Atomic TFCard Base Arduino Tutorial
1. Preparation
Environment Configuration: Refer to the Arduino IDE Quick Start Tutorial to complete the IDE installation, and install the corresponding board management for the development board you are using, as well as the required driver libraries.
Driver libraries used:
Hardware products used:
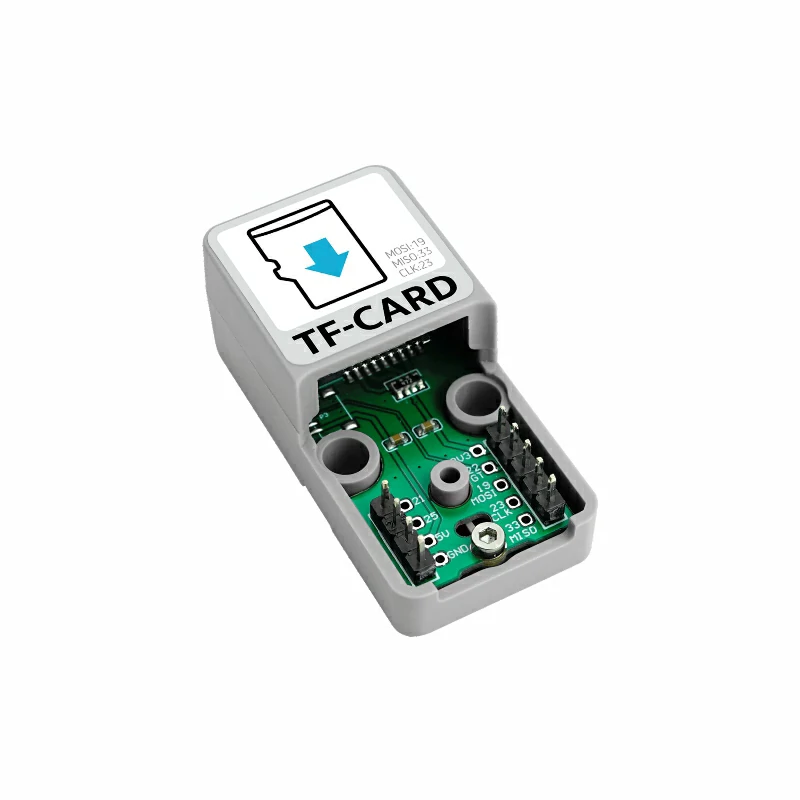


2. Example
- In this tutorial, the main control device used is AtomS3R, paired with the Atomic TFCard Base. This module communicates via SPI. Modify the pin definitions in the program according to the actual circuit connection. After the device is connected, the corresponding SPI pins are
G7 (SCK),G8 (MISO),G6 (MOSI).
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
#include <M5Unified.h>
#include <M5GFX.h>
// ------------------- Pin Definitions -------------------
#define SD_SPI_CS_PIN -1 // Chip Select pin
#define SD_SPI_SCK_PIN 7 // SPI Clock pin
#define SD_SPI_MISO_PIN 8 // SPI MISO pin
#define SD_SPI_MOSI_PIN 6 // SPI MOSI pin
// Function prototypes
void listDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * dirname, uint8_t levels);// List contents of a directory (supports recursive listing with levels)
void createDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * path);// Create a new directory
void removeDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * path);// Remove an existing directory (must be empty)
void readFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path);// Read contents of a file and print to serial
void writeFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message);// Write content to a file (overwrites existing content)
void appendFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message);// Append content to the end of a file (preserves existing content)
void renameFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path1, const char * path2);// Rename a file from path1 to path2
void deleteFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path);// Delete a file
void testFileIO(fs::FS &fs, const char * path);// Test file I/O speed (read and write performance)
void setup() {
M5.begin();
M5.Display.clear();
M5.Display.setFont(&fonts::FreeMonoBold9pt7b);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("<-------Atomic TFCard Base Example------->");
// ------------------- SD Card Initialization -------------------
// Initialize SPI bus with specified pins (SCK, MISO, MOSI, CS)
SPI.begin(SD_SPI_SCK_PIN, SD_SPI_MISO_PIN, SD_SPI_MOSI_PIN, SD_SPI_CS_PIN);
Serial.println("SD Init...");
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SD Init...", 64, 0);
// Attempt to initialize SD card with 25MHz SPI clock speed
if (!SD.begin(SD_SPI_CS_PIN, SPI, 25000000)) {
Serial.println("SD Error!");
M5.Display.clear();
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SD Error!", 64, 50);
while (1); // Infinite loop prevents further execution on failure
} else {
Serial.println("SD Ready");
M5.Display.clear();
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SD Ready", 64, 0);
}
// Get the type of SD card inserted
uint8_t cardType = SD.cardType();
if(cardType == CARD_NONE){
Serial.println("No SD card attached");
return; // Exit setup() early if no card is present
}
M5.Display.setTextColor(TFT_YELLOW);
Serial.print("SD Card Type: ");
if(cardType == CARD_MMC){
Serial.println("MMC");
M5.Display.drawString("MMC", 5, 20);
} else if(cardType == CARD_SD){
Serial.println("SDSC"); // Standard Capacity SD card (<=2GB)
M5.Display.drawString("SDSC", 5, 20);
} else if(cardType == CARD_SDHC){
Serial.println("SDHC"); // High Capacity SD card (2GB-32GB)
M5.Display.drawString("SDHC", 5, 20);
} else {
Serial.println("UNKNOWN"); // Unrecognized card type
M5.Display.drawString("UNKNOWN", 5, 20);
}
// Calculate total and used SD card capacity in MB (1MB = 1024*1024 bytes)
uint64_t cardSize = SD.totalBytes() / (1024 * 1024);
uint64_t usedSize = SD.usedBytes() / (1024 * 1024);
Serial.printf("SD Card Size: %lluMB\n", cardSize);
Serial.printf("SD Card Uesd Size: %lluMB\n", usedSize);
M5.Display.setCursor(5, 40);
M5.Display.printf("%llu/%lluMB", usedSize, cardSize);
// Some delay is required here to ensure that the code above is executed completely; otherwise, the information feedback will be incorrect.
delay(500);
// Execute a sequence of SD card operations to demonstrate functionality
listDir(SD, "/", 0); // List root directory (non-recursive)
createDir(SD, "/mydir"); // Create a new directory named "mydir"
listDir(SD, "/", 0); // List root directory again to verify creation
removeDir(SD, "/mydir"); // Delete the "mydir" directory
listDir(SD, "/", 2); // List root directory with 2 levels of recursion
writeFile(SD, "/hello.txt", "Hello "); // Create "hello.txt" and write initial content
appendFile(SD, "/hello.txt", "World!\n"); // Append content to "hello.txt"
readFile(SD, "/hello.txt"); // Read and print content of "hello.txt"
renameFile(SD, "/hello.txt", "/test.txt"); // Rename "hello.txt" to "test.txt"
readFile(SD, "/test.txt"); // Read renamed file to verify
testFileIO(SD, "/test.txt"); // Test read/write speed of "test.txt"
// Print final total and used space after all operations
Serial.printf("Total space: %lluMB\n", SD.totalBytes() / (1024 * 1024));
Serial.printf("Used space: %lluMB\n", SD.usedBytes() / (1024 * 1024));
deleteFile(SD, "/test.txt"); // Delete the test file to clean up
}
void loop() {
}
// ------------------- Directory Listing Function -------------------
// fs: File system object (e.g., SD for SD card)
// dirname: Path of the directory to list
// levels: Number of recursive levels to list (0 = only current directory)
void listDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * dirname, uint8_t levels){
Serial.printf("Listing directory: %s\n", dirname);
File root = fs.open(dirname);
if(!root){
Serial.println("Failed to open directory");
return;
}
// Verify the opened object is a directory (not a file)
if(!root.isDirectory()){
Serial.println("Not a directory");
return;
}
// Open the first file/directory in the target directory
File file = root.openNextFile();
// Iterate through all files/directories in the target directory
while(file){
if(file.isDirectory()){
Serial.print(" DIR : ");
Serial.println(file.name());
// Recursively list subdirectories if levels > 0
if(levels){
listDir(fs, file.name(), levels - 1);
}
} else {
Serial.print(" FILE: ");
Serial.print(file.name());
Serial.print(" SIZE: ");
Serial.println(file.size());
}
// Move to the next file/directory
file = root.openNextFile();
}
}
// ------------------- Directory Creation Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path: Full path of the directory to create
void createDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
Serial.printf("Creating Dir: %s\n", path);
if(fs.mkdir(path)){
Serial.println("Dir created");
} else {
Serial.println("mkdir failed");
}
}
// ------------------- Directory Removal Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path: Full path of the directory to remove (must be empty)
void removeDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
Serial.printf("Removing Dir: %s\n", path);
if(fs.rmdir(path)){
Serial.println("Dir removed");
} else {
Serial.println("rmdir failed"); // Failure may occur if directory not empty
}
}
// ------------------- File Reading Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path: Full path of the file to read
void readFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
Serial.printf("Reading file: %s\n", path);
// Open file in read mode (default mode for fs.open())
File file = fs.open(path);
if(!file){
Serial.println("Failed to open file for reading");
return;
}
Serial.print("Read from file: ");
// Read all available bytes from file and print to serial
while(file.available()){
Serial.write(file.read());
}
file.close();
}
// ------------------- File Writing Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path: Full path of the file to write
// message: Content to write to the file (overwrites existing content)
void writeFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message){
Serial.printf("Writing file: %s\n", path);
// Open file in write mode (creates file if it doesn't exist, overwrites if it does)
File file = fs.open(path, FILE_WRITE);
if(!file){
Serial.println("Failed to open file for writing");
return;
}
if(file.print(message)){
Serial.println("File written");
} else {
Serial.println("Write failed");
}
file.close();
}
// ------------------- File Appending Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path: Full path of the file to append to
// message: Content to add to the end of the file
void appendFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message){
Serial.printf("Appending to file: %s\n", path);
// Open file in append mode (preserves existing content, writes to end)
File file = fs.open(path, FILE_APPEND);
if(!file){
Serial.println("Failed to open file for appending");
return;
}
if(file.print(message)){
Serial.println("Message appended");
} else {
Serial.println("Append failed");
}
file.close();
}
// ------------------- File Renaming Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path1: Current path/name of the file
// path2: New path/name for the file
void renameFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path1, const char * path2){
Serial.printf("Renaming file %s to %s\n", path1, path2);
if (fs.rename(path1, path2)) {
Serial.println("File renamed");
} else {
Serial.println("Rename failed"); // Failure may occur if target path exists
}
}
// ------------------- File Deletion Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path: Full path of the file to delete
void deleteFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
Serial.printf("Deleting file: %s\n", path);
if(fs.remove(path)){
Serial.println("File deleted");
} else {
Serial.println("Delete failed"); // Failure may occur if file doesn't exist
}
}
// ------------------- File I/O Speed Test Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path: Full path of the file to use for testing
void testFileIO(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
File file = fs.open(path);
// 512-byte buffer for read/write operations (matches typical sector size)
static uint8_t buf[512];
size_t len = 0;
uint32_t start = millis(); // Record start time for timing
uint32_t end = start;
// ------------------- Read Speed Test -------------------
if(file){
len = file.size();
size_t flen = len; // Store original length for output
start = millis(); // Reset start time for read test
// Read file in 512-byte chunks (optimizes for sector size)
while(len){
size_t toRead = len;
if(toRead > 512){
toRead = 512;
}
file.read(buf, toRead); // Read chunk into buffer
len -= toRead; // Decrement remaining bytes to read
}
// Calculate total read time and print results
end = millis() - start;
Serial.printf("%u bytes read for %u ms\n", flen, end);
file.close(); // Close file after read test
} else {
Serial.println("Failed to open file for reading");
}
// ------------------- Write Speed Test -------------------
// Open file in write mode (overwrites existing content)
file = fs.open(path, FILE_WRITE);
if(!file){
Serial.println("Failed to open file for writing");
return;
}
size_t i;
start = millis(); // Reset start time for write test
// Write 2048 chunks of 512 bytes (total 1MB of data)
for(i=0; i<2048; i++){
file.write(buf, 512);
}
// Calculate total write time and print results
end = millis() - start;
Serial.printf("%u bytes written for %u ms\n", 2048 * 512, end);
file.close(); // Close file after write test
}3. Compile and Upload
1. Download Mode: Before flashing the program on different devices, you need to enter download mode. This step may vary depending on the main control device. For details, refer to the list of device program download tutorials at the bottom of the Arduino IDE Quick Start Tutorial page to see the specific operation method.
For AtomS3R, press and hold the reset button (for about 2 seconds) until the internal green LED lights up, then release. At this point, the device has entered download mode and is ready for flashing.

- 2. Select the device port, click the Compile and Upload button in the upper left of Arduino IDE, and wait for the program to complete compilation and upload to the device.
4. Example Effect Demonstration
- After successfully downloading the above example, when the device is powered on, the screen will display as shown in the figure below, and file/folder creation, reading, deletion operations inside the card will be printed in the serial monitor.

FAT32 file system is correctly inserted before running this example.2. The microSD card used in this demonstration is a blank card. The "System Volume Information" folder appearing in the serial output below is an automatically generated hidden folder when the card is inserted into a computer. This directory can be ignored during actual use, and deleted if desired by enabling "show hidden files" on the computer.
- Serial output:
<-------Atomic TFCard Base Example------->
SD Init...
SD Ready
SD Card Type: SDHC
SD Card Size: 15185MB
SD Card Uesd Size: 0MB
Listing directory: /
DIR : System Volume Information
Creating Dir: /mydir
Dir created
Listing directory: /
DIR : System Volume Information
DIR : mydir
Removing Dir: /mydir
Dir removed
Listing directory: /
DIR : System Volume Information
Listing directory: System Volume Information
Failed to open directory
Writing file: /hello.txt
File written
Appending to file: /hello.txt
Message appended
Reading file: /hello.txt
Read from file: Hello World!
Renaming file /hello.txt to /test.txt
File renamed
Reading file: /test.txt
Read from file: Hello World!
13 bytes read for 1 ms
1048576 bytes written for 866 ms
Total space: 15185MB
Used space: 1MB
Deleting file: /test.txt
File deleted