Module GPS v2.0/v2.1 Arduino Tutorial
1. Preparation
1.Environment setup: Refer to Arduino IDE Getting Started Tutorial to complete the IDE installation, and install the corresponding board manager and required driver libraries according to the actual development board used.
2.Required libraries:
3.Required hardware products:



TinyGPSPlus Library Installation
Since the TinyGPSPlus version in Arduino Library Manager is outdated and not fully compatible, you need to visit TinyGPSPlus - M5Stack Github, download it manually, and place it in the Arduino library path.
#> Library path
2. Example Program
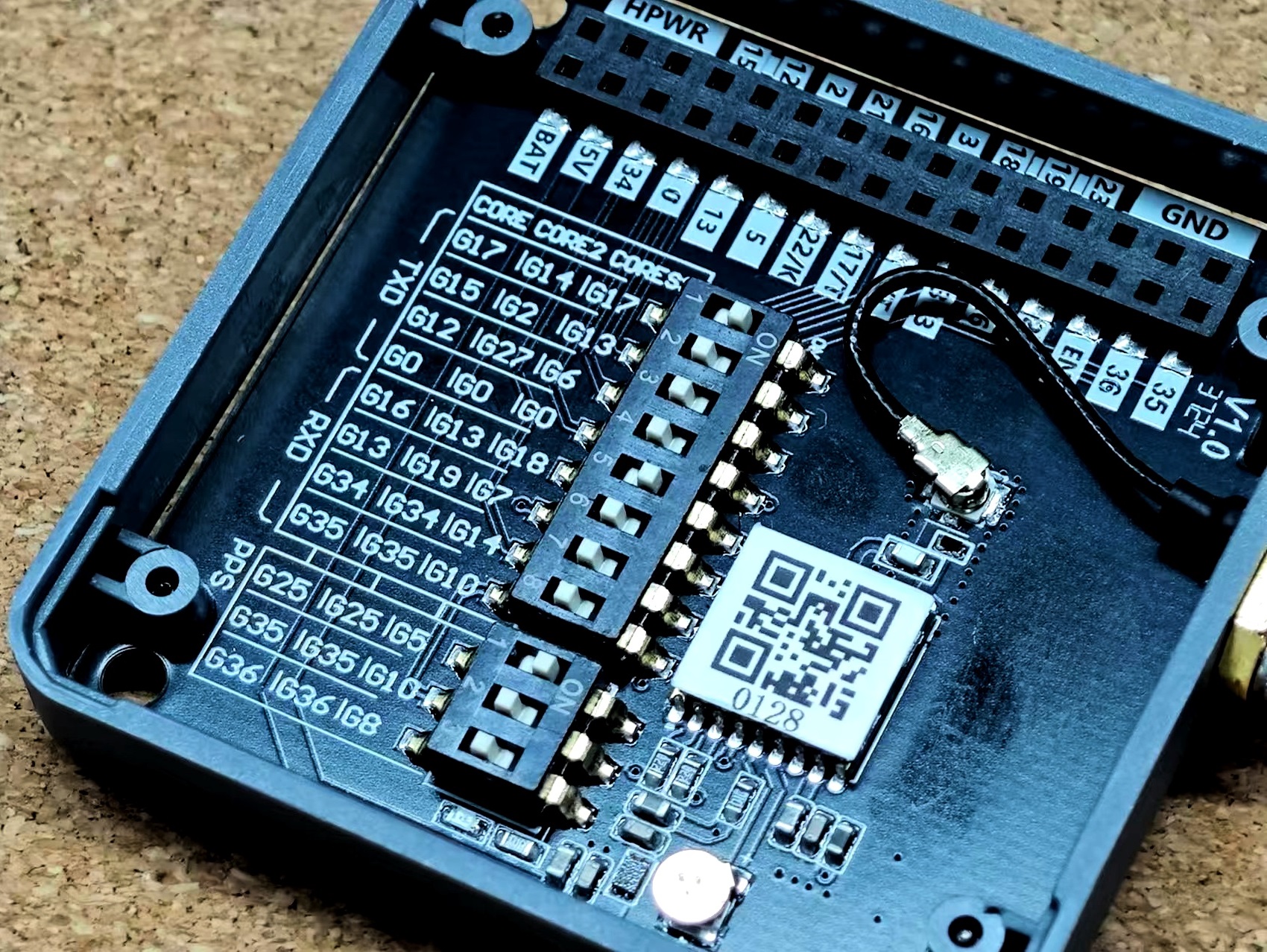
- According to the actual connected device, modify the IO information in the program. In this tutorial, the main control device used is the CoreS3. After stacking Module GPS v2.0/v2.1, the corresponding M5-Bus bus IOs are
G18 (RX),G17 (TX).
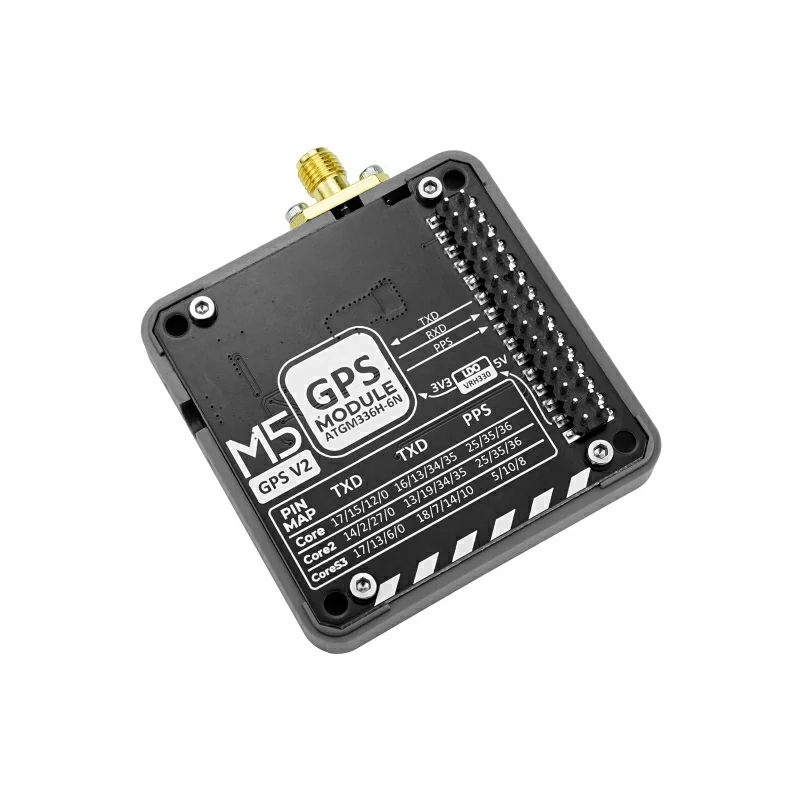
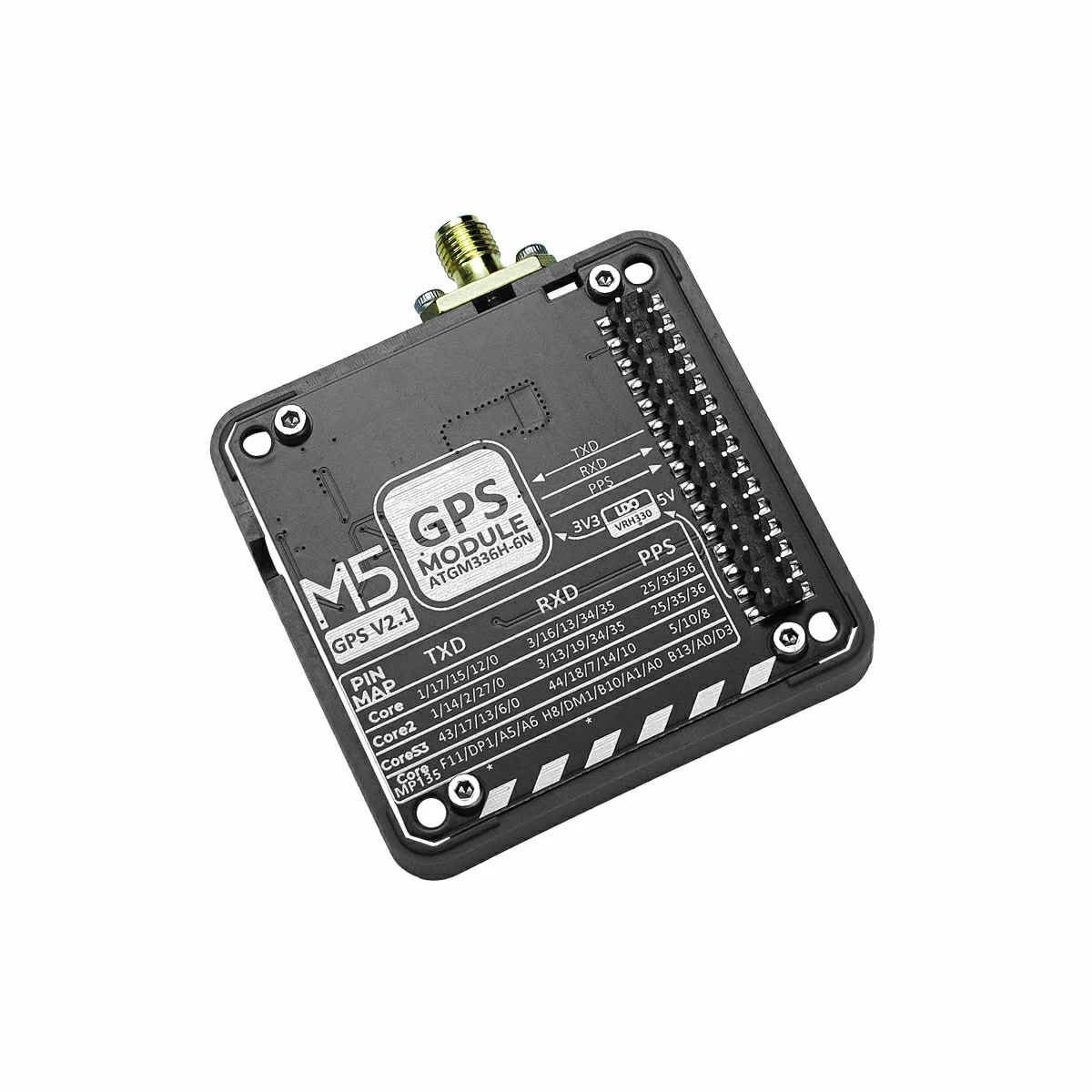
Module GPS v2.0/v2.1 also supports switching pin connections via the DIP switch at the bottom, which can be adjusted as needed. The left image below is Module GPS v2.0, the right image is Module GPS v2.1. The part framed in yellow indicates the additional selectable pins in v2.1 compared to v2.0.
- According to the actual connected device, modify the IO information in the program. In this tutorial, the main control device used is the CoreS3. After stacking Module GPS v2.0/v2.1, the corresponding M5-Bus bus IOs are

- Refer to the
UnitGPSExampleexample program in TinyGPSPlus, modify the corresponding UART initialization pins. Based on M5Unified and M5GFX, add basic coordinate display functionality to the example program.
- Refer to the

cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108
/*
*SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2024 M5Stack Technology CO LTD
*
*SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
*/
#include "M5Unified.h"
#include "M5GFX.h"
#include "MultipleSatellite.h"
static const int RXPin = 18, TXPin = 17;
static const uint32_t GPSBaud = 115200;
MultipleSatellite gps(Serial1, GPSBaud, SERIAL_8N1, RXPin, TXPin);
void displayInfo();
void setup()
{
M5.begin();
Serial.begin(115200);
gps.begin();
gps.setSystemBootMode(BOOT_FACTORY_START);
Serial.println(F("DeviceExample.ino"));
Serial.println(F("A simple demonstration of TinyGPSPlus with an attached GPS module"));
Serial.print(F("Testing TinyGPSPlus library v. "));
Serial.println(TinyGPSPlus::libraryVersion());
Serial.println(F("by Mikal Hart"));
Serial.println();
String version = gps.getGNSSVersion();
Serial.printf("GNSS SW=%s\r\n", version.c_str());
delay(1000);
// Set satellite mode
gps.setSatelliteMode(SATELLITE_MODE_GPS);
M5.Display.setFont(&fonts::FreeMonoBold12pt7b);
}
void loop()
{
// Update data
gps.updateGPS();
displayInfo();
delay(10);
}
void displayInfo()
{
Serial.print(F("Location: "));
Serial.printf("satellites:%d\n", gps.satellites.value());
if (gps.location.isUpdated()) {
Serial.print(gps.location.lat(), 6);
Serial.print(F(","));
Serial.print(gps.location.lng(), 6);
Serial.print(F("\n"));
M5.Display.fillRect(0, 0, 320, 60, BLACK);
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 0);
M5.Display.printf("Location: \nLat: %f\nlng: %f\n", gps.location.lat(), gps.location.lng());
} else {
M5.Display.fillRect(0, 0, 320, 60, BLACK);
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 0);
M5.Display.print("Location: \n");
M5.Display.print("Lat: ---------\n");
M5.Display.print("lng: ---------\n");
Serial.print(F("INVALID\n"));
}
Serial.print(F(" Date/Time: "));
if (gps.date.isUpdated()) {
Serial.print(gps.date.month());
Serial.print(F("/"));
Serial.print(gps.date.day());
Serial.print(F("/"));
Serial.print(gps.date.year());
M5.Display.fillRect(0, 100, 320, 60, BLACK);
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 100);
M5.Display.printf("Date/Time: %d/%d/%d\n", gps.date.month(), gps.date.day(), gps.date.year());
} else {
Serial.print(F("INVALID"));
}
Serial.print(F(" "));
if (gps.time.isUpdated()) {
if (gps.time.hour() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.hour());
Serial.print(F(":"));
if (gps.time.minute() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.minute());
Serial.print(F(":"));
if (gps.time.second() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.second());
Serial.print(F("."));
if (gps.time.centisecond() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.centisecond());
M5.Display.fillRect(0, 160, 320, 60, BLACK);
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 160);
M5.Display.printf("Time: %d:%d:%d.%d\n", gps.time.hour(), gps.time.minute(), gps.time.second(),
gps.time.centisecond());
} else {
Serial.print(F("INVALID"));
}
Serial.println();
delay(1000);
}3. Compile & Upload
- 1.Download Mode: Before flashing programs to different devices, download mode is required. This step may vary depending on the main control device used. For details, refer to the list of device program download tutorials at the bottom of the Arduino IDE Getting Started Tutorial page to see the specific operation method.
- For CoreS3, press and hold the reset button (about 2 seconds) until the internal green LED lights up, then release. At this point, the device has entered download mode and is waiting for flashing.
.gif)
- 2.Select the device port, click the compile/upload button in the upper left corner of the Arduino IDE, and wait for the program to finish compiling and uploading to the device.

4. Satellite Positioning
Connect the matched external antenna, place the antenna near a window or in an open outdoor area, and wait for the device to successfully search satellites and obtain coordinates.

