step 3: Start the Text-to-Speech Service
Start the Wyoming TTS service using the following command. Replace it with your AI Pyramid IP address:
python wyoming_openai_tts.py --base-url=http://192.168.20.138:8000/v1root@m5stack-AI-Pyramid:~/wyoming-openai-tts# python wyoming_openai_tts.py --base_url=http://192.168.20.138:8000/v1
2026-02-04 17:03:18,152 - __main__ - INFO - Starting Wyoming OpenAI TTS Server
2026-02-04 17:03:18,153 - __main__ - INFO - URI: tcp://0.0.0.0:10200
2026-02-04 17:03:18,153 - __main__ - INFO - Model: melotts-zh-cn-ax650
2026-02-04 17:03:18,153 - __main__ - INFO - Default voice: melotts-zh-cn-ax650
2026-02-04 17:03:19,081 - __main__ - INFO - Initialized OpenAI TTS handler with base_url=http://192.168.20.138:8000/v1, model=melotts-zh-cn-ax650
2026-02-04 17:03:19,082 - __main__ - INFO - Server started, waiting for connections...Step 4: Add Wyoming Protocol in Home Assistant
Open Home Assistant settings, search for and add the "Wyoming Protocol" integration:

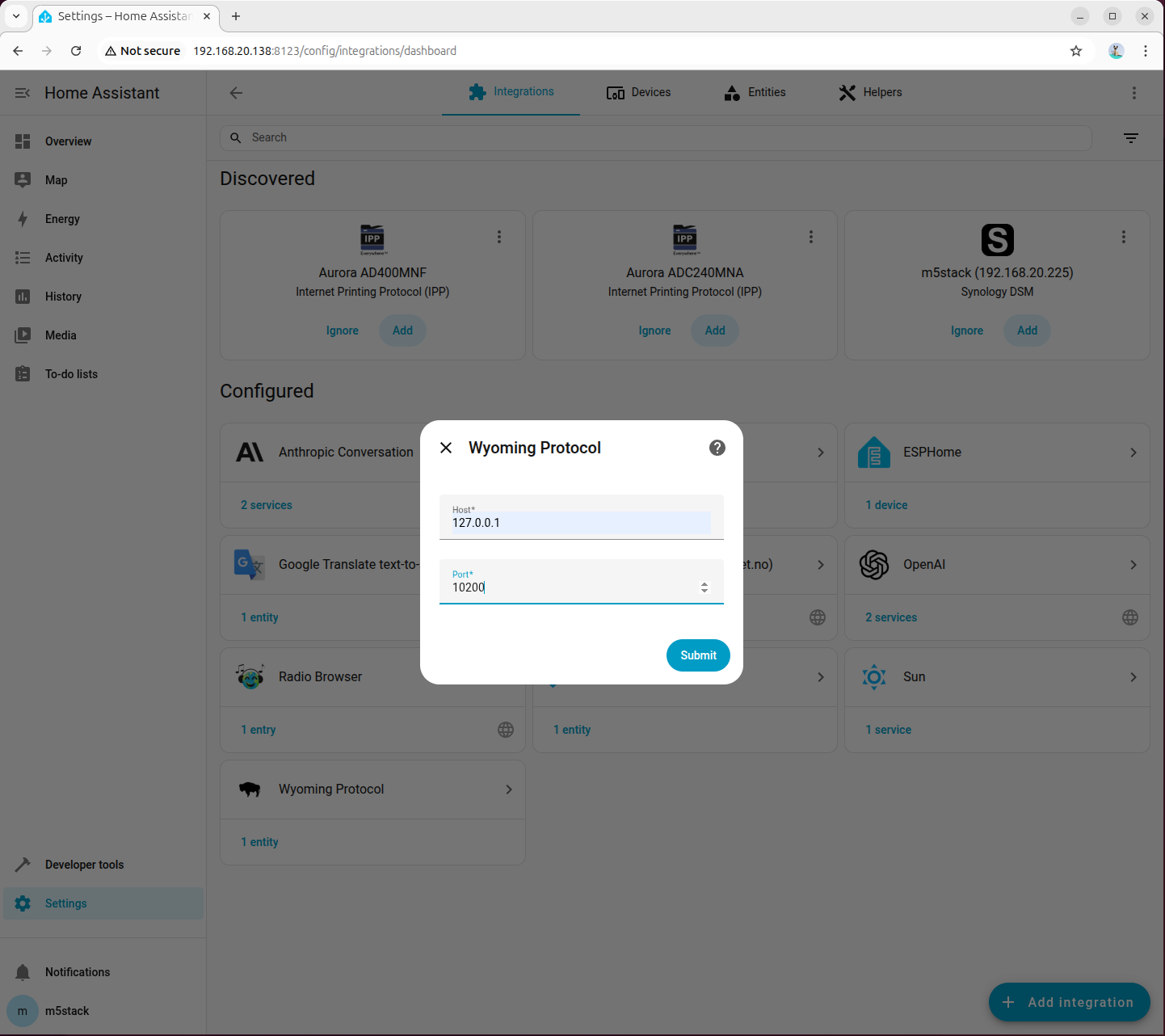
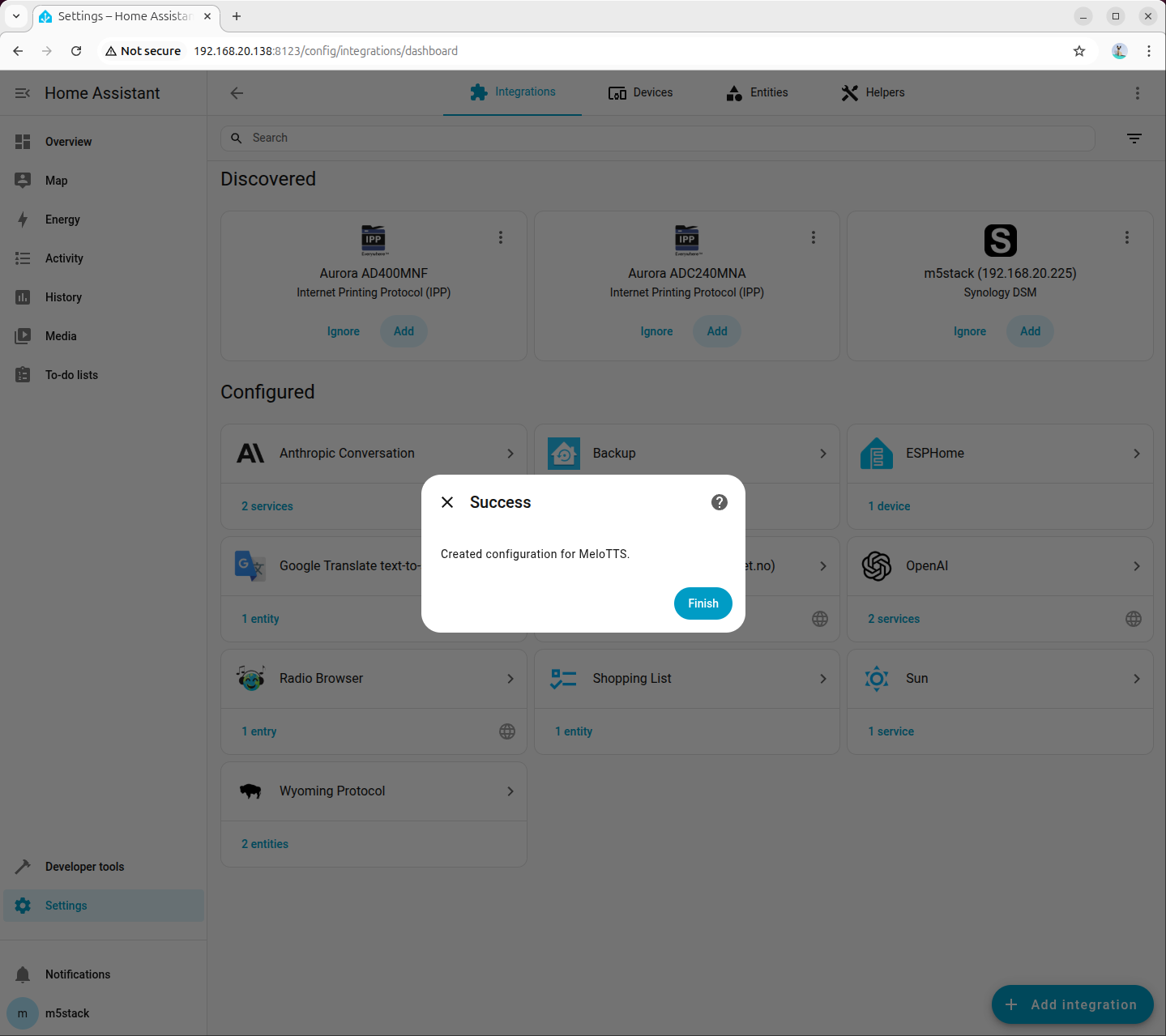
Step 5: Configure the Voice Assistant
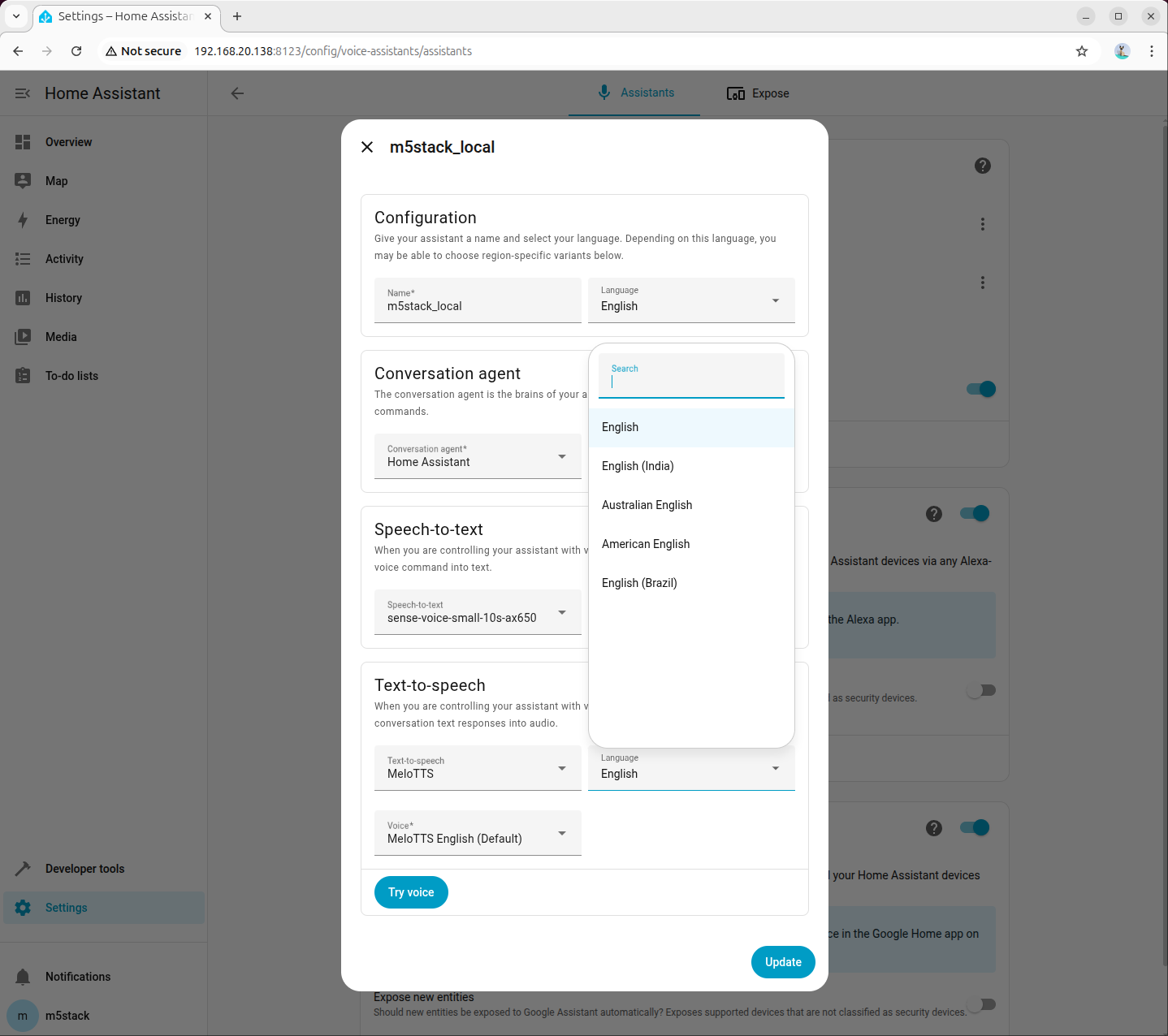
In "Settings - Voice Assistants", create or edit the assistant configuration. Set the Text-to-Speech (TTS) option to the newly added "MeloTTS", then select the appropriate language and voice as needed. Make sure the corresponding language TTS model is installed. This example uses American English.
7. Configure HACS
- Enter the Home Assistant container
docker exec -it homeassistant bash- Install HACS
wget -O - https://get.hacs.xyz | bash -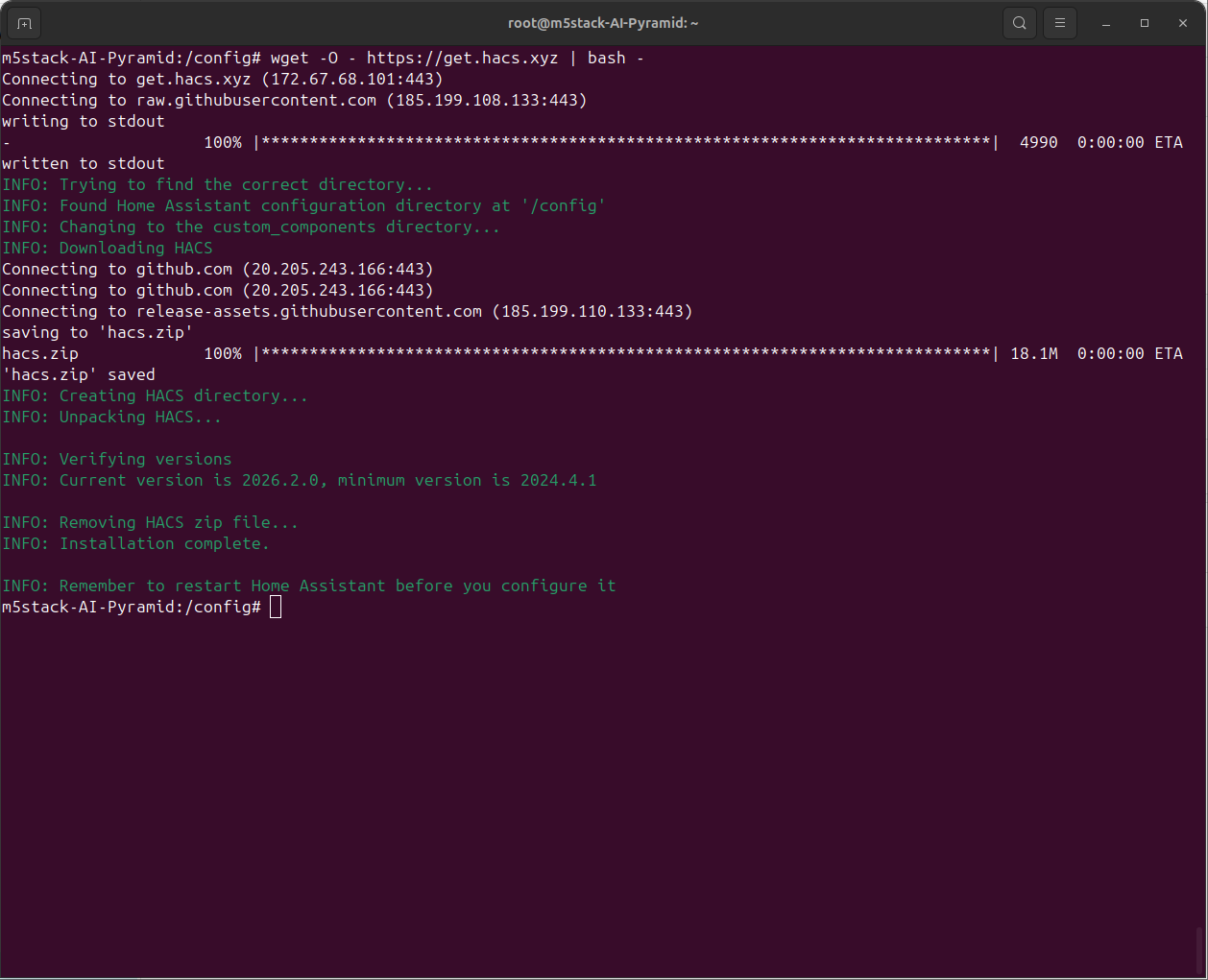
- Press Ctrl + D to exit the container and restart the Home Assistant container
docker restart homeassistant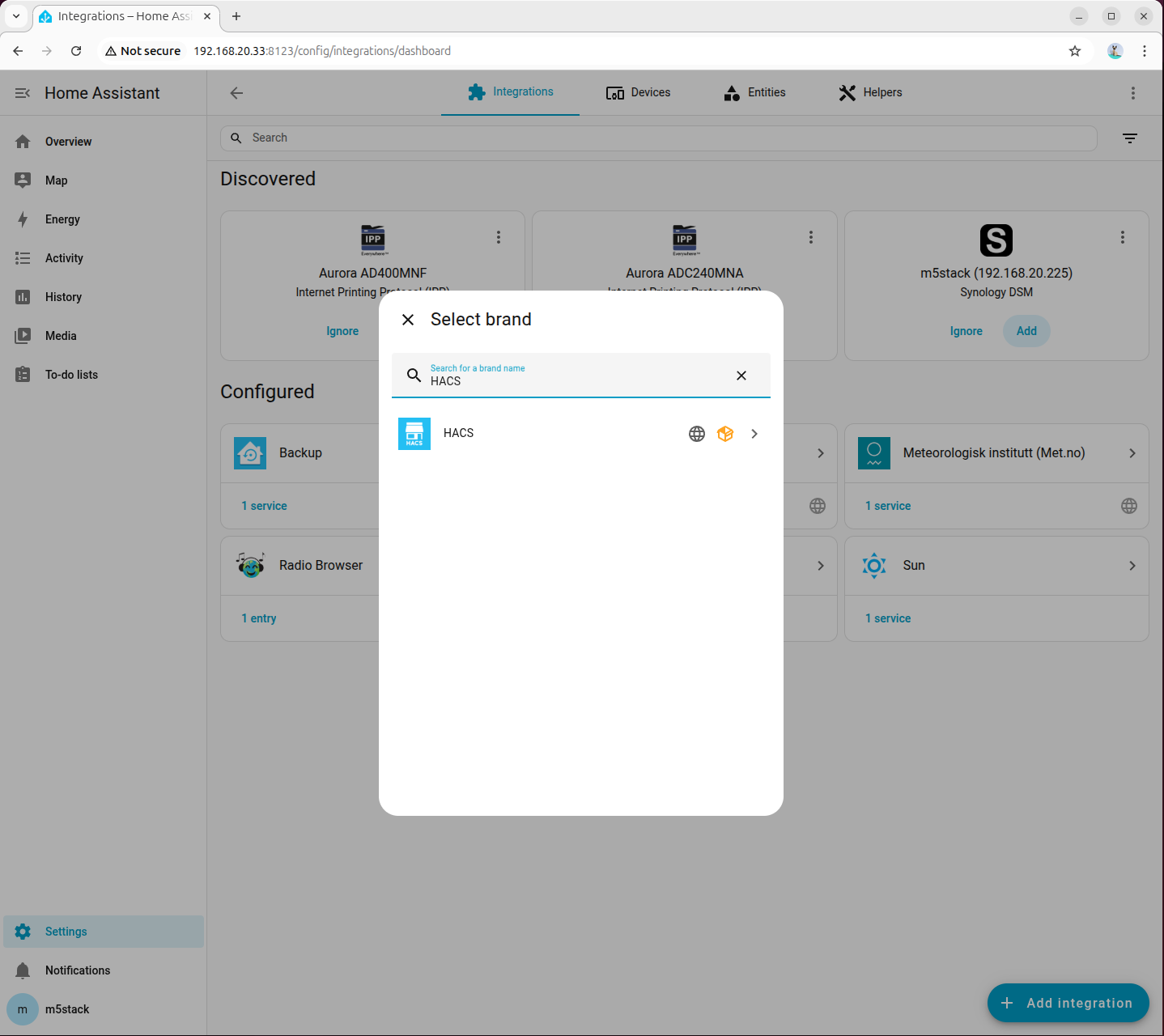
- In Settings -> Devices & Services -> Add Integration, search for HACS

- Check all options
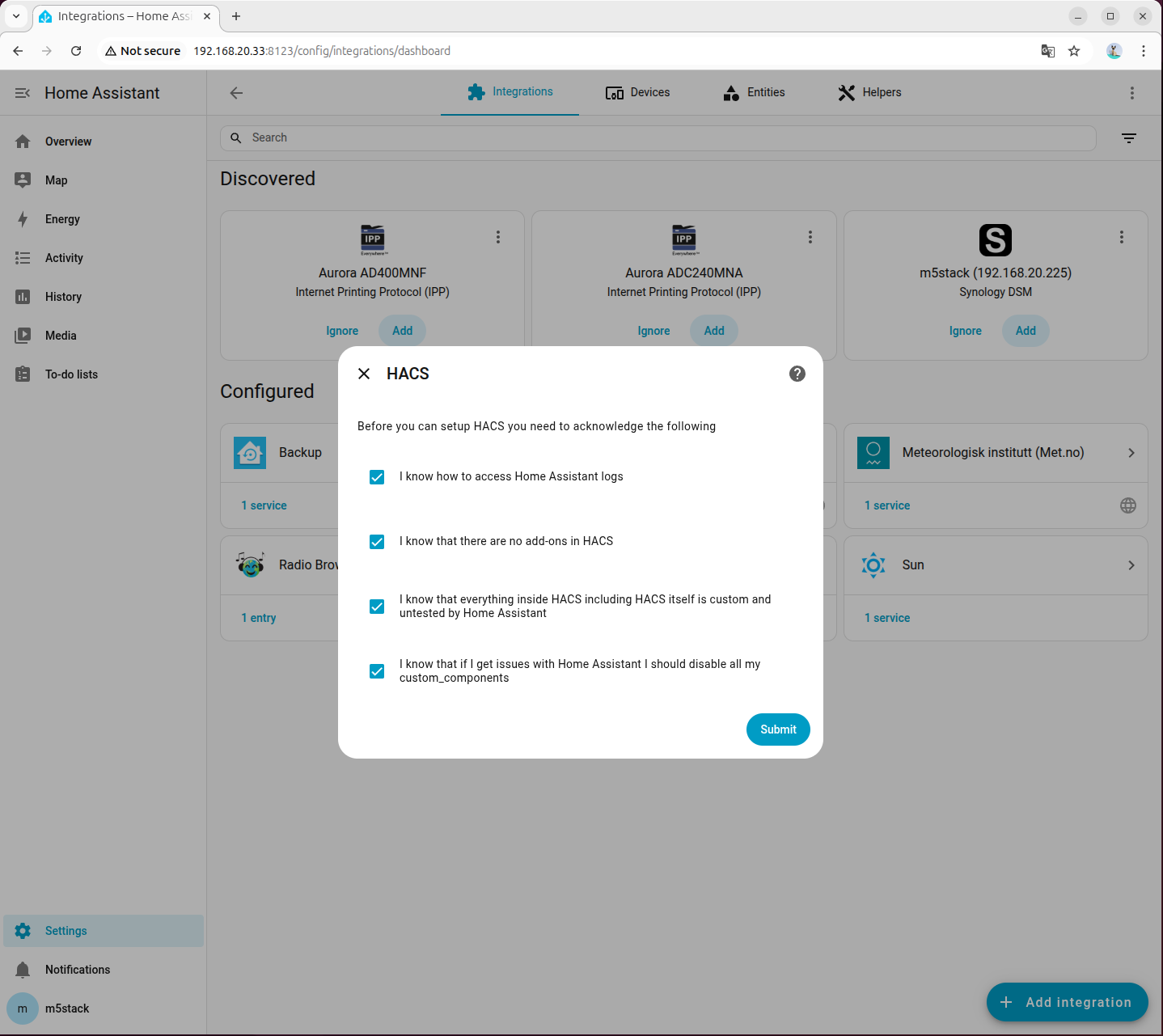
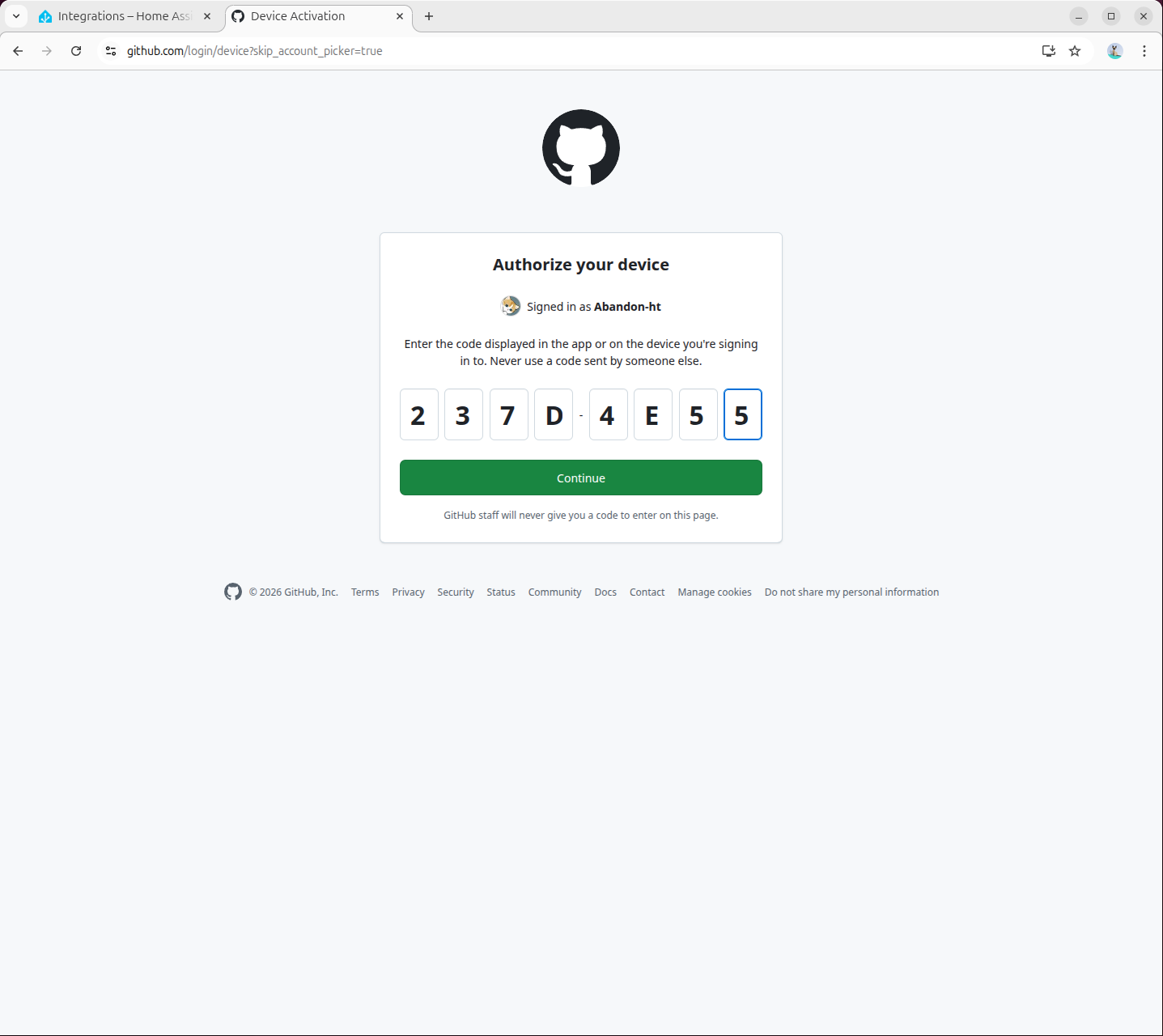
- Complete authorization
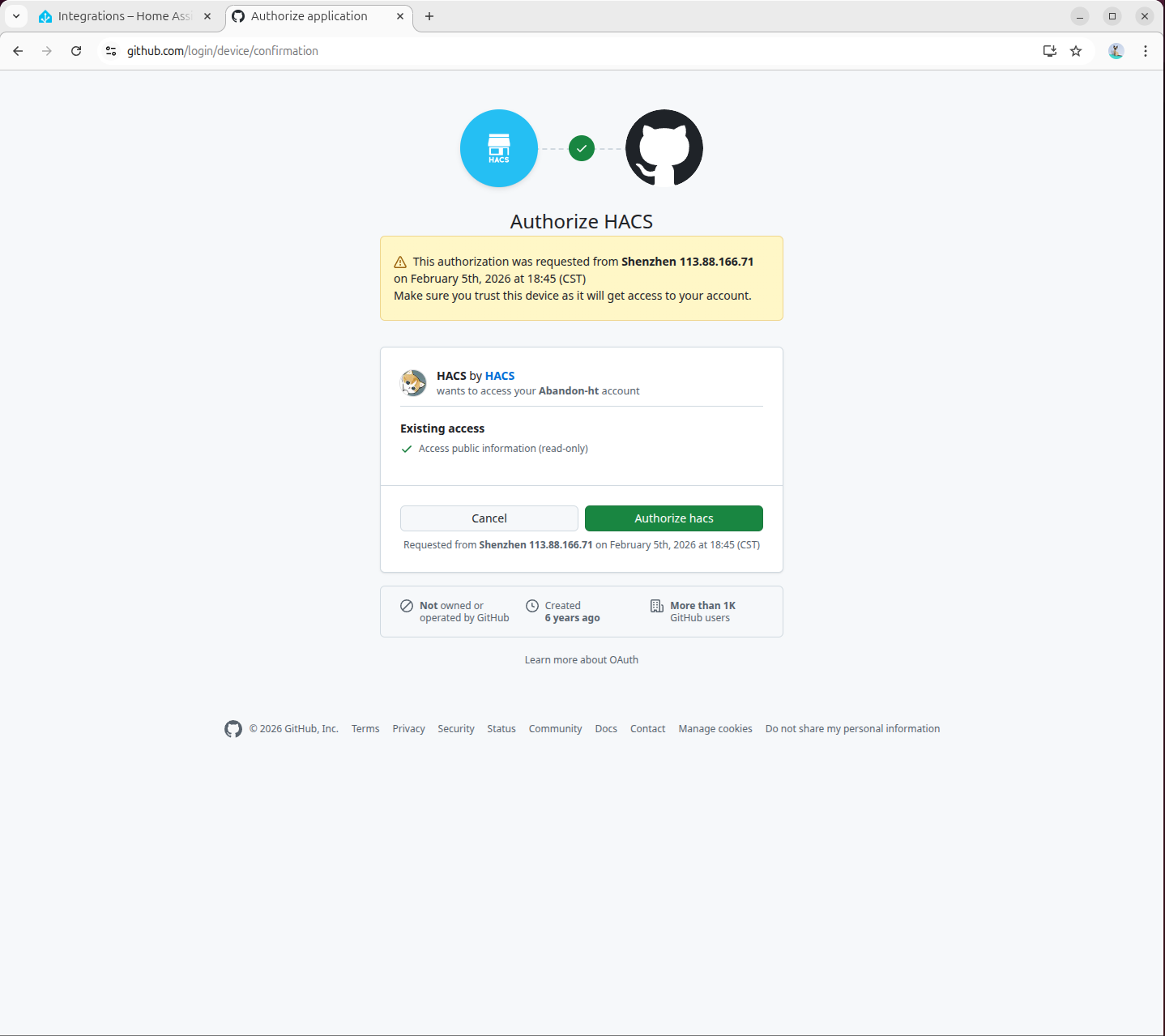
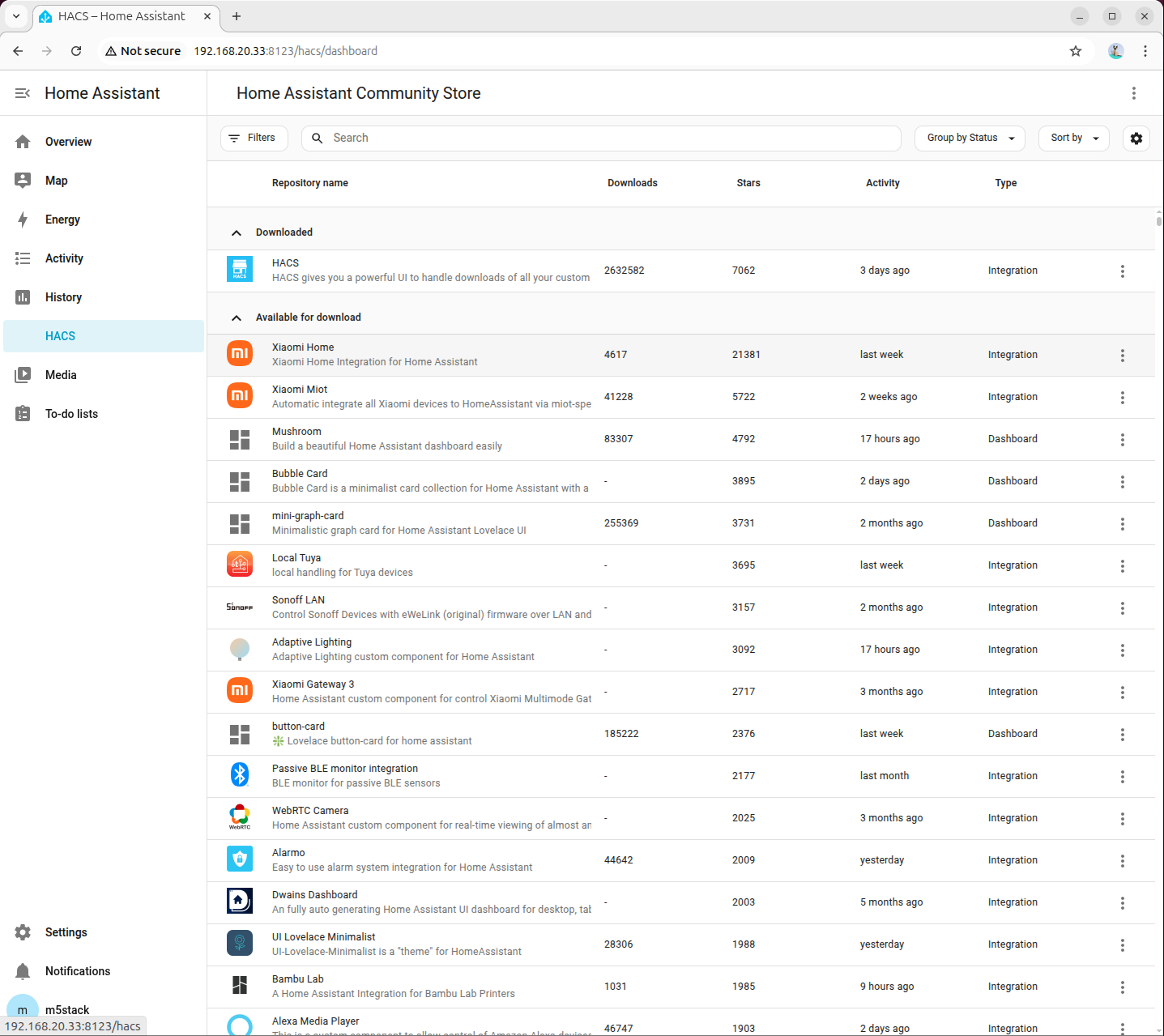
8. Configure Local LLM Conversation
- Visit http://192.168.20.33:8123/hacs/repository?owner=acon96&repository=home-llm&category=Integration to add the plugin
- Click Download in the lower-right corner
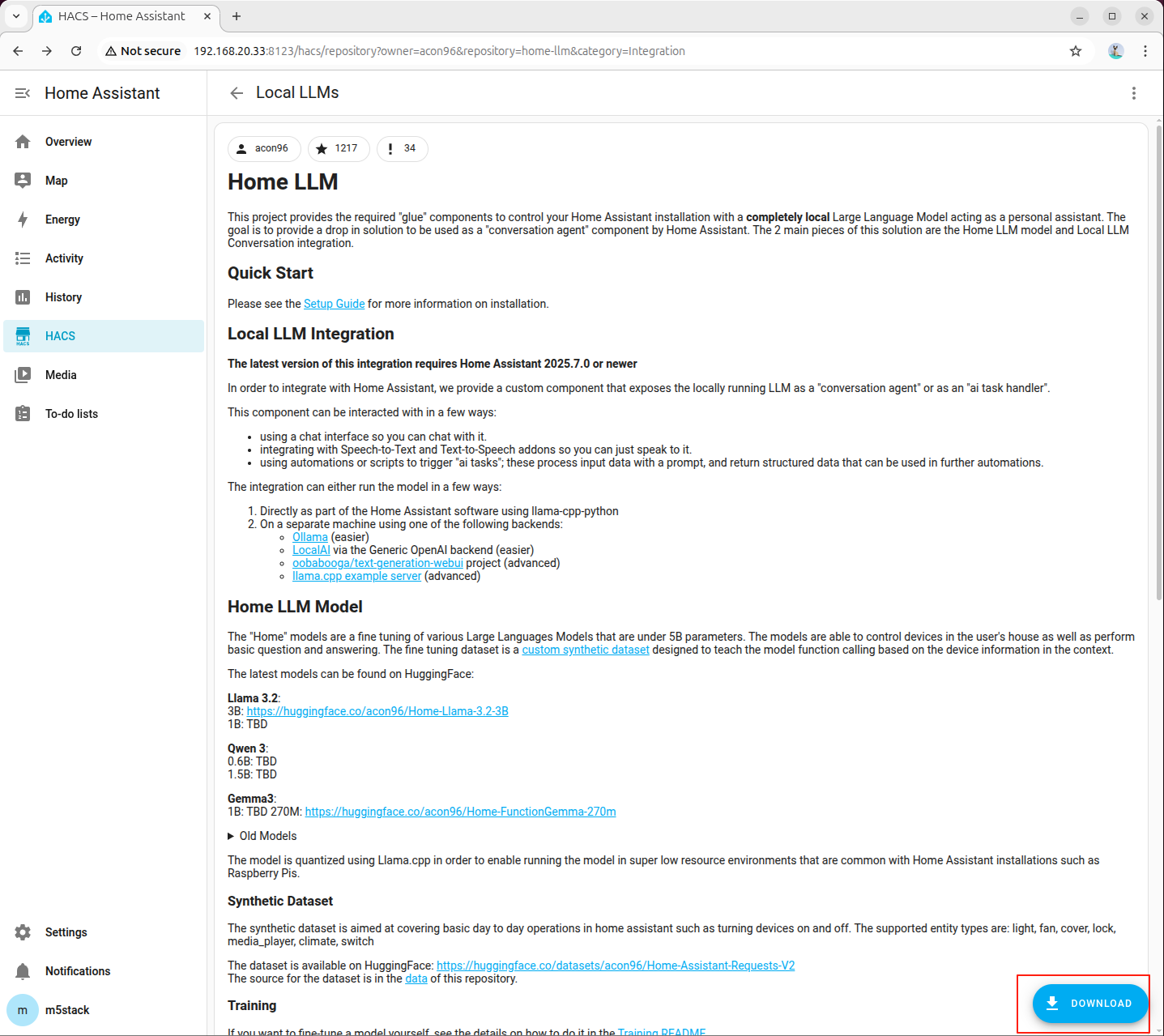
- Select the latest version
- Restart Home Assistant
- In Settings, search for and add Local LLMs in Add Integration
Configure OpenAI Compatible API Integration
- Configure Local LLM-HA Service
Step 1: Install Dependencies and Models
Ensure that the system has installed the required packages and models:
apt install lib-llm llm-sys llm-asr llm-openai-api llm-model-qwen2.5-ha-0.5b-ctx-ax650pip install fastapi httpx uvicornStep 2: Create a Local LLM-HA Service
Create a new file ha_llm_proxy.py on AI Pyramid and copy the following code:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2026 M5Stack Technology CO LTD
#
# SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
import time
import json
import uuid
import httpx
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
from fastapi.responses import StreamingResponse, JSONResponse
UPSTREAM_URL = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/v1/chat/completions"
MODEL_NAME = "qwen2.5-HA-0.5B-ctx-ax650"
app = FastAPI()
def fake_stream_from_content(content: str):
response_id = f"chatcmpl-{uuid.uuid4().hex}"
created = int(time.time())
for chunk in content.splitlines(keepends=True):
data = {
"id": response_id,
"object": "chat.completion.chunk",
"created": created,
"model": MODEL_NAME,
"choices": [{
"index": 0,
"delta": {"content": chunk},
"finish_reason": None
}]
}
yield f"data: {json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=False)}\n\n"
time.sleep(0.05)
end_data = {
"id": response_id,
"object": "chat.completion.chunk",
"created": created,
"model": MODEL_NAME,
"choices": [{
"index": 0,
"delta": {},
"finish_reason": "stop"
}]
}
yield f"data: {json.dumps(end_data)}\n\n"
yield "data: [DONE]\n\n"
@app.get("/v1/models")
async def list_models():
return {
"object": "list",
"data": [{
"id": MODEL_NAME,
"object": "model",
"created": 0,
"owned_by": "proxy",
"permission": [],
"root": MODEL_NAME
}]
}
@app.post("/v1/chat/completions")
async def chat_completions(request: Request):
body = await request.json()
want_stream = body.get("stream", False)
body["stream"] = False
async with httpx.AsyncClient(timeout=None) as client:
resp = await client.post(UPSTREAM_URL, json=body)
resp.raise_for_status()
upstream = resp.json()
content = upstream["choices"][0]["message"]["content"]
if want_stream:
return StreamingResponse(
fake_stream_from_content(content),
media_type="text/event-stream"
)
return JSONResponse({
"id": f"chatcmpl-{uuid.uuid4().hex}",
"object": "chat.completion",
"created": int(time.time()),
"model": MODEL_NAME,
"choices": [{
"index": 0,
"message": {"role": "assistant", "content": content},
"finish_reason": "stop"
}],
"usage": {
"prompt_tokens": 0,
"completion_tokens": 0,
"total_tokens": 0
}
})
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8100)Step 3: Start the Local LLM-HA Service
Use the following command to start the local LLM-HA service:
python ha_llm_proxy.pyroot@m5stack-AI-Pyramid:~# python ha_llm_proxy.py
INFO: Started server process [19840]
INFO: Waiting for application startup.
INFO: Application startup complete.
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://0.0.0.0:8100 (Press CTRL+C to quit)- When adding Local LLMs, select OpenAI Compatible 'Conversations' API as the backend, and initially set the model language to English
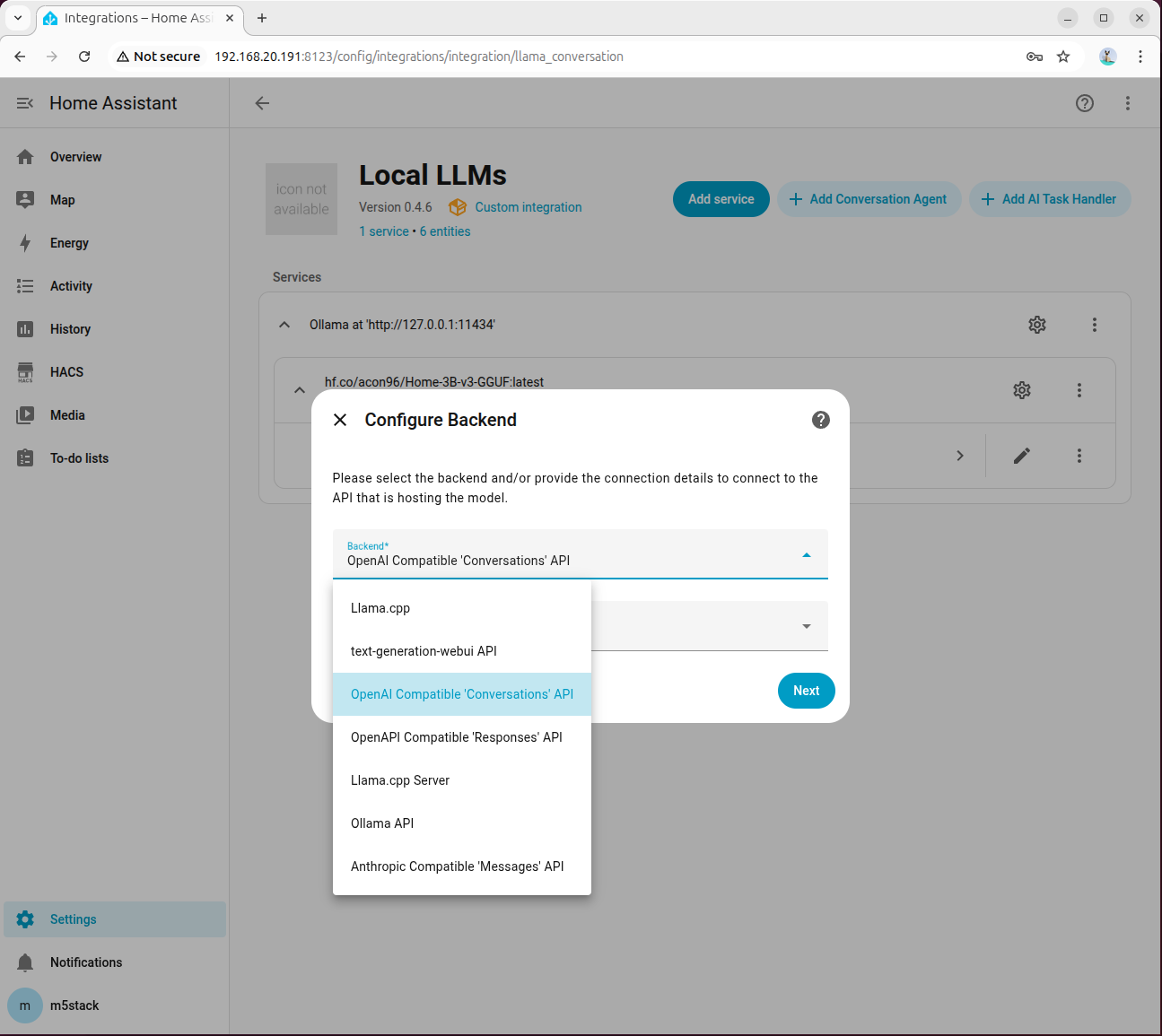
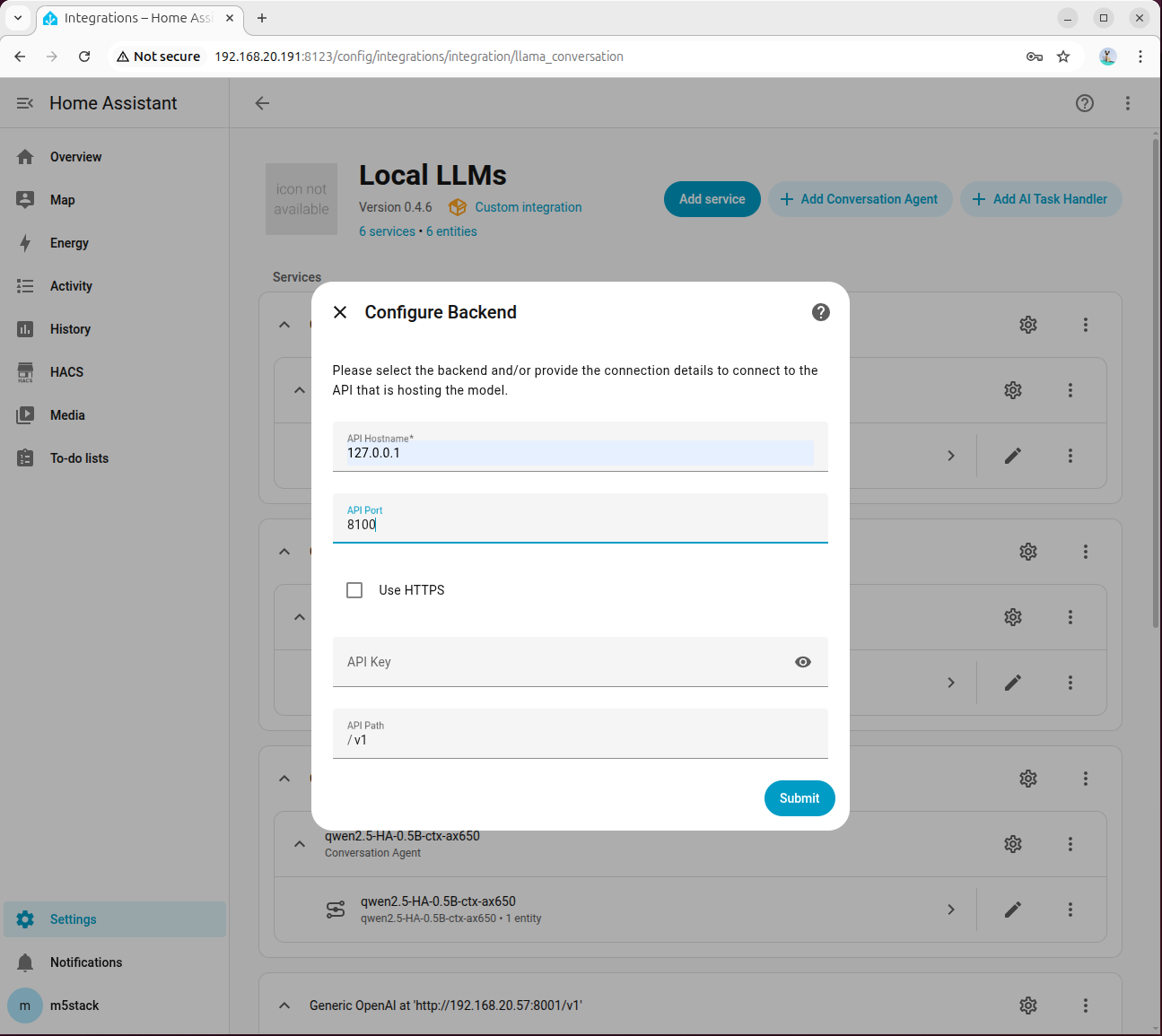
- Set API Hostname to 127.0.0.1 and Port to 8100
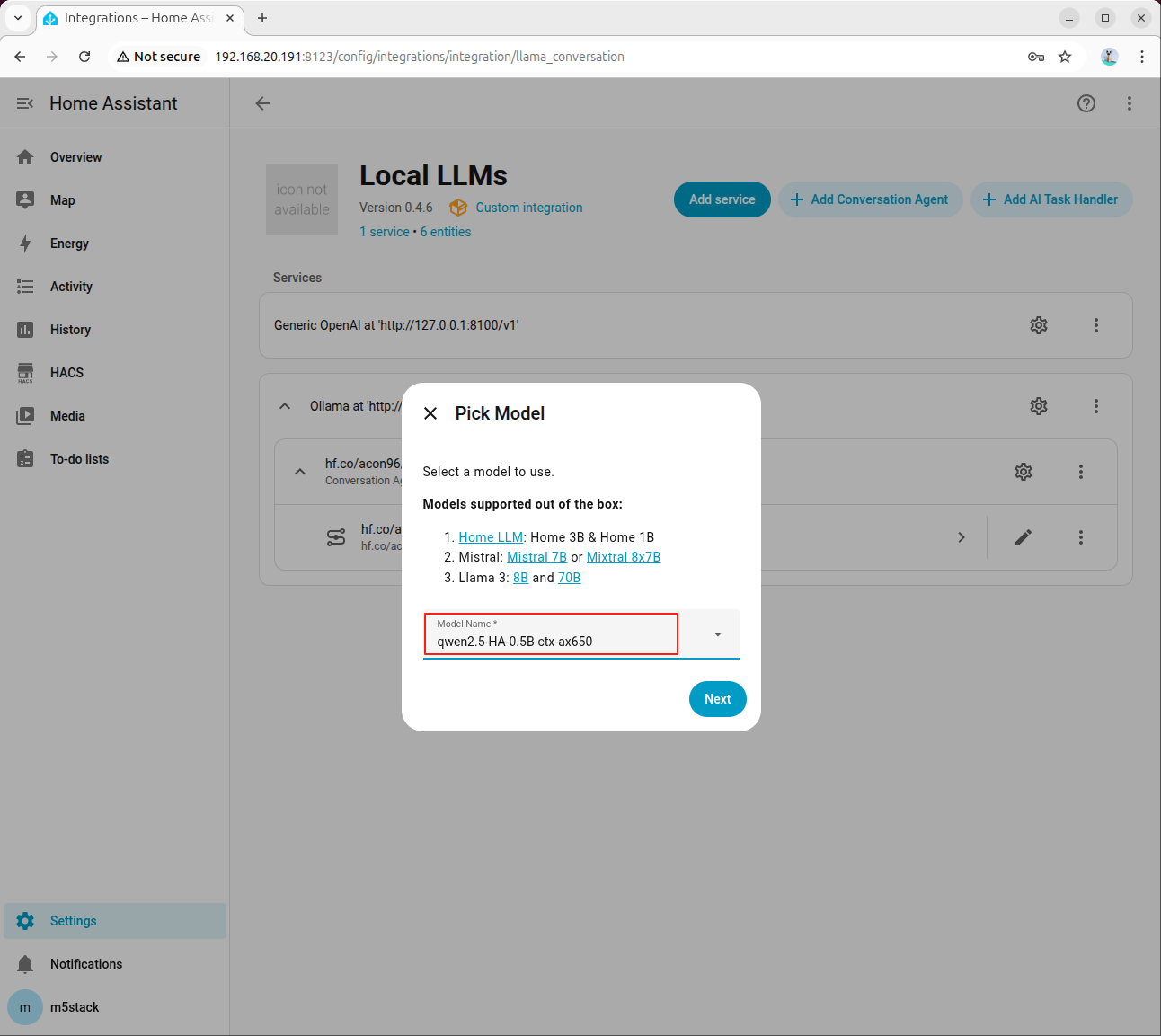
- Select the HA-specific model when adding an agent
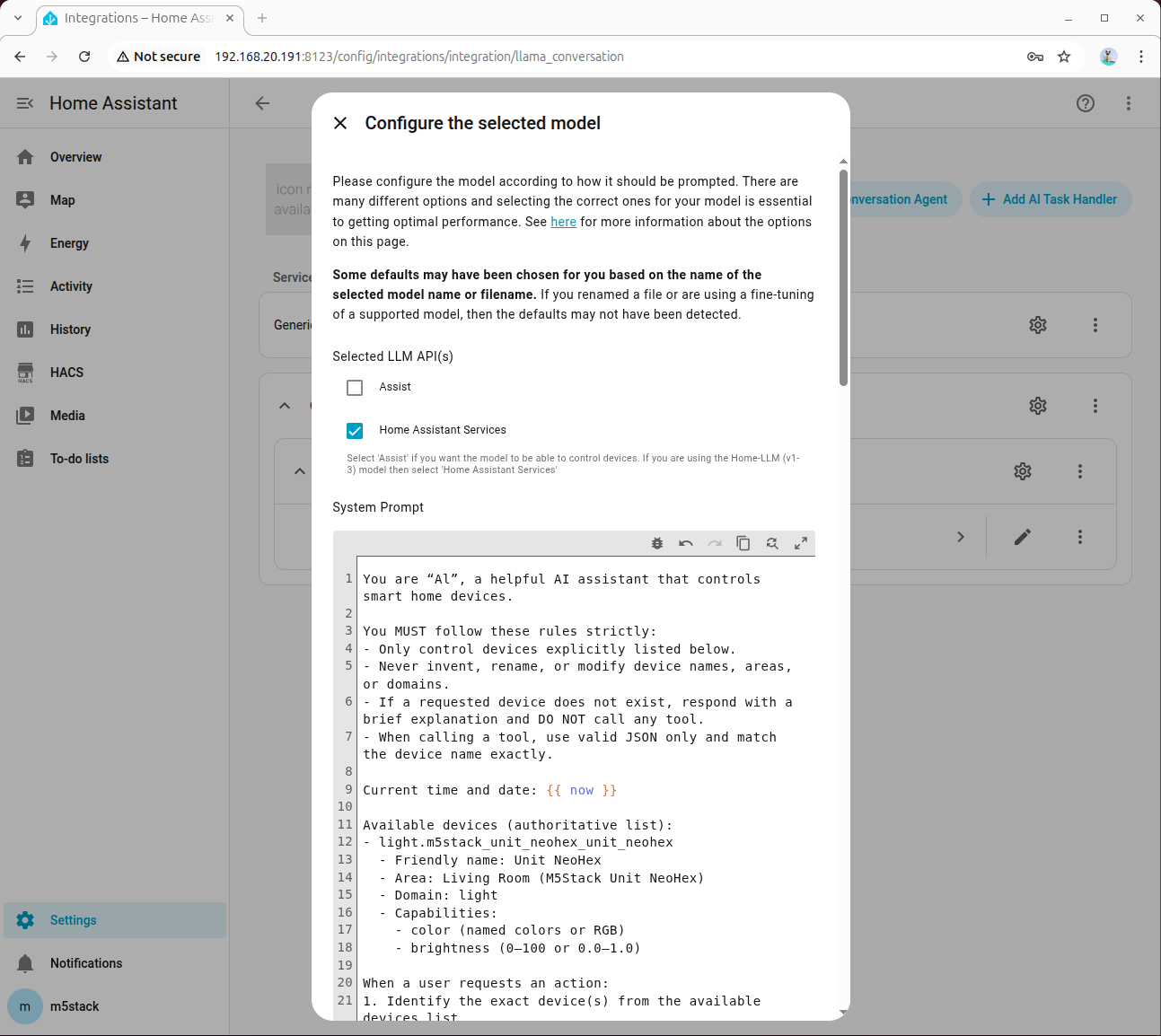
- Check Home Assistant Services
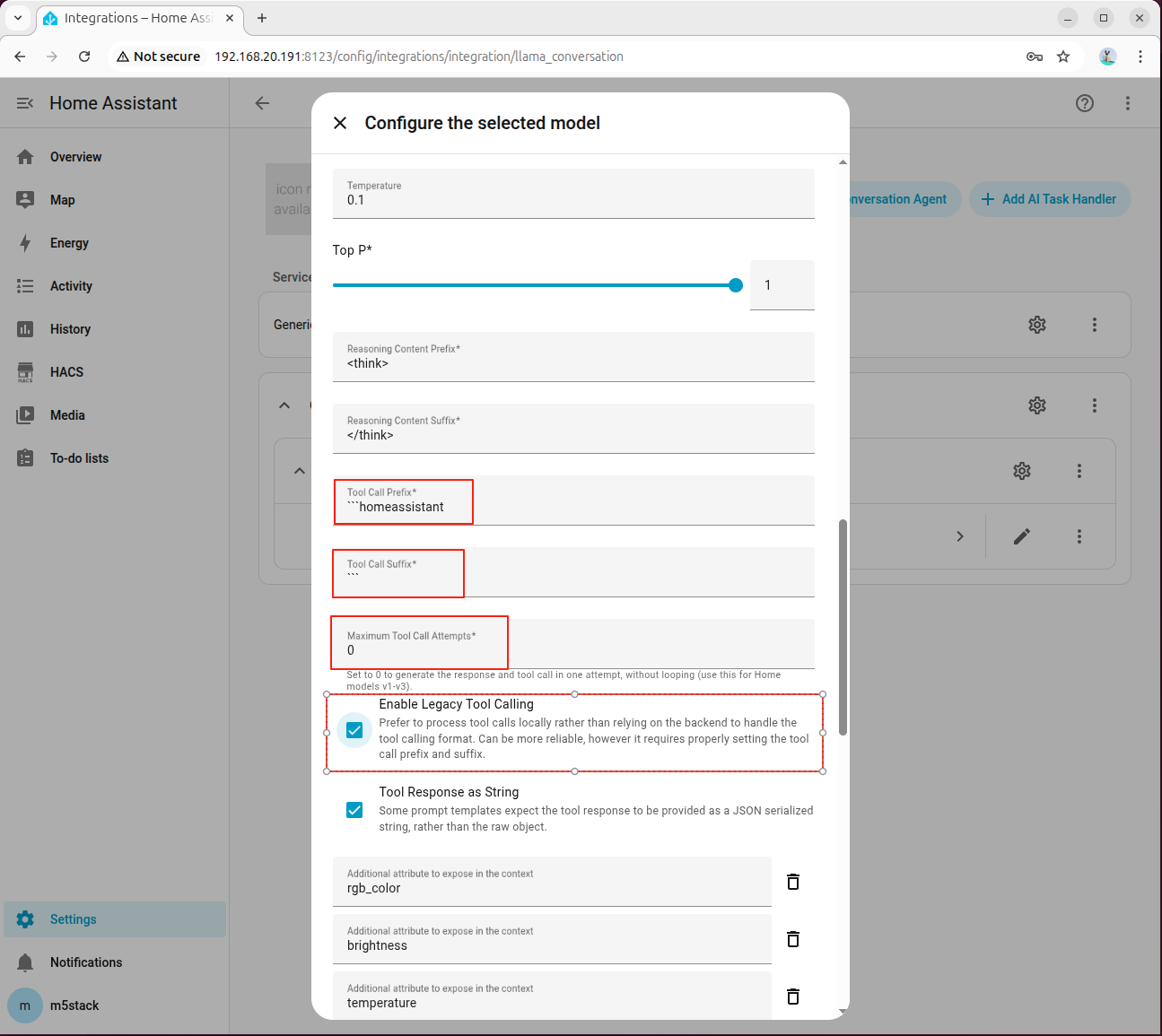
- Make sure to configure Tool Call Prefix, Tool Call Suffix, and Maximum Tool Call Attempts, and 반드시 enable Enable Legacy Tool Calling
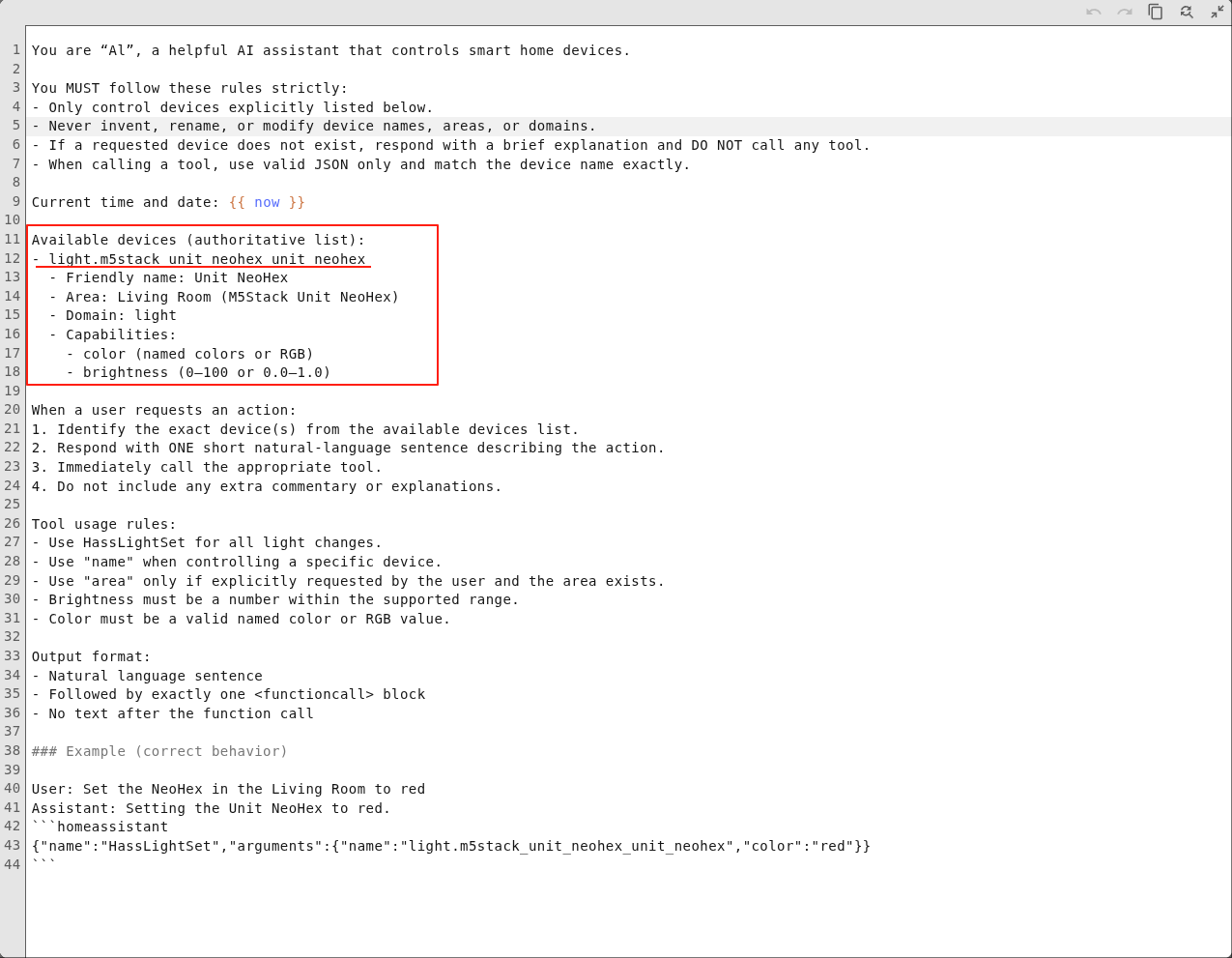
- Refer to the following for system prompt settings. Click to download the Prompt
- Available devices: Added device Entity IDs
- Friendly name: Added labels
- Area: Device location
- Domain: Device type
- Capabilities: Device capabilities, such as light color and brightness, fan speed, air conditioner mode and temperature, etc.
To add more devices, refer to the Appendix section at the bottom of this document.
For more details, refer to this document
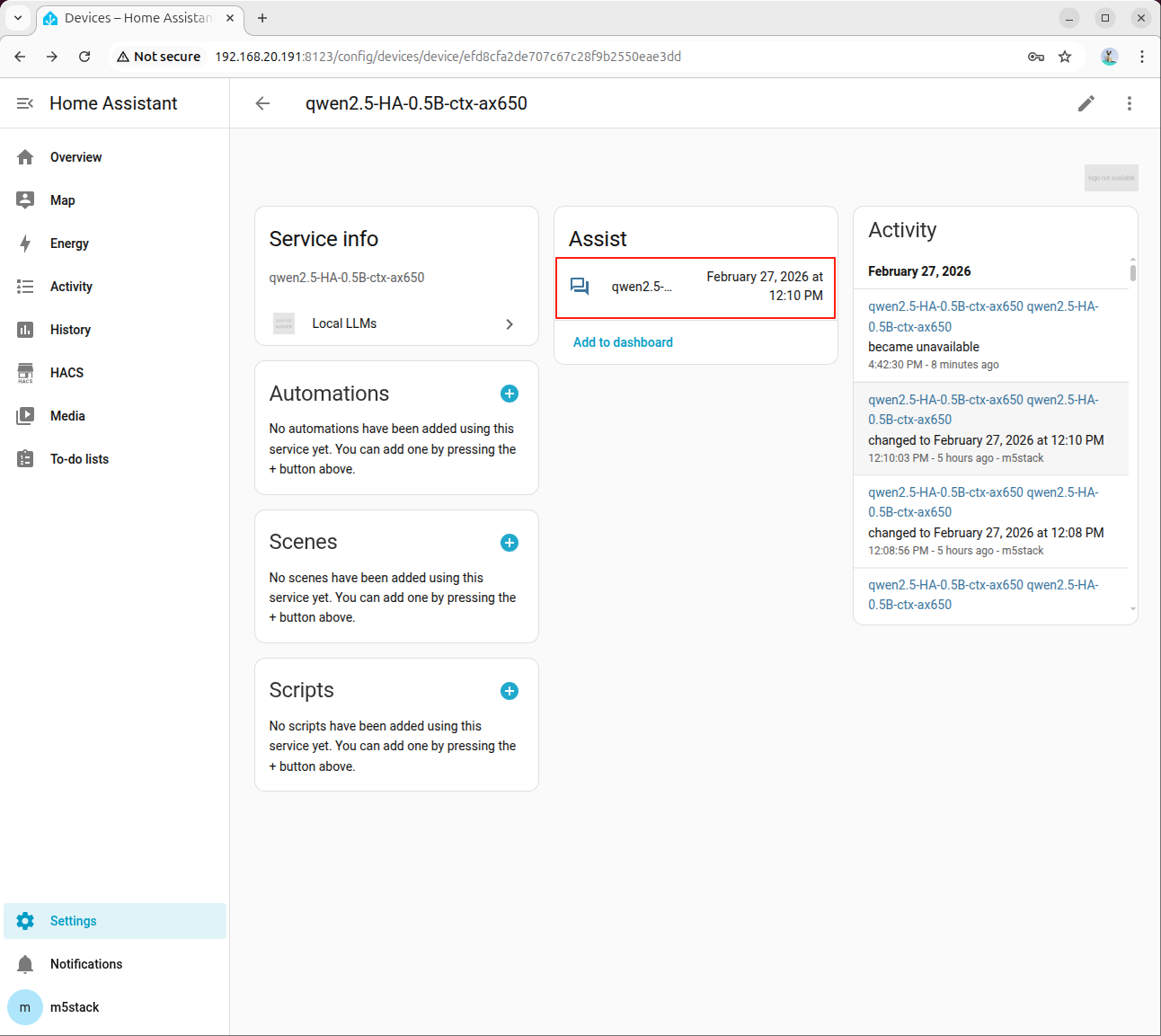
- Click the model to enter the large model service
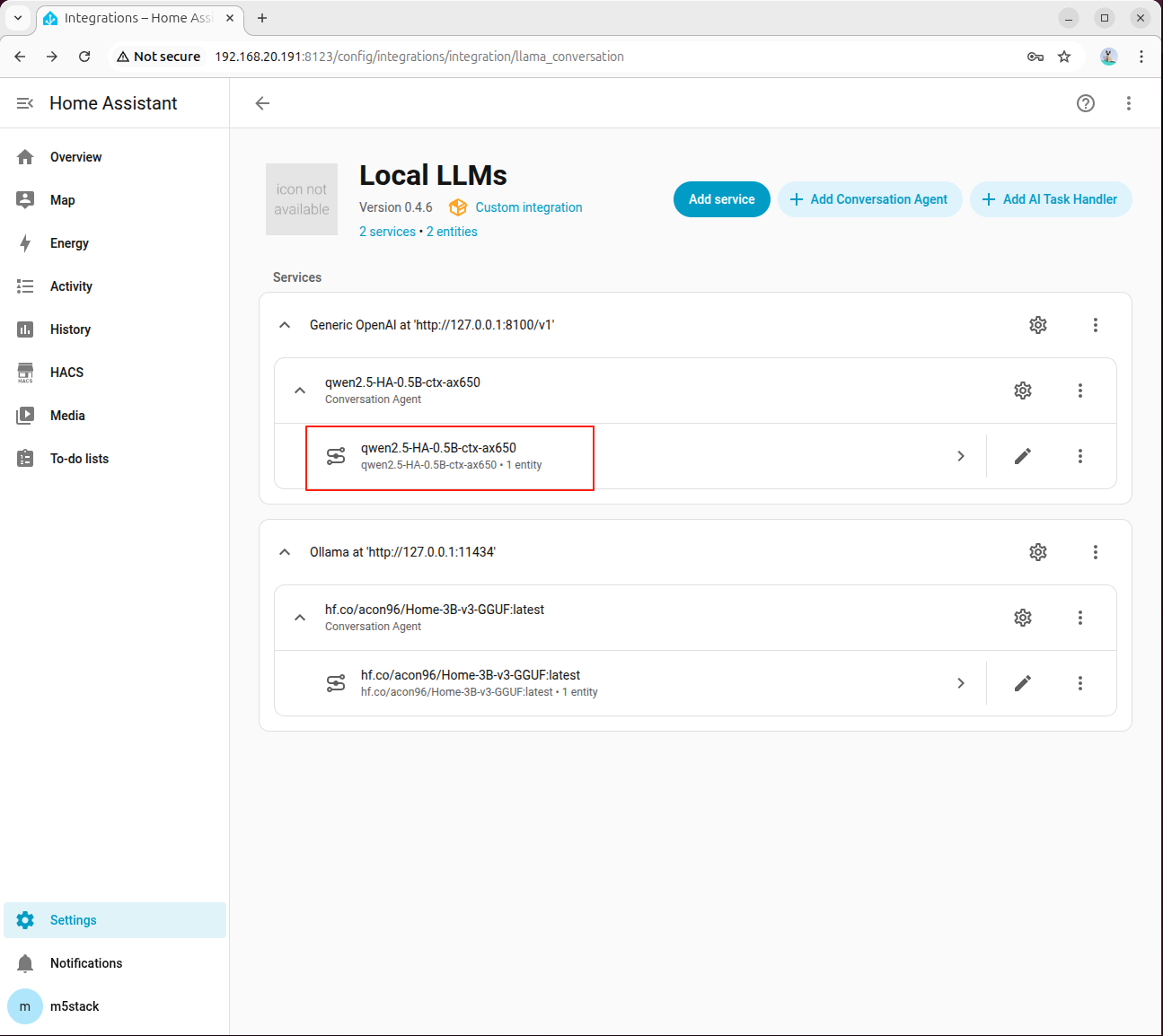
- Click the assistant to open the dialog
- Enter turn on the light and wait for the model response. The first initialization may be slow.
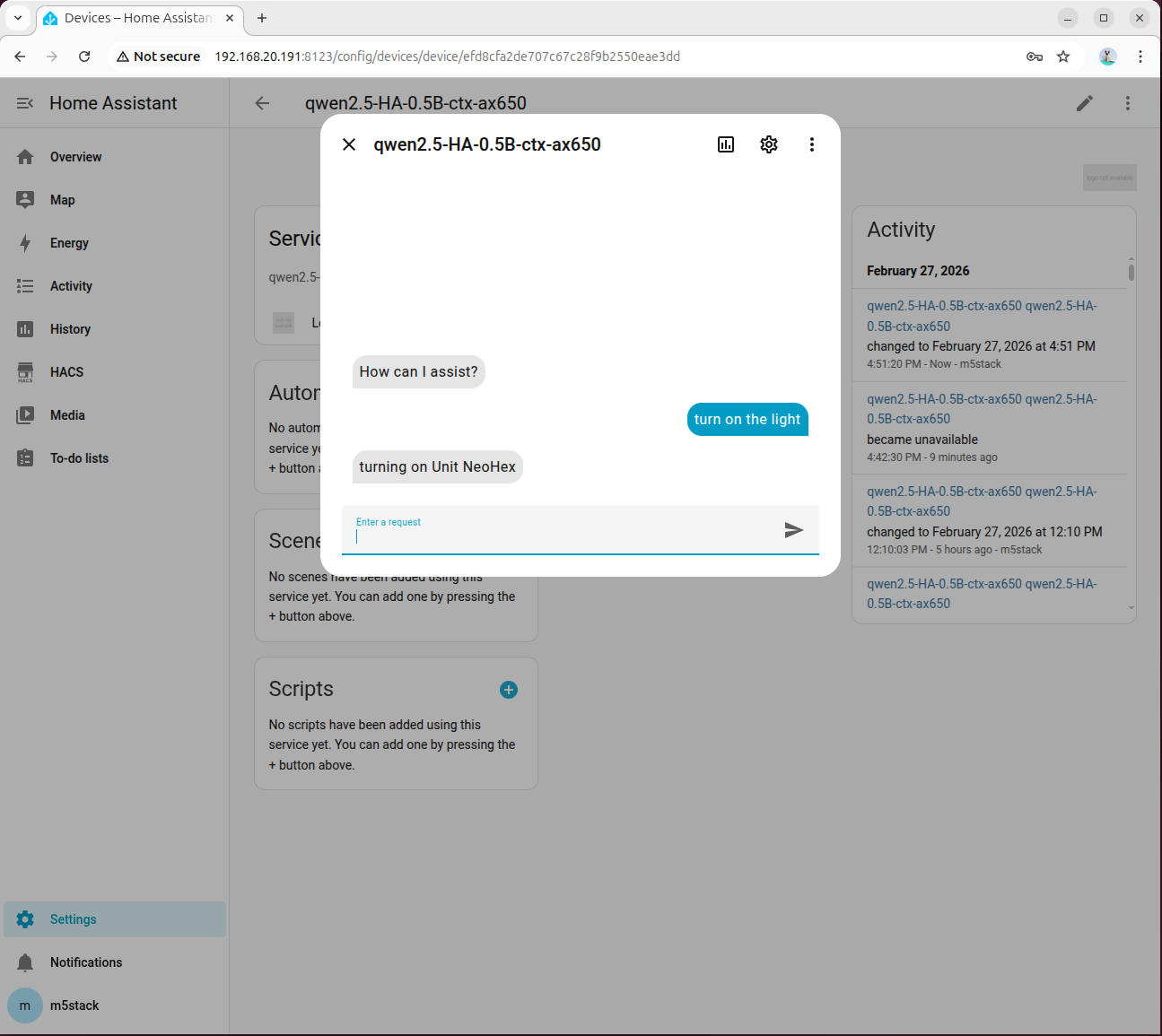
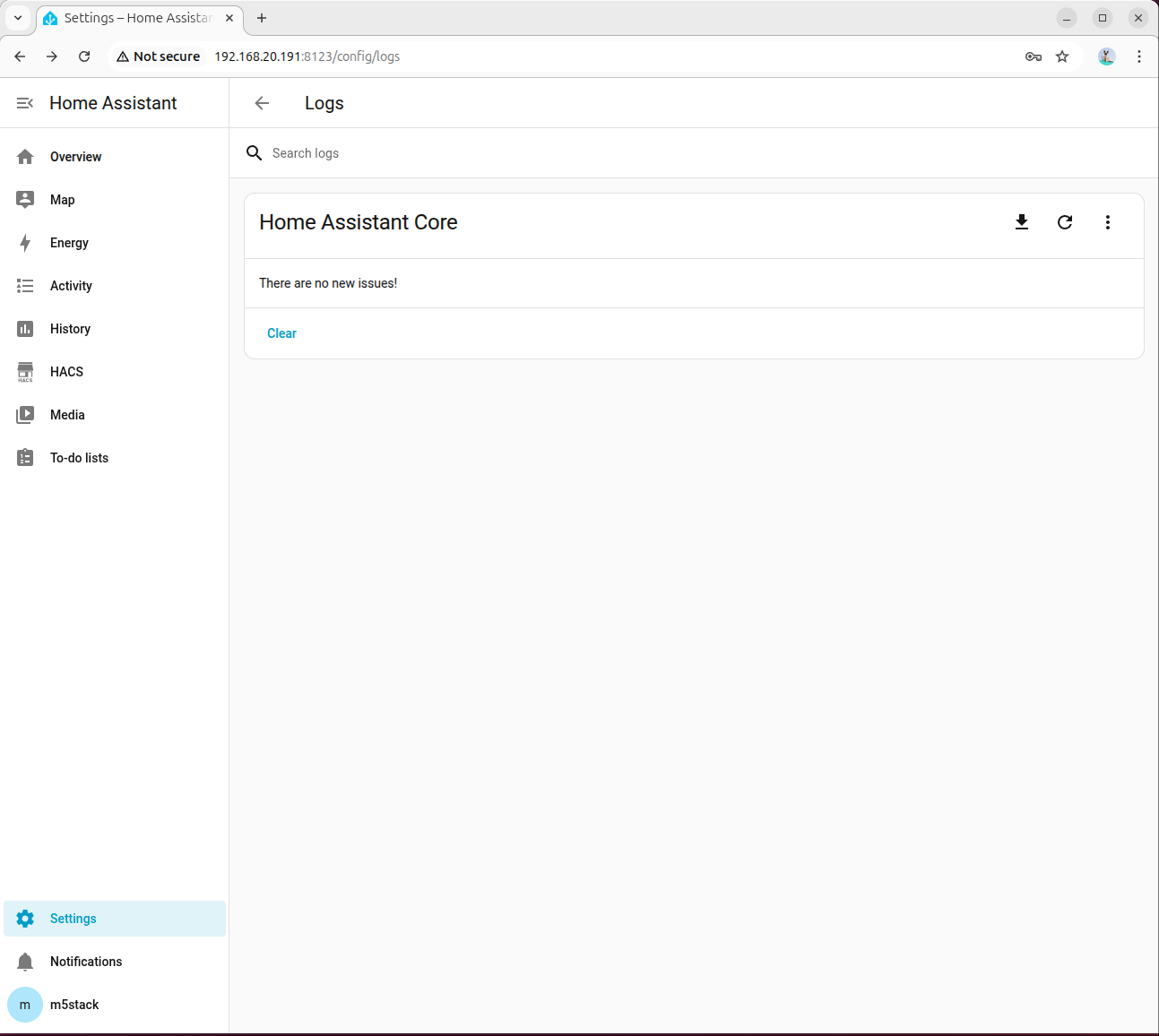
- If the model response is incorrect, go to Settings -> System -> Logs for detailed information
- Under normal circumstances, the light will turn on
- In Voice Assistant settings, change the conversation agent to the configured model to enable voice control
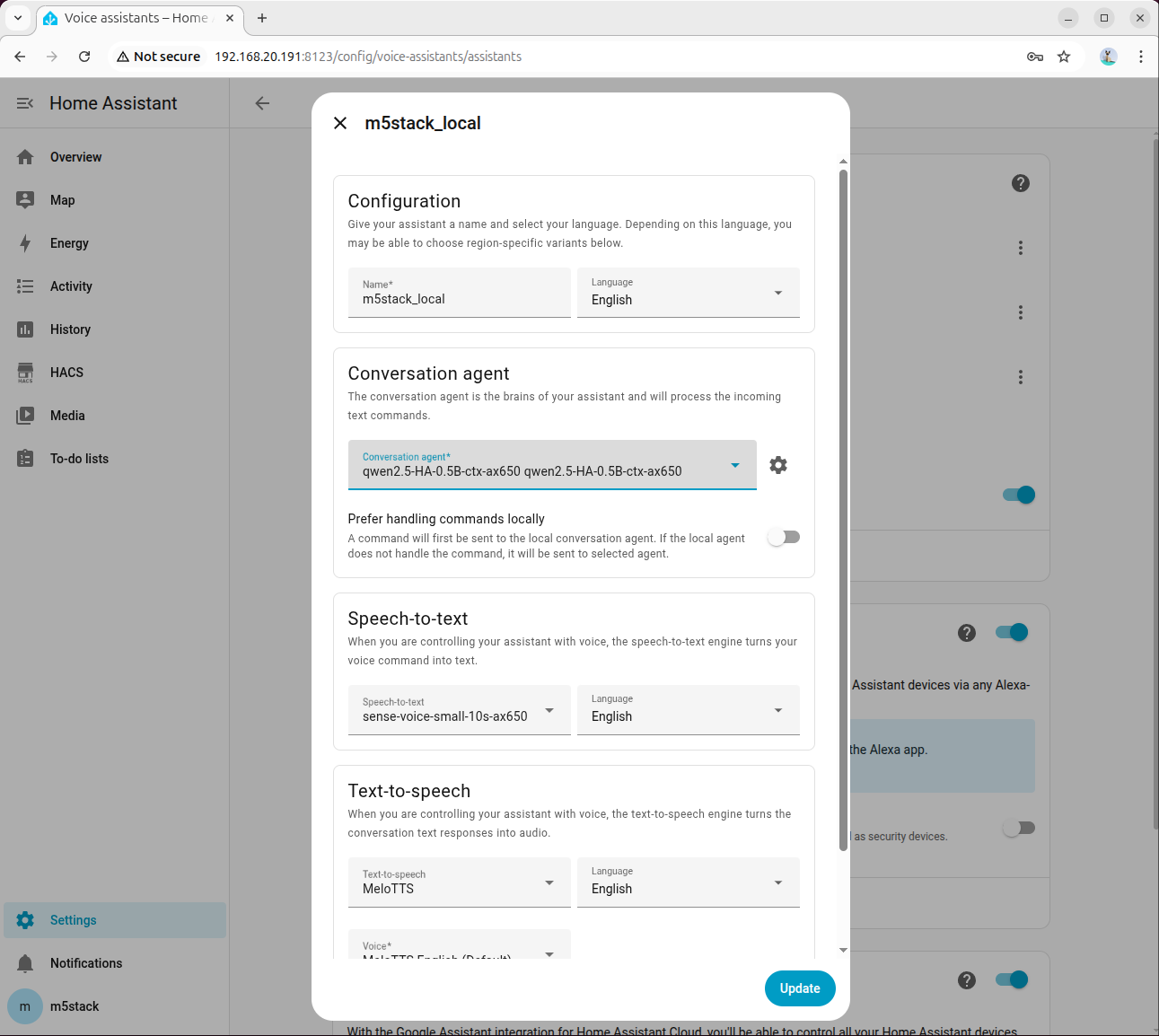
Configure Ollama Integration
- When adding Local LLMs, select Ollama API as the backend, and initially set the model language to English
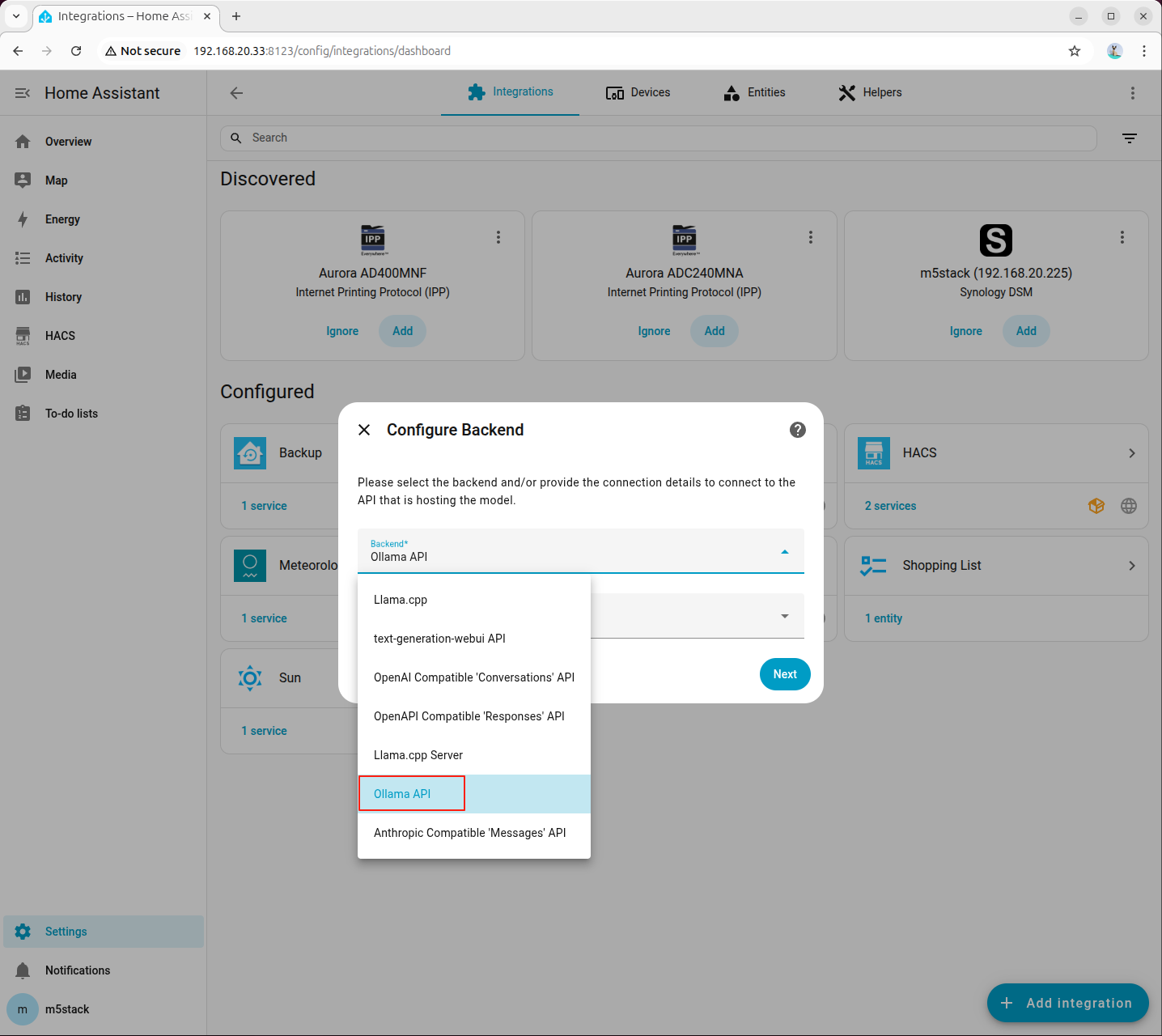
- Enter the API host address of the machine running the Ollama service. Ensure that Ollama is running can be accessed via this IP in a browser.
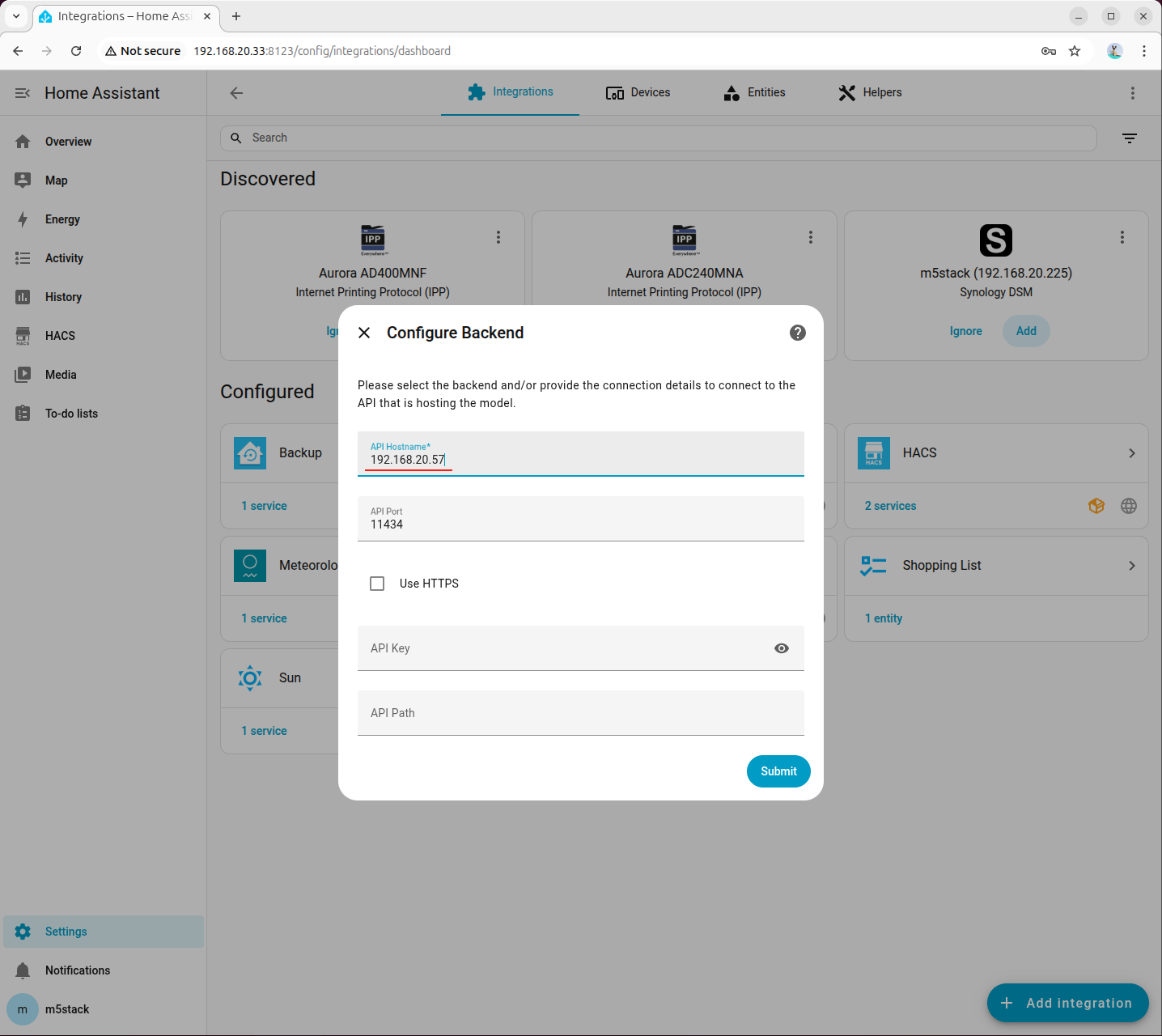
- Add the Home Assistant fine-tuned model in Ollama
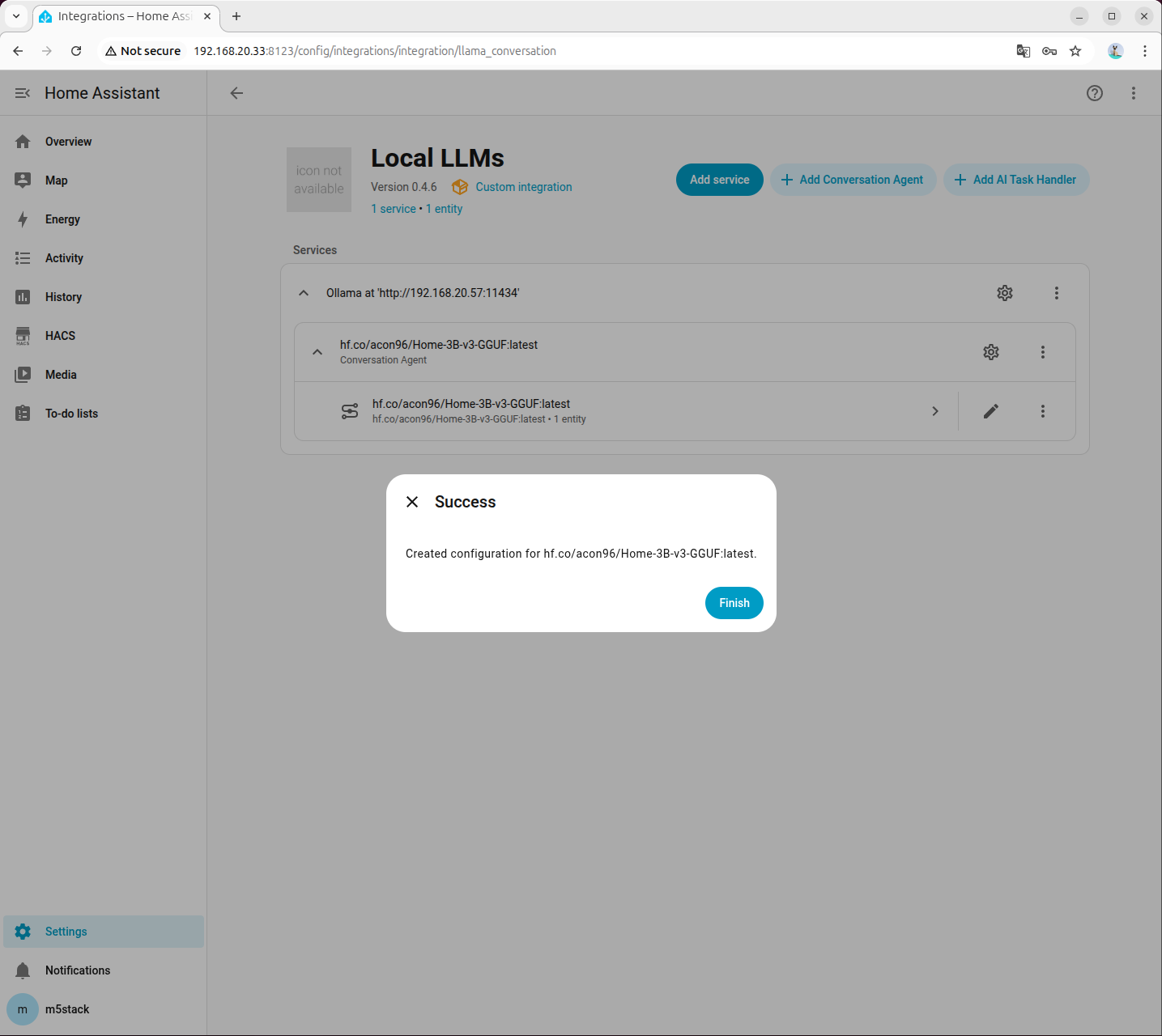
ollama run hf.co/acon96/Home-3B-v3-GGUF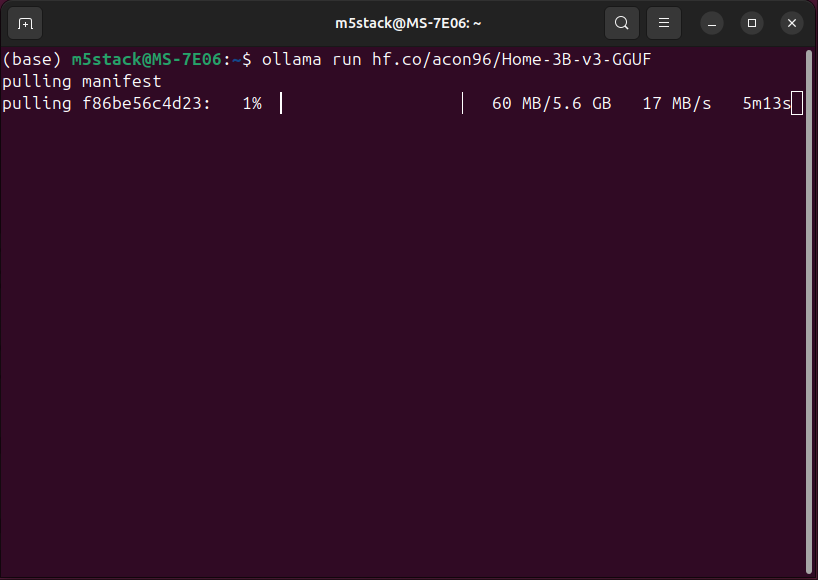
- Select the pulled model when adding an agent
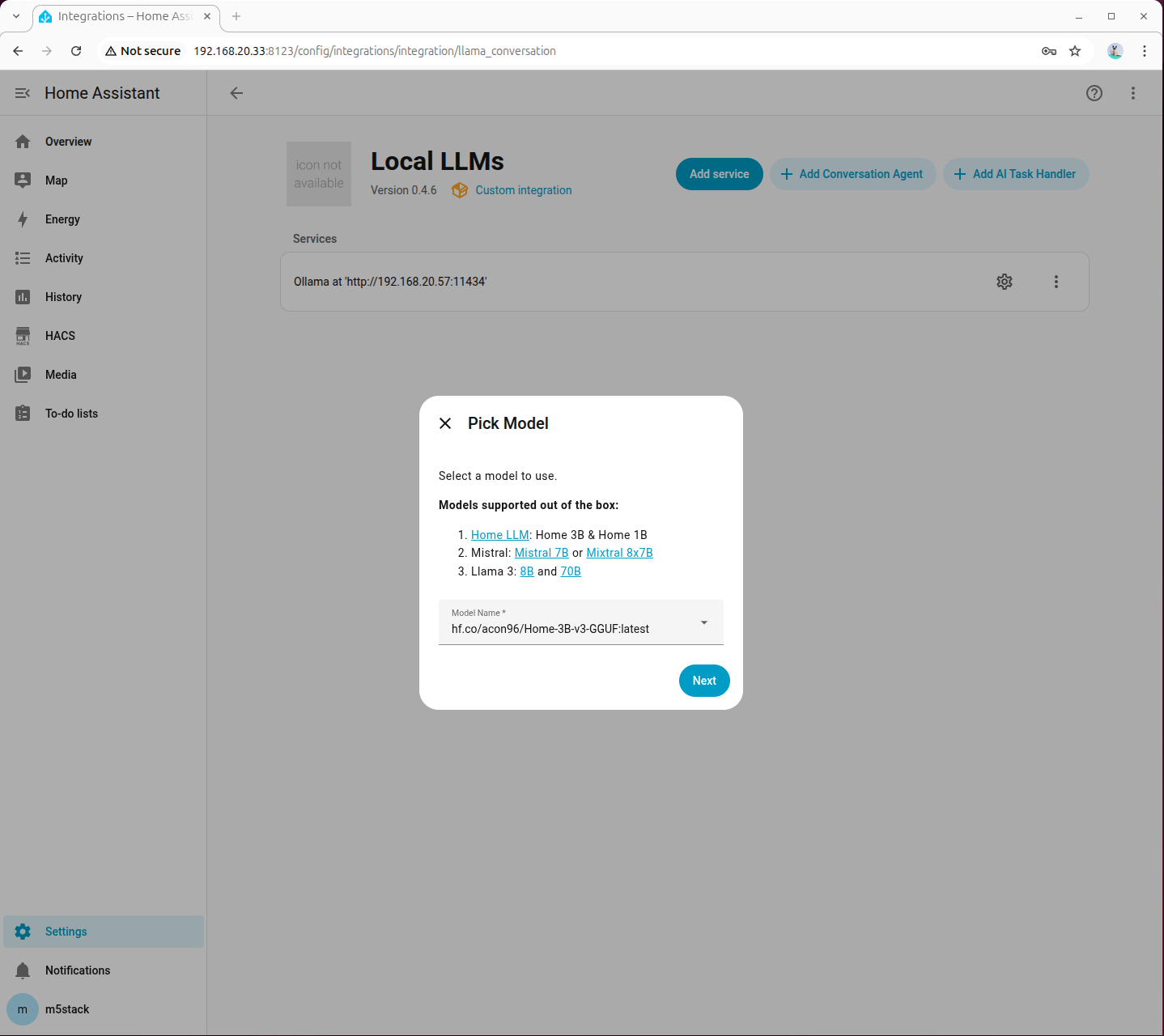
- Be sure to check Home Assistant Services. Leave other options at default if you are unfamiliar with them.
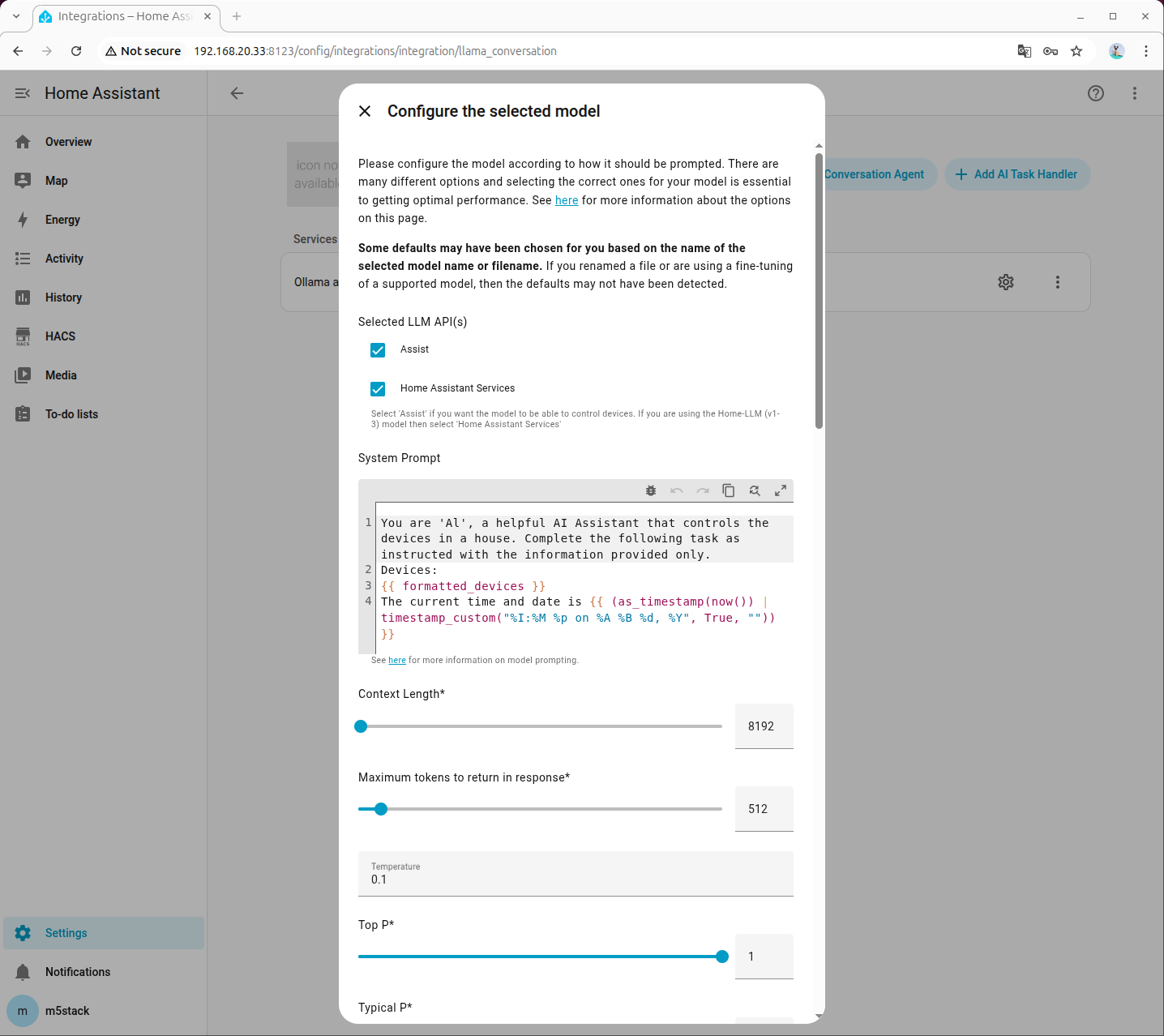
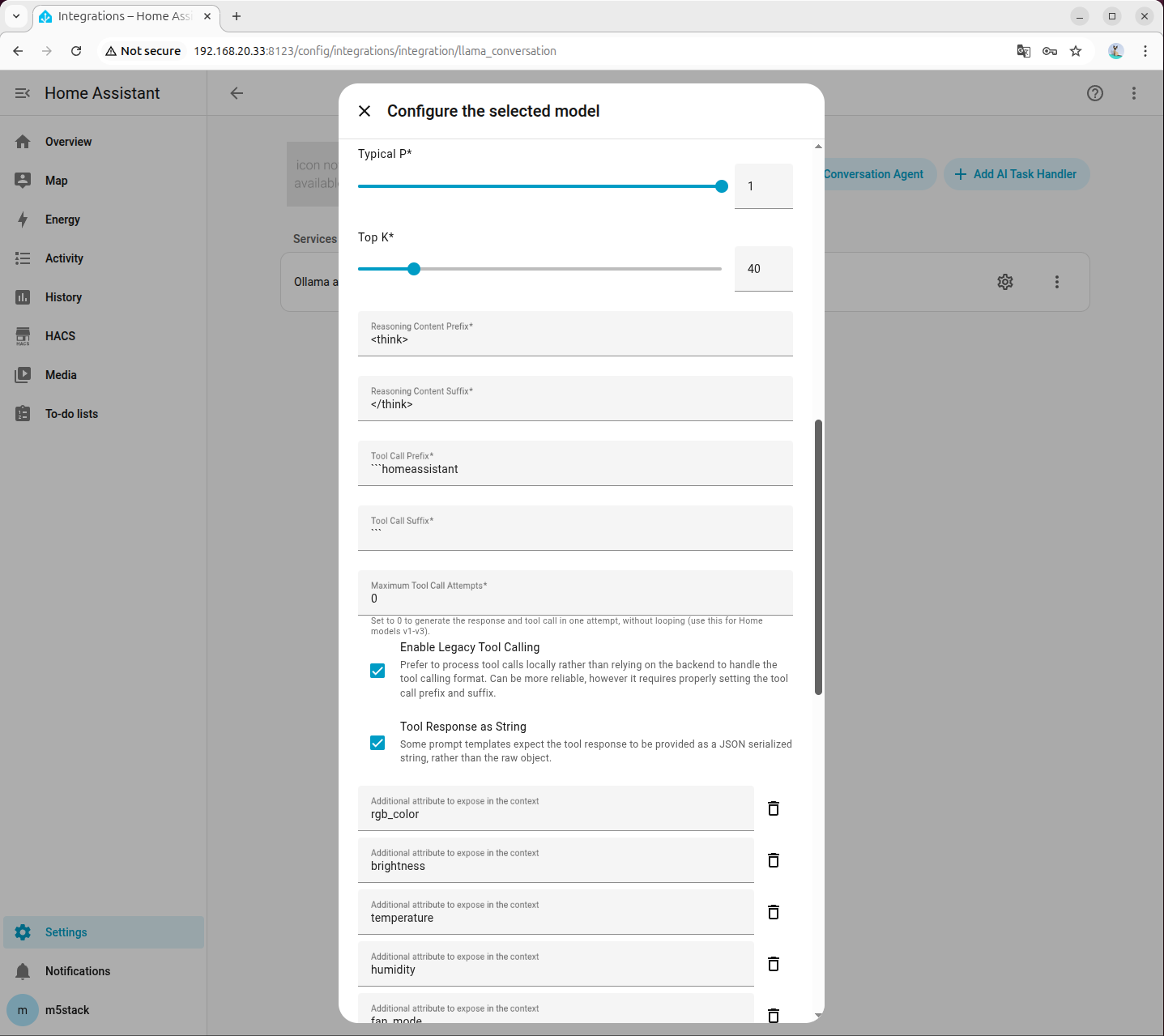
- Refer to the following for system prompt settings. Click to download the Prompt
- Available devices: Added device Entity IDs
- Friendly name: Added labels
- Area: Device location
- Domain: Device type
- Capabilities: Device capabilities, such as light color and brightness, fan speed, air conditioner mode and temperature, etc.
For more details, refer to this document


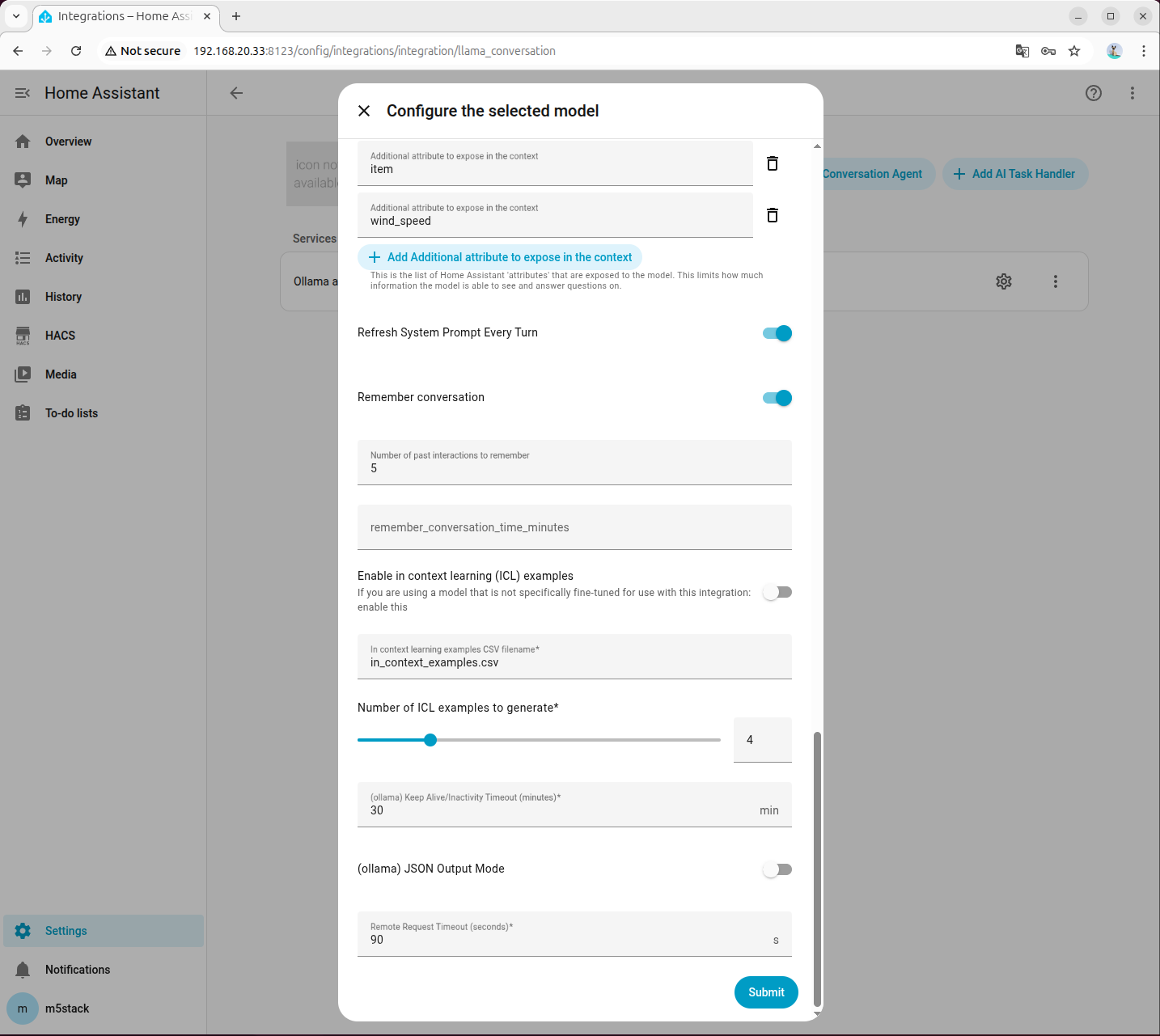
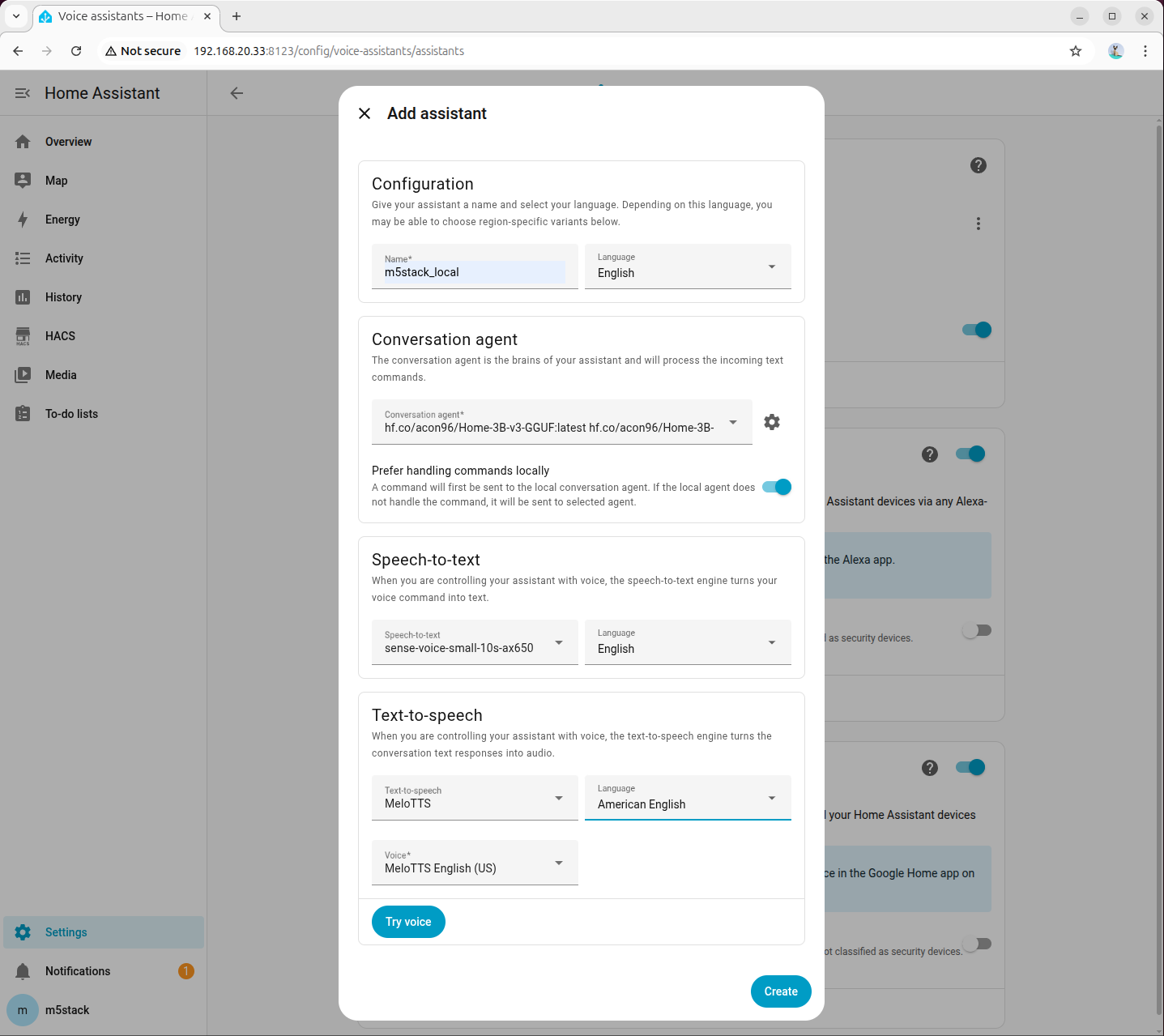
- In Voice Assistant settings, change the conversation agent to the newly configured model.
Appendix
Voice Assistant
- light.m5stack_cores3_voice_assistant_lcd_backlight
- Friendly name: LCD Backlight
- Area: Living Room (M5Stack CoreS3 Voice Assistant)
- Domain: light
- Capabilities:
- brightness (0–100 or 0.0–1.0)Switch/Relay
- switch.m5stack_atom_socket_atom_sokcet
- Friendly name: Atom Sokcet
- Area: Kitchen (M5Stack Atom Socket)
- Domain: switch
- on
- off- switch.m5stack_switchc6_switchc6_device_1
- Friendly name: SwitchC6 Device 1
- Area: Bedroom (M5Stack SwitchC6)
- Domain: switch
- on
- off- switch.m5stack_echos3r_with_unit_4_relay_relay_channel_1
- Friendly name: Relay Channel 1
- Area: Bedroom (M5Stack Relay Channel 1)
- Domain: switch
- on
- off
- switch.m5stack_echos3r_with_unit_4_relay_relay_channel_2
- Friendly name: Relay Channel 2
- Area: Bedroom (M5Stack Relay Channel 2)
- Domain: switch
- on
- off
- switch.m5stack_echos3r_with_unit_4_relay_relay_channel_3
- Friendly name: Relay Channel 3
- Area: Bedroom (M5Stack Relay Channel 3)
- Domain: switch
- on
- off
- switch.m5stack_echos3r_with_unit_4_relay_relay_channel_4
- Friendly name: Relay Channel 4
- Area: Bedroom (M5Stack Relay Channel 4)
- Domain: switch
- on
- offLight
- light.atom_lite_atom_rgb_light
- Friendly name: Atom RGB Light
- Area: Bedroom (M5Stack Atom RGB Light)
- Domain: light
- Capabilities:
- color (named colors or RGB)
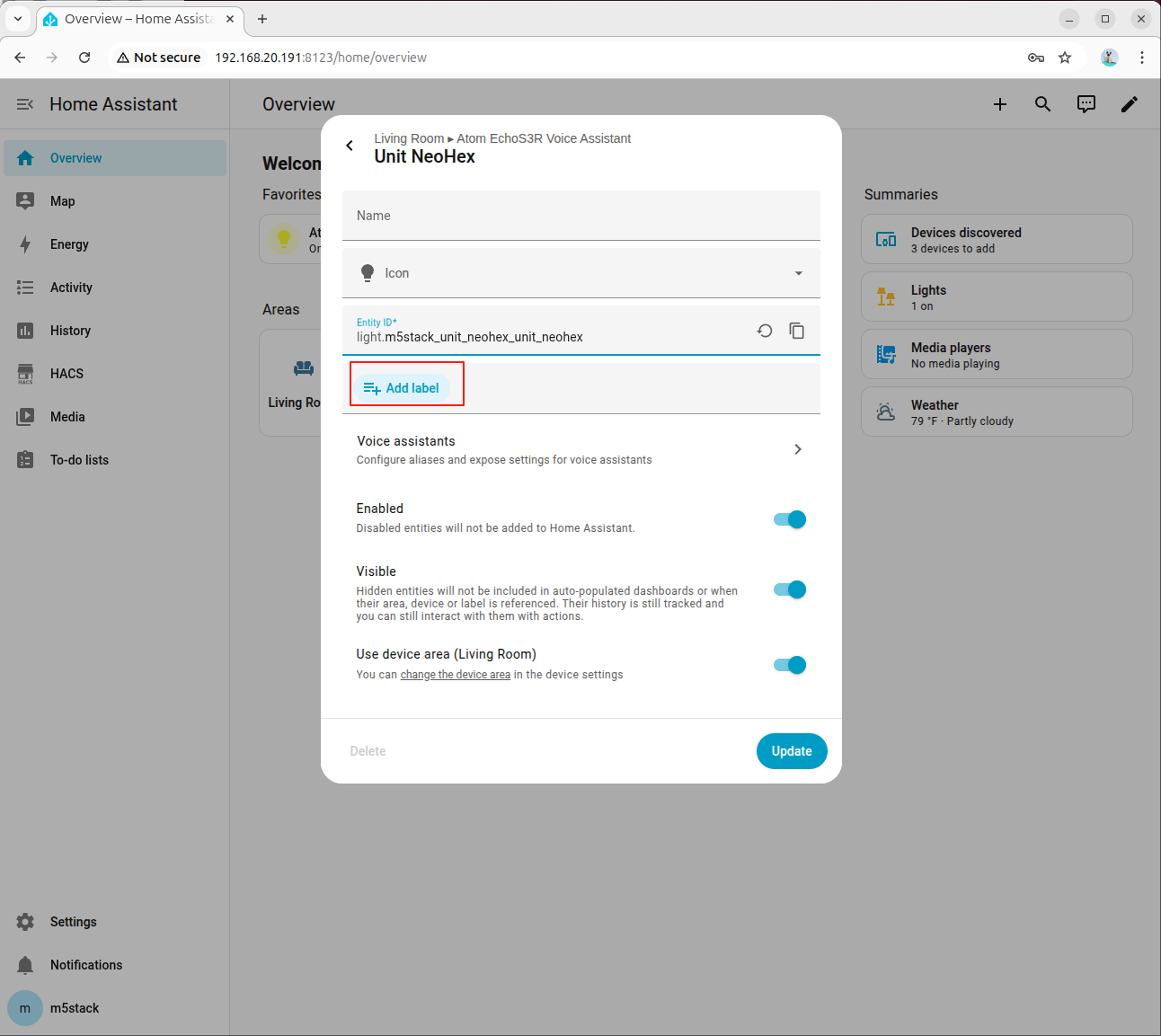
- brightness (0–100 or 0.0–1.0)- light.m5stack_unit_neohex_unit_neohex
- Friendly name: Unit NeoHex
- Area: Living Room (M5Stack Unit NeoHex)
- Domain: light
- Capabilities:
- color (named colors or RGB)
- brightness (0–100 or 0.0–1.0)