PowerHub RTC
APIs and example programs related to the PowerHub RTC (Real-Time Clock).
Example Program
Compile Requirements
- M5Stack board manager version >= 3.2.3
- Board selection = M5PowerHub
- M5Unified library version >= 0.2.11
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98
#define WIFI_SSID "********"
#define WIFI_PSWD "********"
#define NTP_TIMEZONE "UTC-8" // POSIX standard, in which "UTC+0" is UTC London, "UTC-8" is UTC+8 Beijing, "UTC+5" is UTC-5 New York
#define NTP_SERVER1 "0.pool.ntp.org"
#define NTP_SERVER2 "1.pool.ntp.org"
#define NTP_SERVER3 "2.pool.ntp.org"
#include <WiFi.h>
// Different versions of the framework have different SNTP header file names and availability.
#if __has_include(<esp_sntp.h>)
#include <esp_sntp.h>
#define SNTP_ENABLED 1
#elif __has_include(<sntp.h>)
#include <sntp.h>
#define SNTP_ENABLED 1
#endif
#ifndef SNTP_ENABLED
#define SNTP_ENABLED 0
#endif
#include <M5Unified.h>
static constexpr const char* const wd[7] = { "Sun", "Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thr", "Fri", "Sat" };
void setup() {
M5.begin();
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("PowerHub RTC Test");
if (!M5.Rtc.isEnabled()) {
Serial.println("RTC not found");
while (true) {
delay(500);
}
}
Serial.println("RTC found");
Serial.print("WiFi: ");
WiFi.begin(WIFI_SSID, WIFI_PSWD);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.print(".");
delay(500);
}
Serial.println("\nWiFi connected");
configTzTime(NTP_TIMEZONE, NTP_SERVER1, NTP_SERVER2, NTP_SERVER3);
Serial.print("NTP: ");
#if SNTP_ENABLED
while (sntp_get_sync_status() != SNTP_SYNC_STATUS_COMPLETED) {
Serial.print(".");
delay(500);
}
#else
struct tm timeInfo;
while (!getLocalTime(&timeInfo, 1000)) {
Serial.print(".");
delay(500);
}
#endif
Serial.println("\nNTP connected");
time_t t = time(nullptr) + 1; // Advance one second
while (t > time(nullptr))
; // Synchronization in seconds
M5.Rtc.setDateTime(gmtime(&t));
delay(1000);
}
void loop() {
M5.update();
// RTC timer
auto dt = M5.Rtc.getDateTime();
Serial.printf("RTC UTC : ");
Serial.printf("%04d/%02d/%02d(%s) ", dt.date.year, dt.date.month, dt.date.date, wd[dt.date.weekDay]);
Serial.printf("%02d:%02d:%02d\n", dt.time.hours, dt.time.minutes, dt.time.seconds);
// ESP32 internal timer
auto t = time(nullptr);
{
auto tm = gmtime(&t); // for UTC
Serial.printf("ESP32 UTC : ");
Serial.printf("%04d/%02d/%02d(%s) ", tm->tm_year + 1900, tm->tm_mon + 1, tm->tm_mday, wd[tm->tm_wday]);
Serial.printf("%02d:%02d:%02d\n", tm->tm_hour, tm->tm_min, tm->tm_sec);
}
{
auto tm = localtime(&t); // for local timezone
Serial.printf("ESP32 %s: ", NTP_TIMEZONE);
Serial.printf("%04d/%02d/%02d(%s) ", tm->tm_year + 1900, tm->tm_mon + 1, tm->tm_mday, wd[tm->tm_wday]);
Serial.printf("%02d:%02d:%02d\n\n", tm->tm_hour, tm->tm_min, tm->tm_sec);
}
delay(1000);
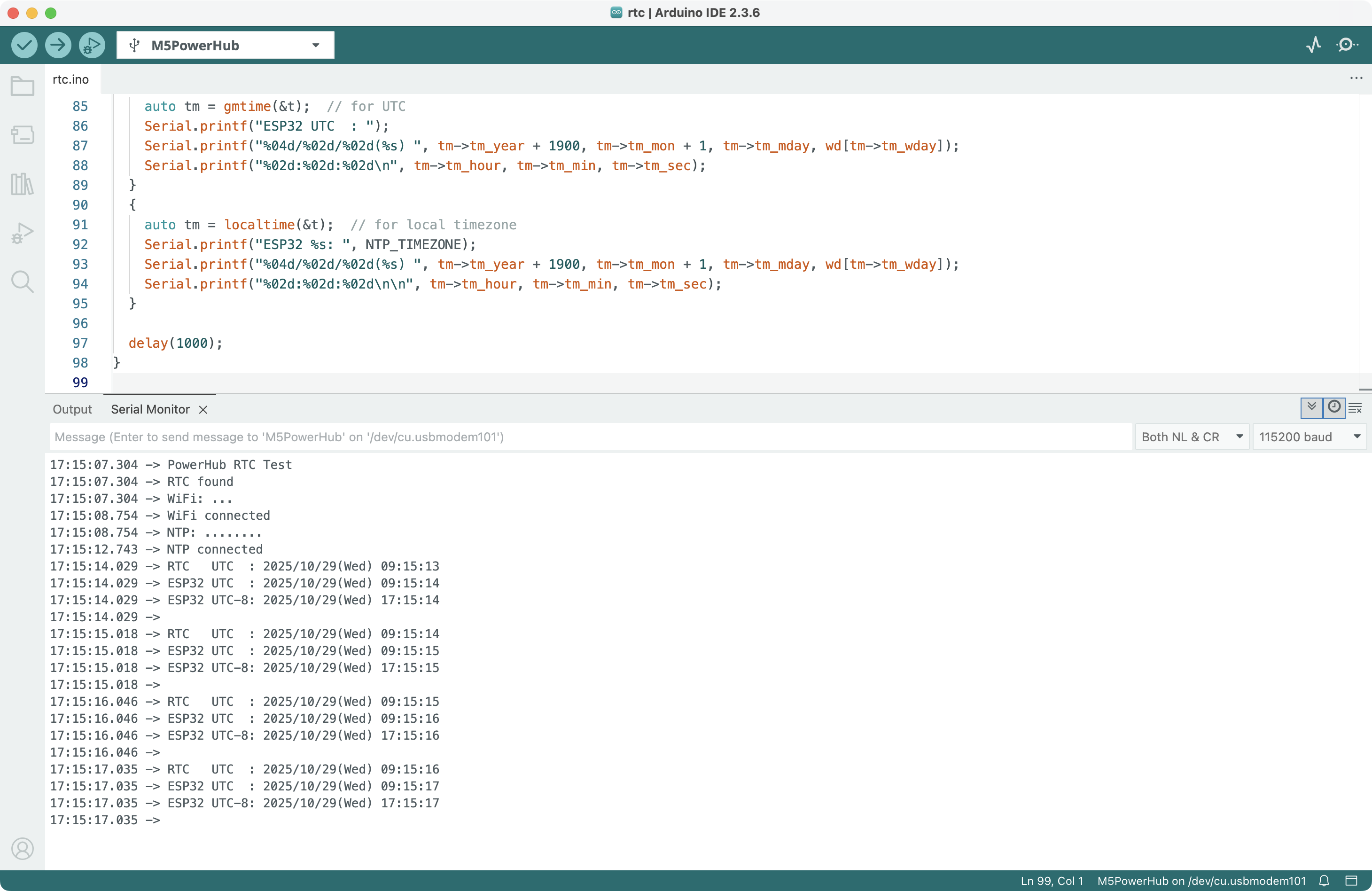
}In the program, fill in the Wi-Fi name and password you want to connect to, as well as your local time zone. Click the Upload button to upload the program to the PowerHub. After uploading, open the Serial Monitor to view the real-time clock.
Note
The time zone definition
NTP_TIMEZONE in the program follows the POSIX standard, which is opposite to the common human-readable format. For example: "UTC+0" means UTC London, "UTC-8" means UTC+8 Beijing, "UTC+5" means UTC-5 New York.
API
The PowerHub RTC (Real-Time Clock) driver uses the RTC8563_Class from the M5Unified library. For more related APIs, refer to the following documentation:
