Unit C6L LoRa Communication
APIs and example programs related to Unit C6L LoRa communication.
Note
Unit C6L uses the SX1262 LoRa transceiver. When developing, be sure to select the corresponding class.
Example Program
Compilation Requirements
- M5Stack Board Manager version >= 3.2.3
- Board option = M5UnitC6L
- RadioLib library version >= 7.3.0
Transmitter
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73
#include <RadioLib.h>
#include <M5Unified.h>
// SX1262: CS, IRQ, NRST, BUSY
SX1262 radio = new Module(23, 7, RADIOLIB_NC, 19);
int transmitState = RADIOLIB_ERR_NONE; // save transmission state between loops
bool transmitFlag = false; // flag to indicate that a packet was sent
int count = 0; // counter of transmitted packets
// function to be called when a complete packet is transmitted
void setFlag(void) {
transmitFlag = true;
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
M5.begin();
delay(1000);
auto& ioe = M5.getIOExpander(0);
ioe.digitalWrite(7, false);
delay(100);
ioe.digitalWrite(7, true); // re-enable SX_NRST
ioe.digitalWrite(6, true); // enable SX_ANT_SW
ioe.digitalWrite(5, true); // enable SX_LNA_EN
// initialize SX1262
Serial.print("\n[SX1262] Initializing... ");
// frequency MHz, bandwidth kHz, spreading factor, coding rate denominator, sync word,
// output power dBm, preamble length, TCXO reference voltage, useRegulatorLDO
int beginState = radio.begin(868.0, 125.0, 12, 5, 0x34, 22, 20, 3.0, true);
if (beginState == RADIOLIB_ERR_NONE) {
Serial.println("Succeeded!");
} else {
Serial.print("Failed, code: ");
Serial.println(beginState);
while (true) { delay(100); }
}
// set the function to be called when packet transmission is finished
radio.setPacketSentAction(setFlag);
// start transmitting the first packet
Serial.print("[SX1262] Sending the first packet... ");
// you can transmit C-string or Arduino string up to 256 characters long
transmitState = radio.startTransmit("Hello world from M5Stack! #0");
}
void loop() {
if (transmitFlag) { // check if the previous transmission is finished
transmitFlag = false; // reset the flag
if (transmitState == RADIOLIB_ERR_NONE) { // packet was sent successfully
Serial.println("Succeeded!");
} else {
Serial.print("Failed, code: ");
Serial.println(transmitState);
}
// clean up after transmission is finished. This will ensure transmitter is disabled, RF switch is powered down, etc.
radio.finishTransmit();
delay(1000);
// send another packet
count++;
Serial.printf("[SX1262] Sending packet #%d... ", count);
String str = "Hello world from M5Stack! #" + String(count);
transmitState = radio.startTransmit(str);
}
}Receiver
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86
#include <RadioLib.h>
#include <M5Unified.h>
// SX1262: CS, IRQ, NRST, BUSY
SX1262 radio = new Module(23, 7, RADIOLIB_NC, 19);
bool receiveFlag = false; // flag to indicate that a packet was received
// function to be called when a complete packet is received
void setFlag(void) {
receiveFlag = true;
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
M5.begin();
delay(1000);
auto& ioe = M5.getIOExpander(0);
ioe.digitalWrite(7, false);
delay(100);
ioe.digitalWrite(7, true); // re-enable SX_NRST
ioe.digitalWrite(6, true); // enable SX_ANT_SW
ioe.digitalWrite(5, true); // enable SX_LNA_EN
// initialize SX1262
Serial.print("\n[SX1262] Initializing... ");
// frequency MHz, bandwidth kHz, spreading factor, coding rate denominator, sync word,
// output power dBm, preamble length, TCXO reference voltage, useRegulatorLDO
int beginState = radio.begin(868.0, 125.0, 12, 5, 0x34, 22, 20, 3.0, true);
if (beginState == RADIOLIB_ERR_NONE) {
Serial.println("Succeeded!");
} else {
Serial.print("Failed, code: ");
Serial.println(beginState);
while (true) { delay(100); }
}
// set the function to be called when a new packet is received
radio.setPacketReceivedAction(setFlag);
// start listening for LoRa packets
Serial.print("[SX1262] Starting to listen... ");
int receiveState = radio.startReceive();
if (receiveState == RADIOLIB_ERR_NONE) {
Serial.println("Succeeded!");
} else {
Serial.print("Failed, code: ");
Serial.println(receiveState);
while (true) { delay(100); }
}
}
void loop() {
if (receiveFlag) { // check if a new packet is received
receiveFlag = false; // reset the flag
String str; // read the received data as an Arduino String
int readState = radio.readData(str);
if (readState == RADIOLIB_ERR_NONE) { // packet was received successfully
Serial.println("\n[SX1262] Received packet!");
Serial.print("[SX1262] Data: ");
Serial.println(str);
Serial.print("[SX1262] RSSI: ");
Serial.print(radio.getRSSI()); // Received Signal Strength Indicator
Serial.println(" dBm");
Serial.print("[SX1262] SNR: ");
Serial.print(radio.getSNR()); // Signal-to-Noise Ratio
Serial.println(" dB");
Serial.print("[SX1262] Frequency error: ");
Serial.print(radio.getFrequencyError());
Serial.println(" Hz");
} else if (readState == RADIOLIB_ERR_CRC_MISMATCH) { // packet was received but malformed
Serial.println("CRC error!");
} else { // some other error occurred
Serial.print("Failed, code: ");
Serial.println(readState);
}
}
}Run Results
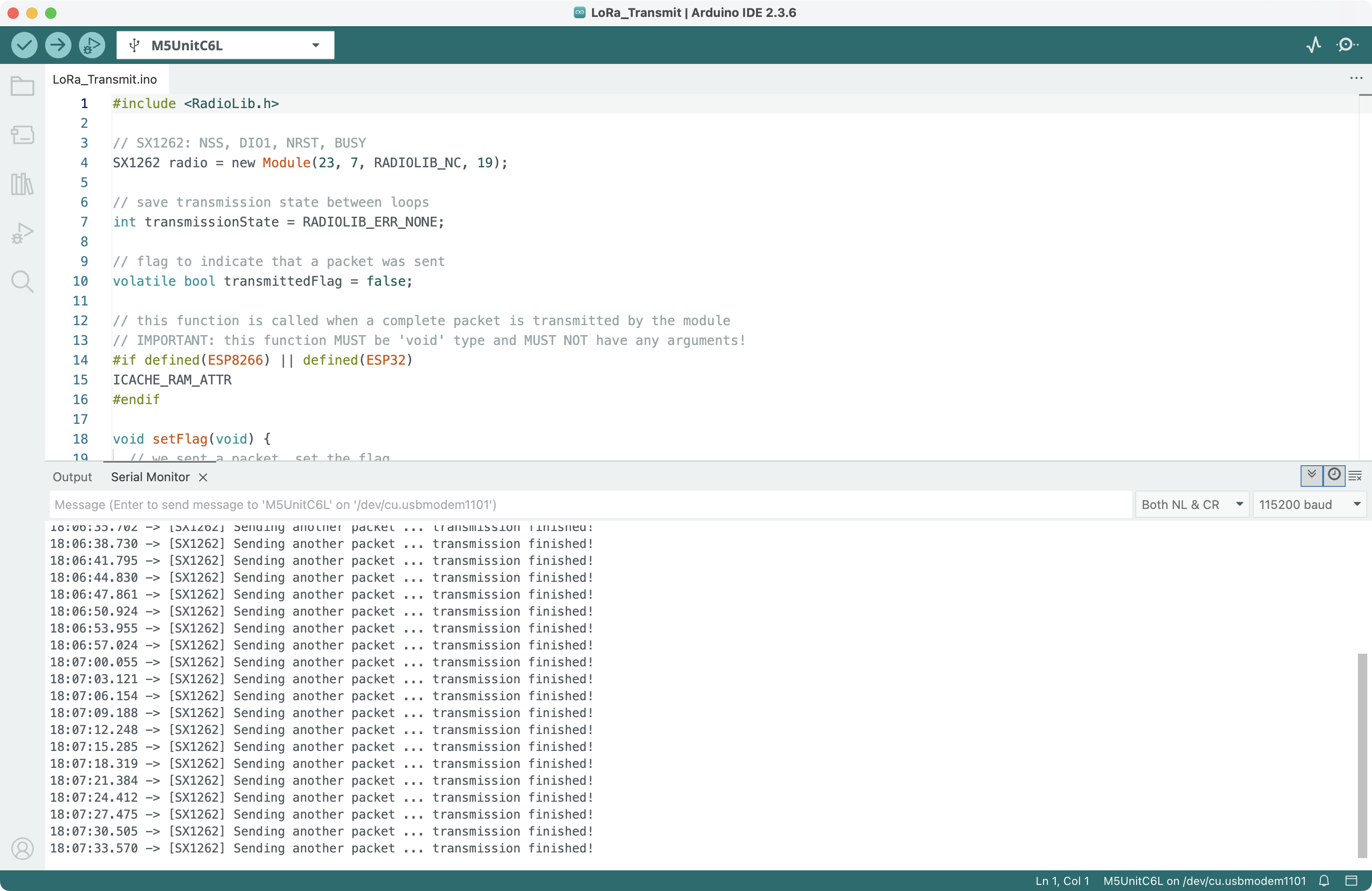
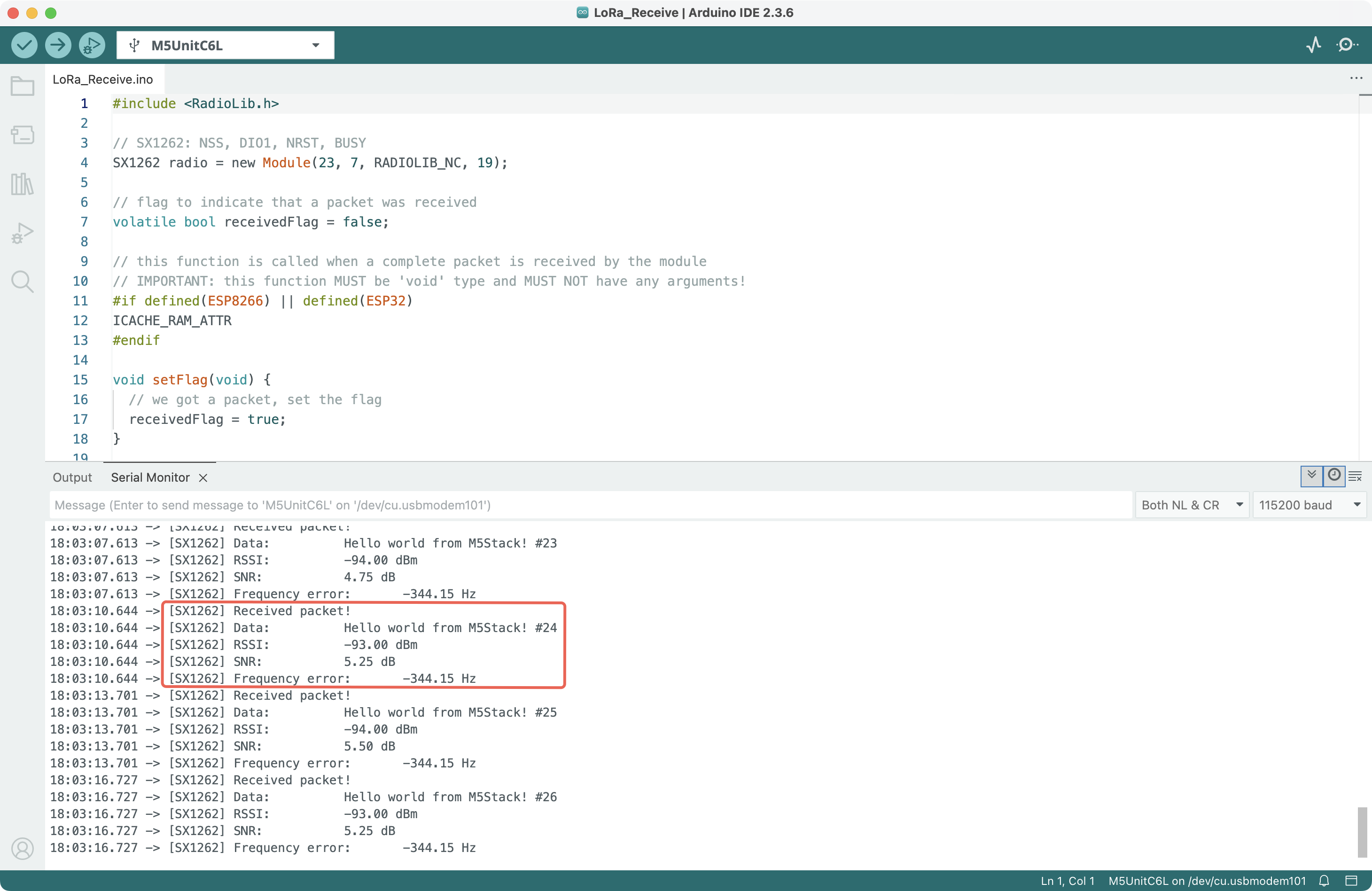
Compile and upload the two sketches to two Unit C6L respectively. The transmitter will send LoRa signal, and the receiver will capture this signal. Their serial output is shown below:
API
The Unit C6L LoRa communication uses the RadioLib library as the driver. For more related APIs, please refer to the following documentation:
