TimerCamera Series Home Assistant Integration
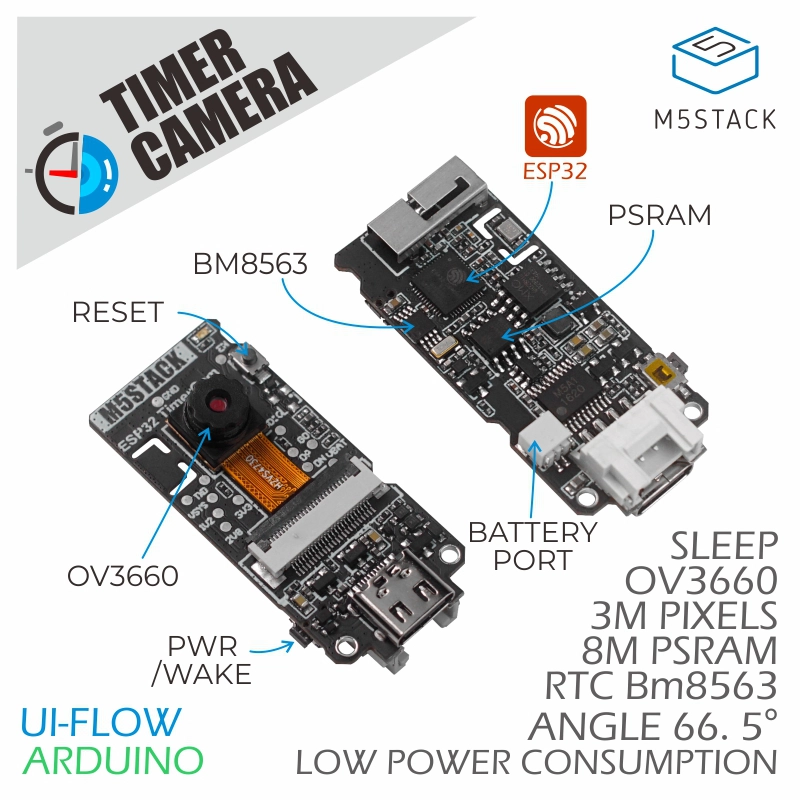


The TimerCamera series is a camera module based on ESP32-D0WDQ6-V3 with onboard 8 MB PSRAM and a 3 MP camera (OV3660). DFOV is 66.5° (TimerCamera-F is 120°). It can capture photos up to 2048x1536 resolution. It has a status LED and RESET button, and focuses on ultra-low power consumption. With the RTC (BM8563), it supports scheduled sleep and wake-up.
See the latest configuration examples on ESPHome
Prerequisites
- Home Assistant host
- Install and enable ESPHome Builder in Home Assistant
Open ESPHome Builder and click NEW DEVICE in the lower-right to create a new device.
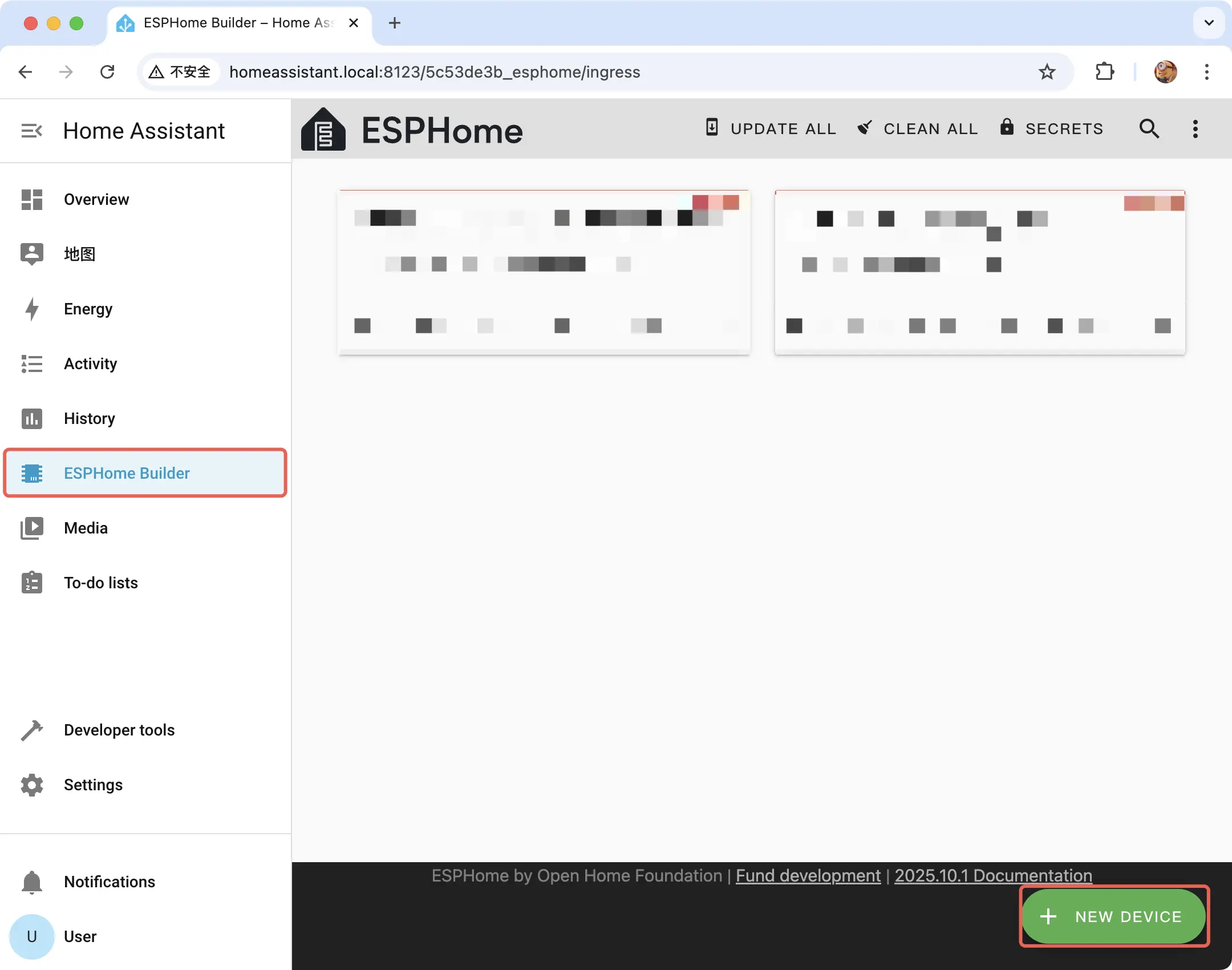
In the popup, click CONTINUE.
Choose New Device Setup to create a new configuration file.
Name the new configuration file.
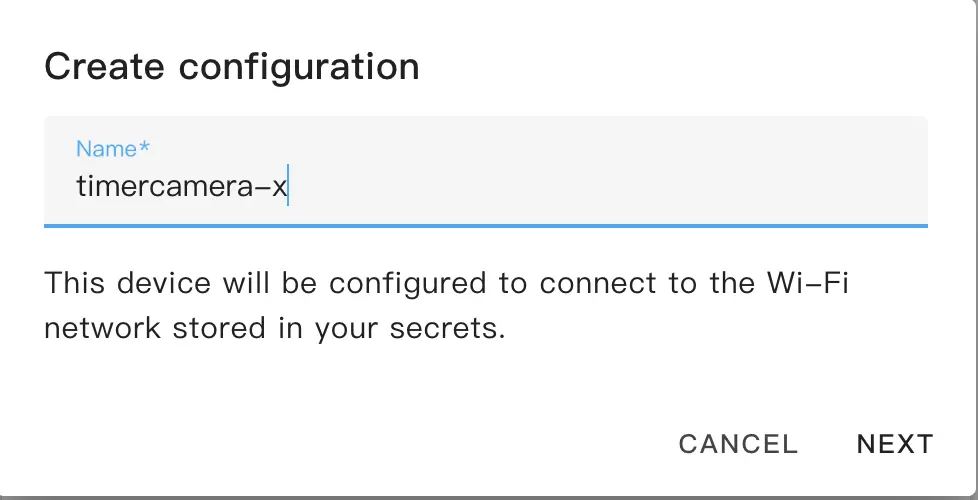
Choose the device type. Keep the default and select ESP32.
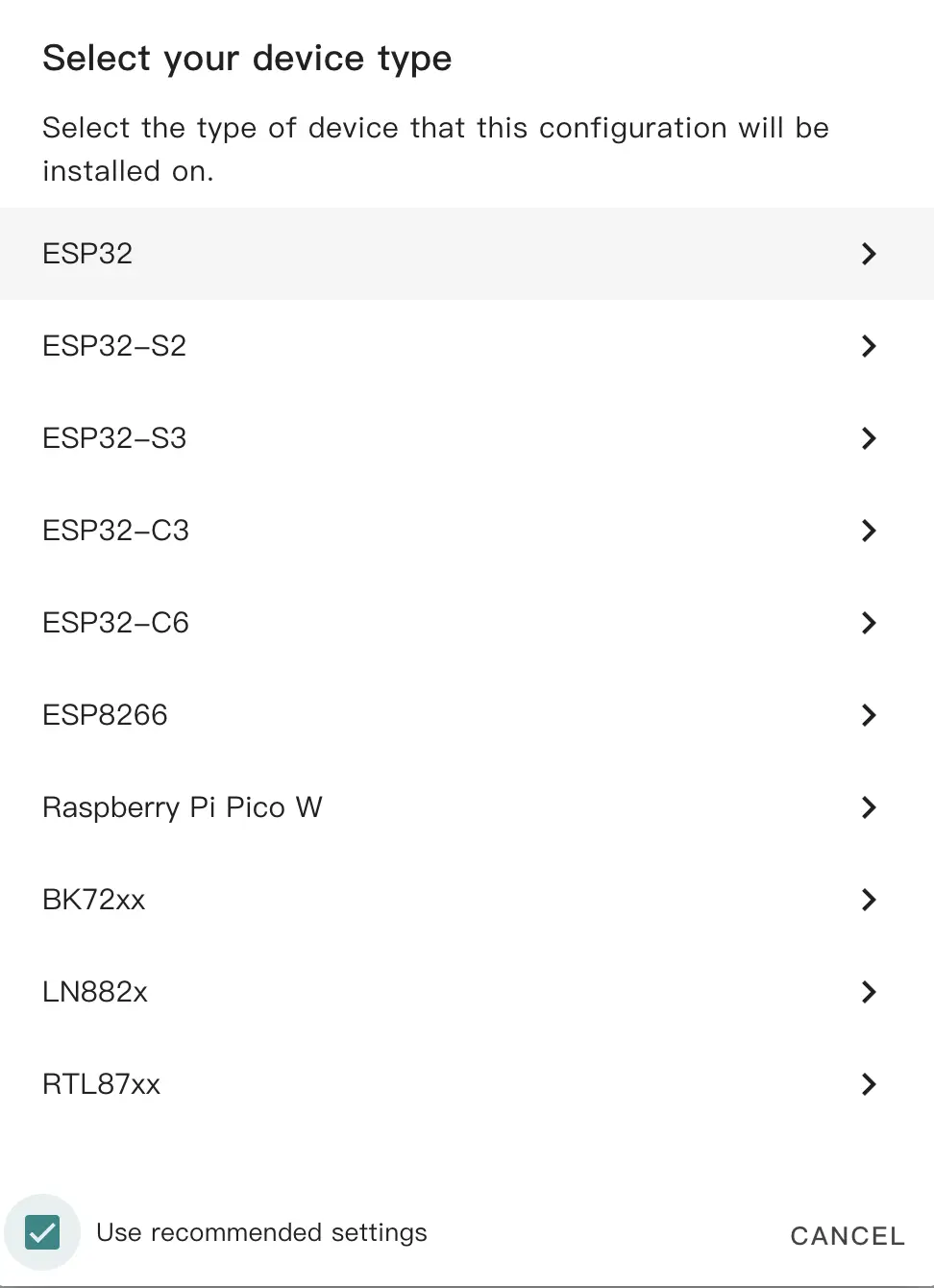
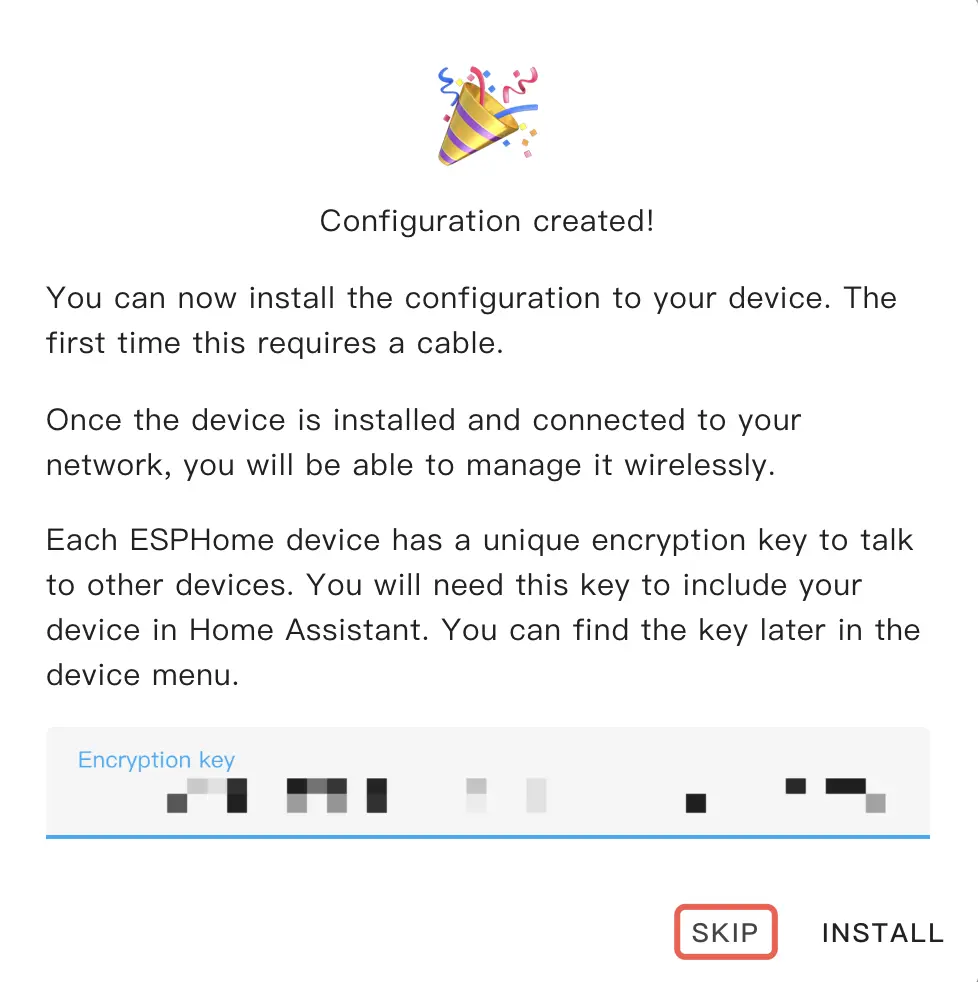
Copy the Encryption Key for later and click SKIP to continue.
Configure the Device
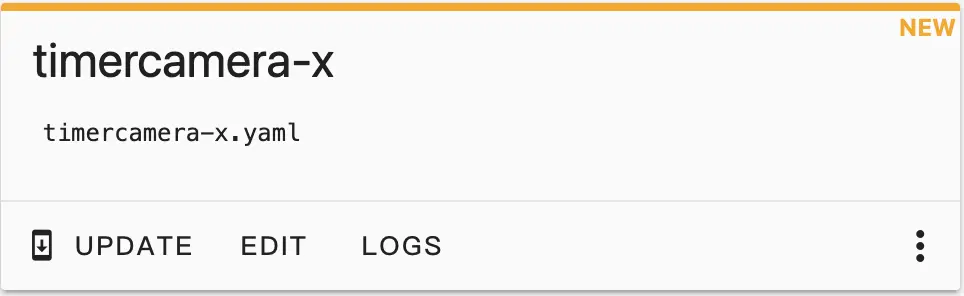
On the generated configuration card, click EDIT to edit:
Open the configuration file and make the following changes.
- Add the PSRAM component
psram:
mode: quad
speed: 80MHz- Add I2C and ESP32 Camera components
i2c:
- id: bsp_i2c
sda: GPIO12
scl: GPIO14
- id: cam_i2c
sda: GPIO25
scl: GPIO23
esp32_camera:
name: OV3660 Camera
external_clock:
pin: GPIO27
frequency: 20MHz
i2c_id: cam_i2c
data_pins: [GPIO32, GPIO35, GPIO34, GPIO5, GPIO39, GPIO18, GPIO36, GPIO19]
vsync_pin: GPIO22
href_pin: GPIO26
pixel_clock_pin: GPIO21
reset_pin: GPIO15
resolution: 640x480
jpeg_quality: 10This uses the default image configuration. Refer to ESPHome examples if you want to adjust it.
- Add the RTC Time component
esphome:
name: timercamera-x
friendly_name: timercamera-x
...
on_boot:
then:
# read the RTC time once when the system boots
bm8563.read_time:
...
time:
- platform: bm8563
i2c_id: bsp_i2c
# repeated synchronization is not necessary unless the external RTC
# is much more accurate than the internal clock
update_interval: never
- platform: homeassistant
# instead try to synchronize via network repeatedly ...
on_time_sync:
then:
# ... and update the RTC when the synchronization was successful
bm8563.write_time:The system reads the time from the RTC at startup. After connecting to Home Assistant, it automatically syncs the time from Home Assistant.
- Configure the LED
output:
- platform: ledc
id: blue_led
pin: GPIO2
light:
- platform: monochromatic
output: blue_led
name: "Blue LED"
restore_mode: RESTORE_DEFAULT_ONThe blue LED is on by default after power-up and can be controlled (on/off, brightness) in Home Assistant.
- Use the battery
switch:
- platform: gpio
id: bat_hold_pin
name: "Battery Hold Pin"
pin: GPIO33
restore_mode: RESTORE_DEFAULT_ONGPIO33 controls whether to use the battery. Keeping it high enables battery operation. By default it stays high. If you turn this off and there is no external power, the device will shut down.
- Monitor battery level
TimerCamera-X and TimerCamera-F include an internal battery. You can read the ADC value on GPIO38 to get the battery voltage and convert it to an approximate battery percentage:
sensor:
- platform: adc
pin: GPIO38
attenuation: 12dB
name: "Battery Voltage"
id: battery_voltage
update_interval: 10s
filters:
- multiply: 1.51
- platform: template
id: battery_percent
name: "Battery Percentage"
unit_of_measurement: "%"
accuracy_decimals: 0
lambda: |-
float voltage = id(battery_voltage).state;
float min_voltage = 3.350f;
float max_voltage = 4.150f;
if (voltage <= min_voltage) return 0.0;
if (voltage >= max_voltage) return 100.0;
float percent = ((voltage - min_voltage) / (max_voltage - min_voltage)) * 100.0;
return percent;BAT_HOLD_Pin (GPIO33) is kept high. Without HOLD, the device will not use battery power and the ADC reading will be very low (< 1 V). If external USB power is connected and HOLD is high, the voltage shown is the charging voltage.After making changes, click SAVE and INSTALL in the top-right corner, then choose Manual Download in the popup.

After compilation finishes, click Download and choose Factory Format to download the firmware.
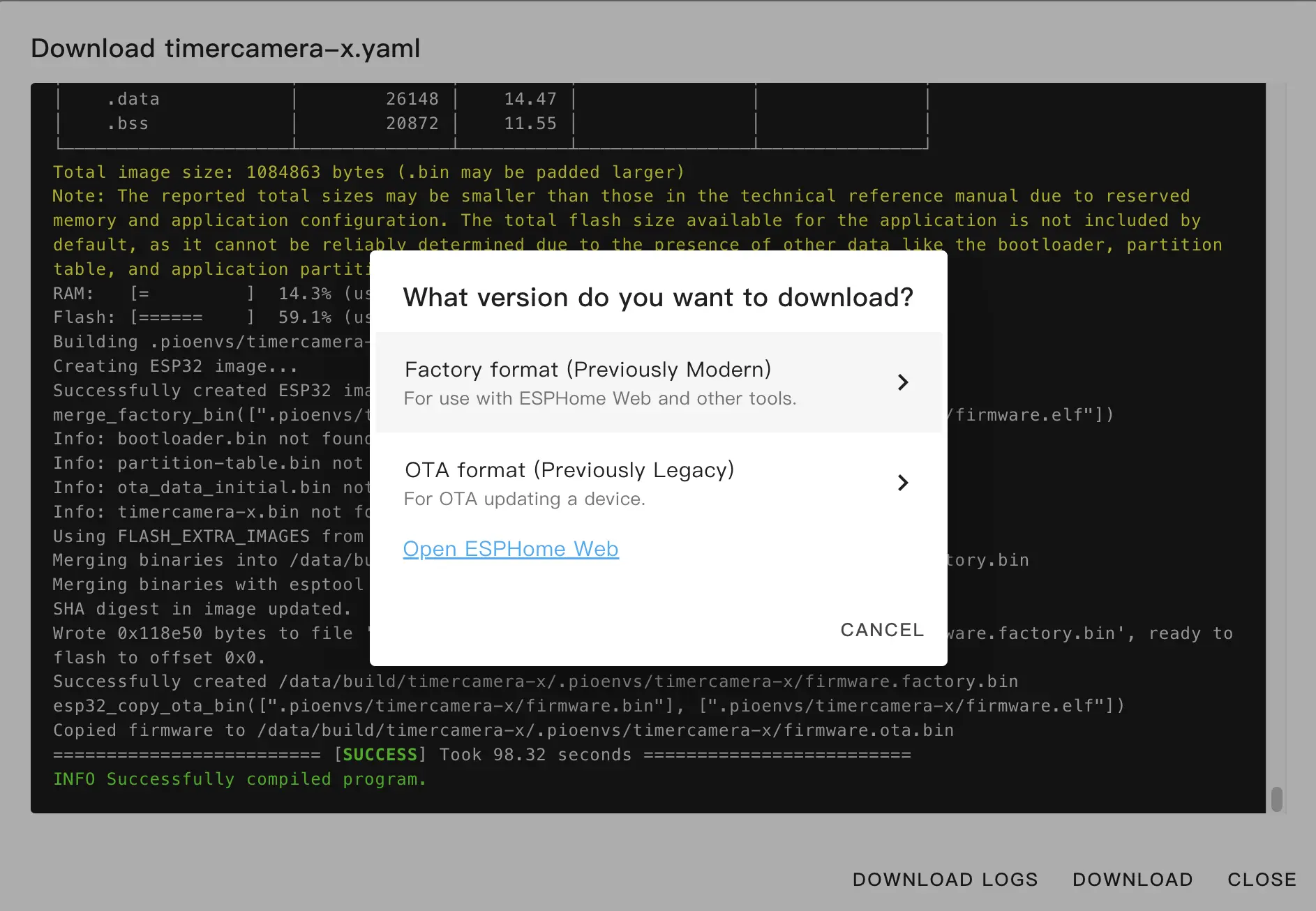
Upload Firmware
Connect the device to your host via a USB Type‑C cable. Open ESPHome Web and click CONNECT to connect to the device.
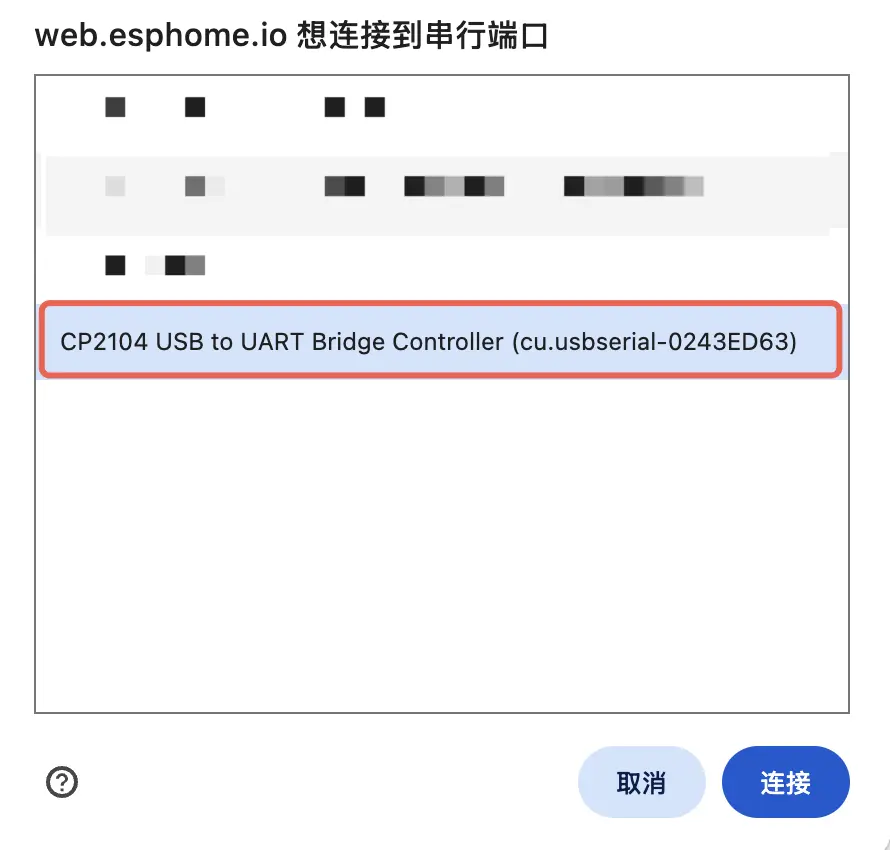
Then click INSTALL and select the previously compiled firmware to upload.

Click INSTALL again to flash and wait for it to complete.
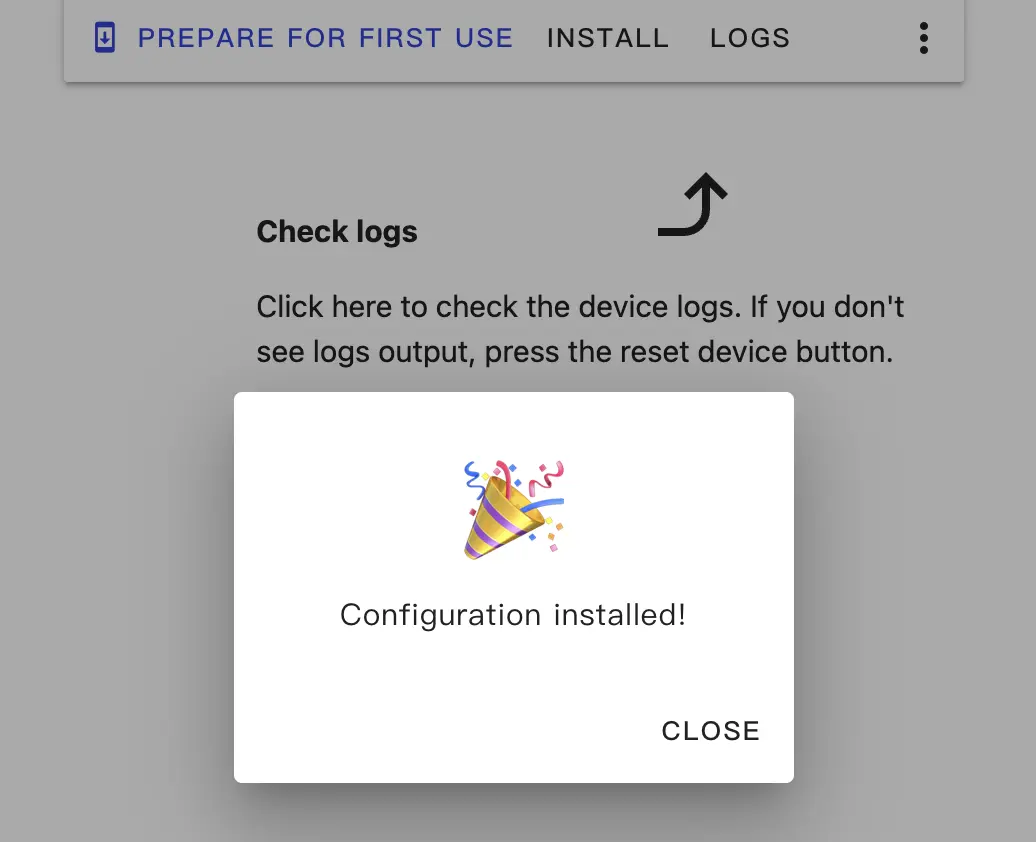
Add the Device to Home Assistant
After flashing, the device will automatically connect to Wi‑Fi on boot. Navigate to Settings -> Device & services to check the device. Click Add to add it to Home Assistant.

Dashboard example:
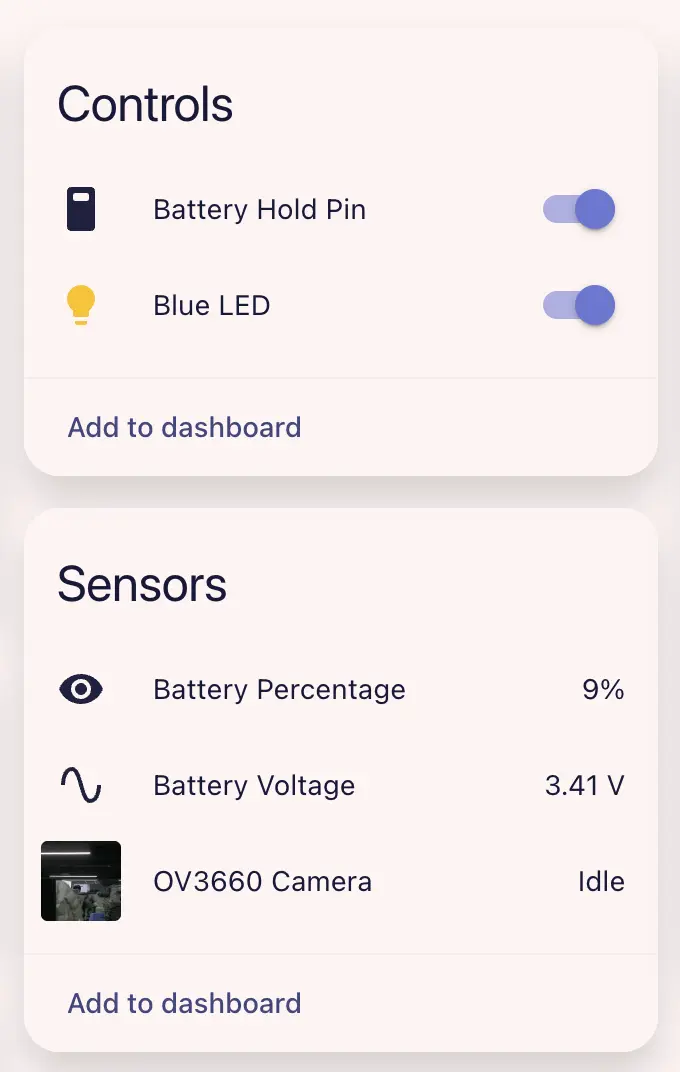
Click the camera entity to view the live preview.
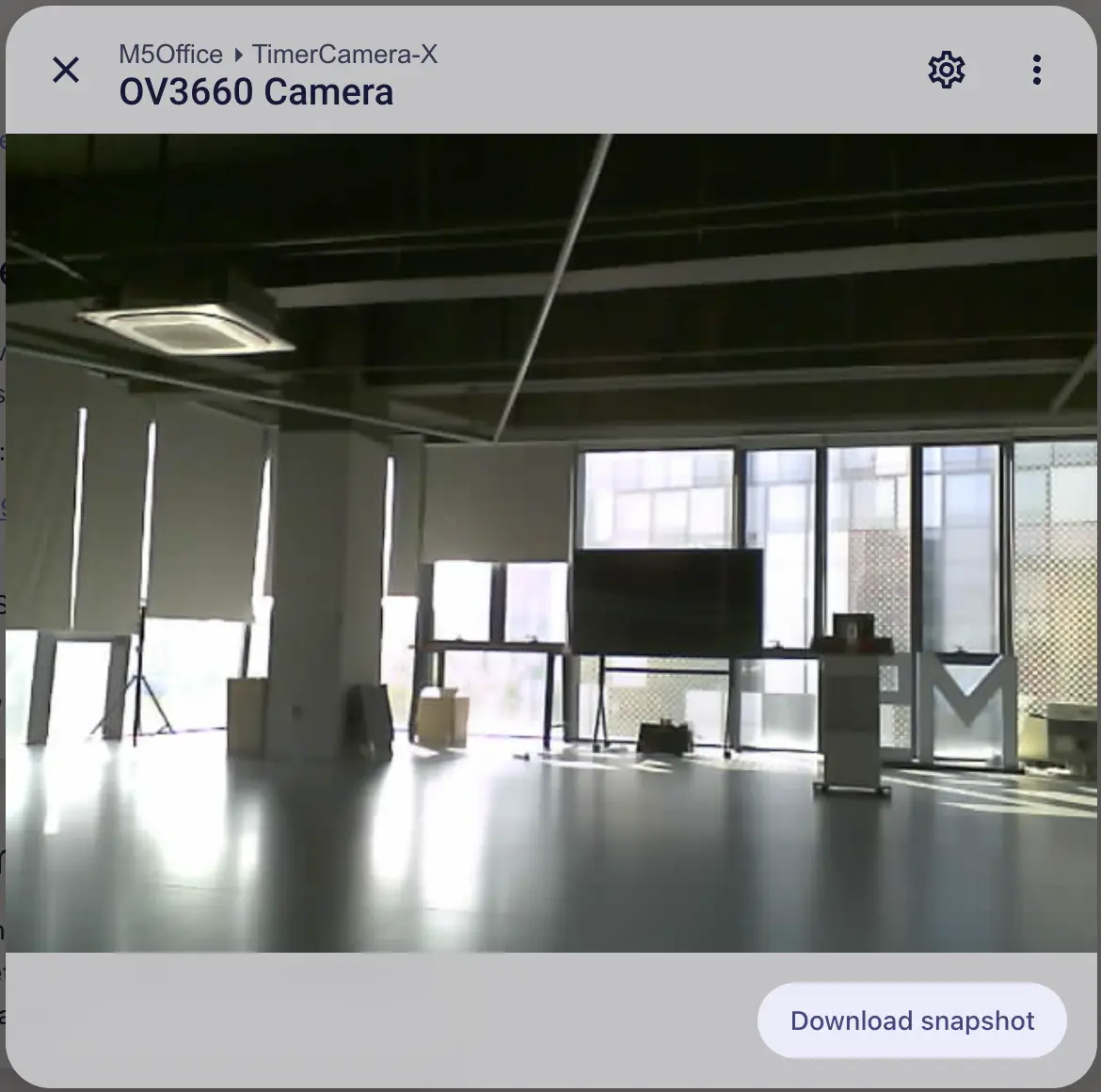
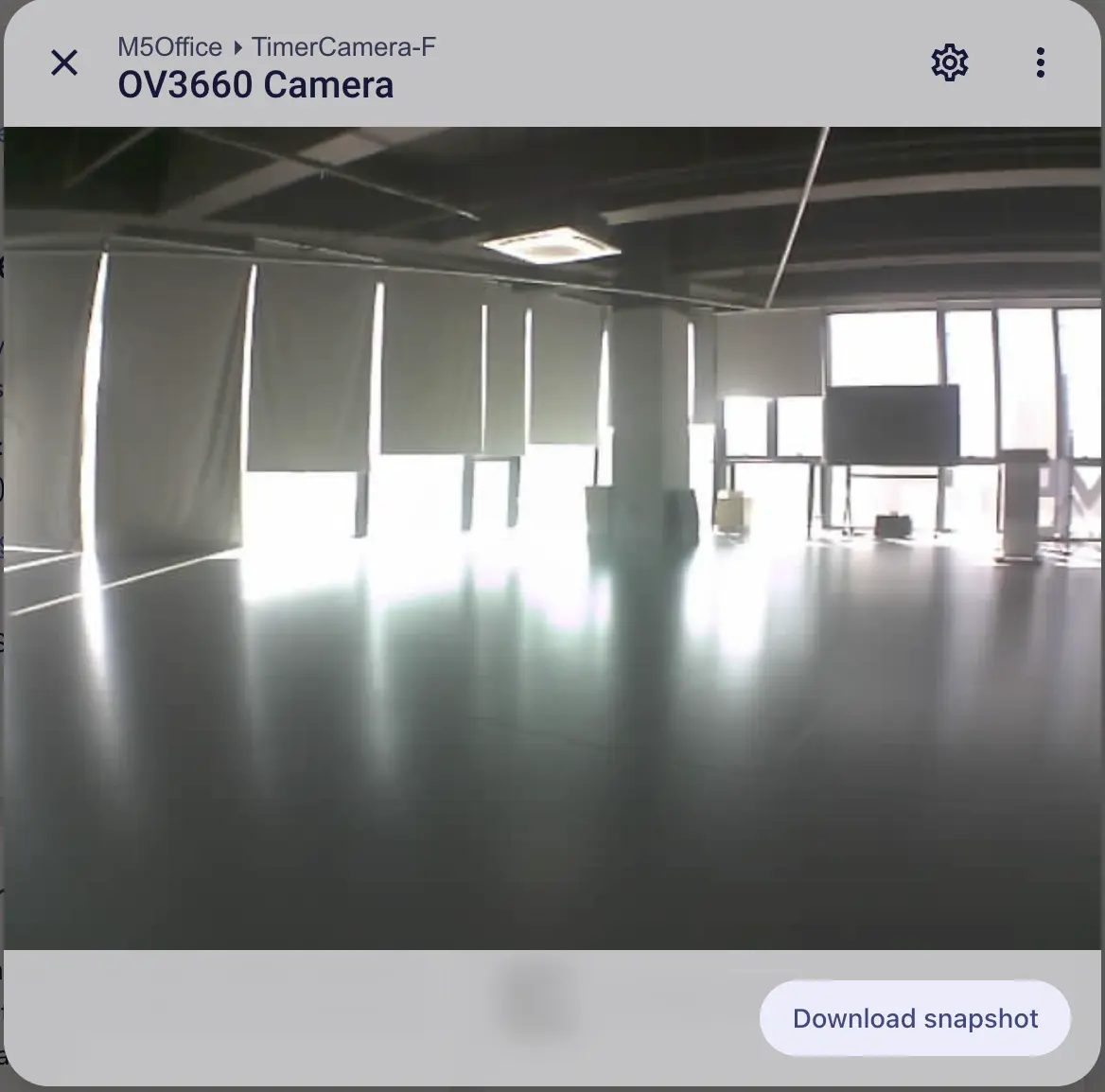
TimerCamera (TimerCamera‑X) is shown on the left. TimerCamera‑F uses a fisheye lens, producing the view shown on the right.
