Atomic GPS Base Arduino Tutorial
1. Preparation
Environment setup: Refer to Arduino IDE Quick Start to complete IDE installation, install the corresponding board package for the development board in use, as well as the required driver libraries.
Required libraries:
Note
You need to download the library version adapted for M5Stack devices from GitHub. Library link: TinyGPSPlus - M5Stack GitHub. Do not download from the Arduino Library Manager. (If you have questions, refer to this tutorial)
- Required hardware products:


2. Example Program
- In this tutorial, the main controller is AtomS3R paired with the Atomic GPS Base. The GPS module in this base communicates via UART, but the main controller can only receive data returned by the module and cannot send data to it. The microSD card part communicates via SPI. Modify the pin definitions in the program according to the actual wiring; when stacked, the corresponding IOs are
G5 (RX),G6 (MOSI),G7 (CLK), andG8 (MISO).
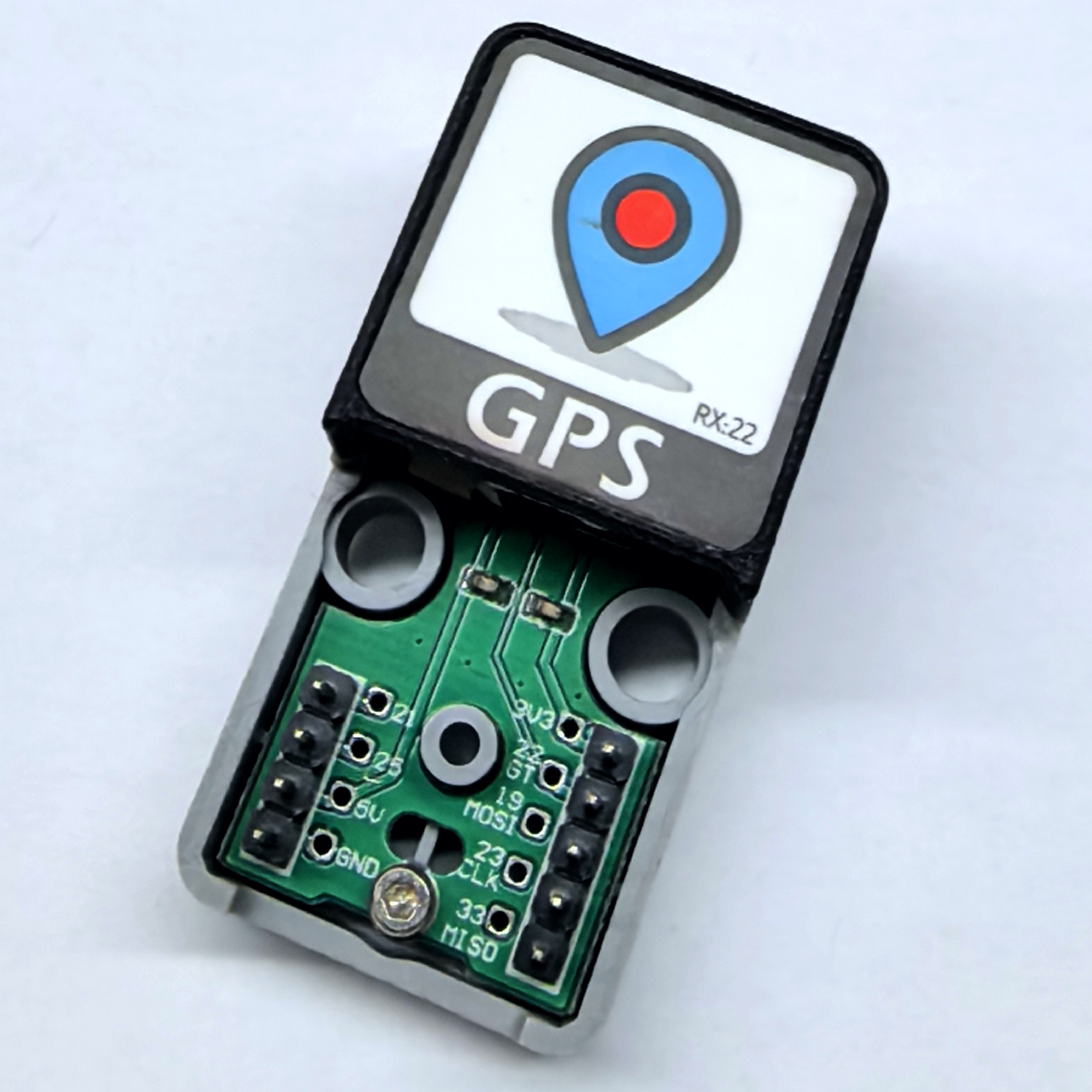


2.1 GPS Data Acquisition
Note
The baud rate of this GPS module is fixed at 9600 and cannot be changed; otherwise, data cannot be effectively obtained.
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90
#include "M5Unified.h"
#include "M5GFX.h"
#include "MultipleSatellite.h"
static const int RXPin = 5, TXPin = -1;// RXPin should be connected to GPS TX, TXPin is not used in this module.
MultipleSatellite gps(Serial2, 9600, SERIAL_8N1, RXPin, TXPin);// Baud rate is fixed at 9600 for this module.
void setup() {
M5.begin();
Serial.begin(115200);
gps.begin();
Serial.println(F("A simple demonstration of TinyGPSPlus with Atomic GPS Base"));
Serial.print(F("Testing TinyGPSPlus library v. "));
Serial.println(TinyGPSPlus::libraryVersion());
Serial.println();
delay(1000);
M5.Display.setFont(&fonts::FreeMonoBold9pt7b);
}
void loop() {
// Update data
gps.updateGPS();
displayInfo();
delay(100);
}
void displayInfo(void) {
Serial.print(F("Location: "));
Serial.printf("satellites:%d\n", gps.satellites.value());
if (gps.location.isUpdated()) {
Serial.print(gps.location.lat(), 6);
Serial.print(F(","));
Serial.print(gps.location.lng(), 6);
Serial.print(F("\n"));
M5.Display.fillRect(0, 0, 128, 128, BLACK);
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 0);
M5.Display.printf("Sat: %d\nLat: %d\nlng: %d\n",
(uint8_t)gps.satellites.value(),
(uint8_t)gps.location.lat(),
(uint8_t)gps.location.lng());
} else {
M5.Display.fillRect(0, 0, 128, 128, BLACK);
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 0);
M5.Display.print("Sat: ----\n");
M5.Display.print("Lat: ----\n");
M5.Display.print("Lng: ----\n");
Serial.print(F("Location no update\n"));
}
Serial.print(F("Date/Time: "));
if (gps.date.isUpdated()) {
Serial.print(gps.date.month());
Serial.print(F("/"));
Serial.print(gps.date.day());
Serial.print(F("/"));
Serial.print(gps.date.year());
M5.Display.fillRect(0, 80, 128, 128, BLACK);
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 80);
M5.Display.printf("%d/%d/%d\n", gps.date.month(),
gps.date.day(), gps.date.year());
} else {
Serial.print(F("Date no update"));
}
Serial.print(F(" "));
if (gps.time.isUpdated()) {
if (gps.time.hour() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.hour());
Serial.print(F(":"));
if (gps.time.minute() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.minute());
Serial.print(F(":"));
if (gps.time.second() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.second());
Serial.print(F("."));
if (gps.time.centisecond() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.centisecond());
M5.Display.fillRect(0, 128, 128, 60, BLACK);
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 96);
M5.Display.printf("Time: \n%d:%d:%d.%d", gps.time.hour(), gps.time.minute(),
gps.time.second(),gps.time.centisecond());
} else {
Serial.print(F("Time no update"));
}
Serial.println();
delay(1000);
}2.2 SD Card Read/Write
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
#include <M5Unified.h>
#include <M5GFX.h>
// ------------------- Pin Definitions -------------------
#define SD_SPI_CS_PIN -1 // Chip Select pin
#define SD_SPI_SCK_PIN 7 // SPI Clock pin
#define SD_SPI_MISO_PIN 8 // SPI MISO pin
#define SD_SPI_MOSI_PIN 6 // SPI MOSI pin
// Function prototypes
void listDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * dirname, uint8_t levels);// List contents of a directory (supports recursive listing with levels)
void createDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * path);// Create a new directory
void removeDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * path);// Remove an existing directory (must be empty)
void readFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path);// Read contents of a file and print to serial
void writeFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message);// Write content to a file (overwrites existing content)
void appendFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message);// Append content to the end of a file (preserves existing content)
void renameFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path1, const char * path2);// Rename a file from path1 to path2
void deleteFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path);// Delete a file
void testFileIO(fs::FS &fs, const char * path);// Test file I/O speed (read and write performance)
void setup() {
M5.begin();
M5.Display.clear();
M5.Display.setFont(&fonts::FreeMonoBold9pt7b);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("<-------microSD Example------->");
// ------------------- SD Card Initialization -------------------
// Initialize SPI bus with specified pins (SCK, MISO, MOSI, CS)
SPI.begin(SD_SPI_SCK_PIN, SD_SPI_MISO_PIN, SD_SPI_MOSI_PIN, SD_SPI_CS_PIN);
Serial.println("SD Init...");
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SD Init...", 64, 0);
// Attempt to initialize SD card with 25MHz SPI clock speed
if (!SD.begin(SD_SPI_CS_PIN, SPI, 25000000)) {
Serial.println("SD Error!");
M5.Display.clear();
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SD Error!", 64, 50);
while (1); // Infinite loop prevents further execution on failure
} else {
Serial.println("SD Ready");
M5.Display.clear();
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SD Ready", 64, 0);
}
// Get the type of SD card inserted
uint8_t cardType = SD.cardType();
if(cardType == CARD_NONE){
Serial.println("No SD card attached");
return; // Exit setup() early if no card is present
}
M5.Display.setTextColor(TFT_YELLOW);
Serial.print("SD Card Type: ");
if(cardType == CARD_MMC){
Serial.println("MMC");
M5.Display.drawString("MMC", 5, 20);
} else if(cardType == CARD_SD){
Serial.println("SDSC"); // Standard Capacity SD card (<=2GB)
M5.Display.drawString("SDSC", 5, 20);
} else if(cardType == CARD_SDHC){
Serial.println("SDHC"); // High Capacity SD card (2GB-32GB)
M5.Display.drawString("SDHC", 5, 20);
} else {
Serial.println("UNKNOWN"); // Unrecognized card type
M5.Display.drawString("UNKNOWN", 5, 20);
}
// Calculate total and used SD card capacity in MB (1MB = 1024*1024 bytes)
uint64_t cardSize = SD.totalBytes() / (1024 * 1024);
uint64_t usedSize = SD.usedBytes() / (1024 * 1024);
Serial.printf("SD Card Size: %lluMB\n", cardSize);
Serial.printf("SD Card Uesd Size: %lluMB\n", usedSize);
M5.Display.setCursor(5, 40);
M5.Display.printf("%llu/%lluMB", usedSize, cardSize);
// Some delay is required here to ensure that the code above is executed completely; otherwise, the information feedback will be incorrect.
delay(500);
// Execute a sequence of SD card operations to demonstrate functionality
listDir(SD, "/", 0); // List root directory (non-recursive)
createDir(SD, "/mydir"); // Create a new directory named "mydir"
listDir(SD, "/", 0); // List root directory again to verify creation
removeDir(SD, "/mydir"); // Delete the "mydir" directory
listDir(SD, "/", 2); // List root directory with 2 levels of recursion
writeFile(SD, "/hello.txt", "Hello "); // Create "hello.txt" and write initial content
appendFile(SD, "/hello.txt", "World!\n"); // Append content to "hello.txt"
readFile(SD, "/hello.txt"); // Read and print content of "hello.txt"
renameFile(SD, "/hello.txt", "/test.txt"); // Rename "hello.txt" to "test.txt"
readFile(SD, "/test.txt"); // Read renamed file to verify
testFileIO(SD, "/test.txt"); // Test read/write speed of "test.txt"
// Print final total and used space after all operations
Serial.printf("Total space: %lluMB\n", SD.totalBytes() / (1024 * 1024));
Serial.printf("Used space: %lluMB\n", SD.usedBytes() / (1024 * 1024));
deleteFile(SD, "/test.txt"); // Delete the test file to clean up
}
void loop() {
}
// ------------------- Directory Listing Function -------------------
// fs: File system object (e.g., SD for SD card)
// dirname: Path of the directory to list
// levels: Number of recursive levels to list (0 = only current directory)
void listDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * dirname, uint8_t levels){
Serial.printf("Listing directory: %s\n", dirname);
File root = fs.open(dirname);
if(!root){
Serial.println("Failed to open directory");
return;
}
// Verify the opened object is a directory (not a file)
if(!root.isDirectory()){
Serial.println("Not a directory");
return;
}
// Open the first file/directory in the target directory
File file = root.openNextFile();
// Iterate through all files/directories in the target directory
while(file){
if(file.isDirectory()){
Serial.print(" DIR : ");
Serial.println(file.name());
// Recursively list subdirectories if levels > 0
if(levels){
listDir(fs, file.name(), levels - 1);
}
} else {
Serial.print(" FILE: ");
Serial.print(file.name());
Serial.print(" SIZE: ");
Serial.println(file.size());
}
// Move to the next file/directory
file = root.openNextFile();
}
}
// ------------------- Directory Creation Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path: Full path of the directory to create
void createDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
Serial.printf("Creating Dir: %s\n", path);
if(fs.mkdir(path)){
Serial.println("Dir created");
} else {
Serial.println("mkdir failed");
}
}
// ------------------- Directory Removal Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path: Full path of the directory to remove (must be empty)
void removeDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
Serial.printf("Removing Dir: %s\n", path);
if(fs.rmdir(path)){
Serial.println("Dir removed");
} else {
Serial.println("rmdir failed"); // Failure may occur if directory not empty
}
}
// ------------------- File Reading Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path: Full path of the file to read
void readFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
Serial.printf("Reading file: %s\n", path);
// Open file in read mode (default mode for fs.open())
File file = fs.open(path);
if(!file){
Serial.println("Failed to open file for reading");
return;
}
Serial.print("Read from file: ");
// Read all available bytes from file and print to serial
while(file.available()){
Serial.write(file.read());
}
file.close();
}
// ------------------- File Writing Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path: Full path of the file to write
// message: Content to write to the file (overwrites existing content)
void writeFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message){
Serial.printf("Writing file: %s\n", path);
// Open file in write mode (creates file if it doesn't exist, overwrites if it does)
File file = fs.open(path, FILE_WRITE);
if(!file){
Serial.println("Failed to open file for writing");
return;
}
if(file.print(message)){
Serial.println("File written");
} else {
Serial.println("Write failed");
}
file.close();
}
// ------------------- File Appending Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path: Full path of the file to append to
// message: Content to add to the end of the file
void appendFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message){
Serial.printf("Appending to file: %s\n", path);
// Open file in append mode (preserves existing content, writes to end)
File file = fs.open(path, FILE_APPEND);
if(!file){
Serial.println("Failed to open file for appending");
return;
}
if(file.print(message)){
Serial.println("Message appended");
} else {
Serial.println("Append failed");
}
file.close();
}
// ------------------- File Renaming Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path1: Current path/name of the file
// path2: New path/name for the file
void renameFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path1, const char * path2){
Serial.printf("Renaming file %s to %s\n", path1, path2);
if (fs.rename(path1, path2)) {
Serial.println("File renamed");
} else {
Serial.println("Rename failed"); // Failure may occur if target path exists
}
}
// ------------------- File Deletion Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path: Full path of the file to delete
void deleteFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
Serial.printf("Deleting file: %s\n", path);
if(fs.remove(path)){
Serial.println("File deleted");
} else {
Serial.println("Delete failed"); // Failure may occur if file doesn't exist
}
}
// ------------------- File I/O Speed Test Function -------------------
// fs: File system object
// path: Full path of the file to use for testing
void testFileIO(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
File file = fs.open(path);
// 512-byte buffer for read/write operations (matches typical sector size)
static uint8_t buf[512];
size_t len = 0;
uint32_t start = millis(); // Record start time for timing
uint32_t end = start;
// ------------------- Read Speed Test -------------------
if(file){
len = file.size();
size_t flen = len; // Store original length for output
start = millis(); // Reset start time for read test
// Read file in 512-byte chunks (optimizes for sector size)
while(len){
size_t toRead = len;
if(toRead > 512){
toRead = 512;
}
file.read(buf, toRead); // Read chunk into buffer
len -= toRead; // Decrement remaining bytes to read
}
// Calculate total read time and print results
end = millis() - start;
Serial.printf("%u bytes read for %u ms\n", flen, end);
file.close(); // Close file after read test
} else {
Serial.println("Failed to open file for reading");
}
// ------------------- Write Speed Test -------------------
// Open file in write mode (overwrites existing content)
file = fs.open(path, FILE_WRITE);
if(!file){
Serial.println("Failed to open file for writing");
return;
}
size_t i;
start = millis(); // Reset start time for write test
// Write 2048 chunks of 512 bytes (total 1MB of data)
for(i=0; i<2048; i++){
file.write(buf, 512);
}
// Calculate total write time and print results
end = millis() - start;
Serial.printf("%u bytes written for %u ms\n", 2048 * 512, end);
file.close(); // Close file after write test
}3. Compile and Upload
- Download mode: Devices must enter download mode before program flashing; this varies with the main controller. See the Arduino IDE Quick Start page's device program download tutorial list for specific instructions.
- For AtomS3R, press and hold the reset button (about 2 seconds) until the internal green LED lights up, then release. The device is now in download mode and ready for flashing.

- Select the device port, click the compile/upload button in the top left of Arduino IDE, and wait for compilation and upload to complete.
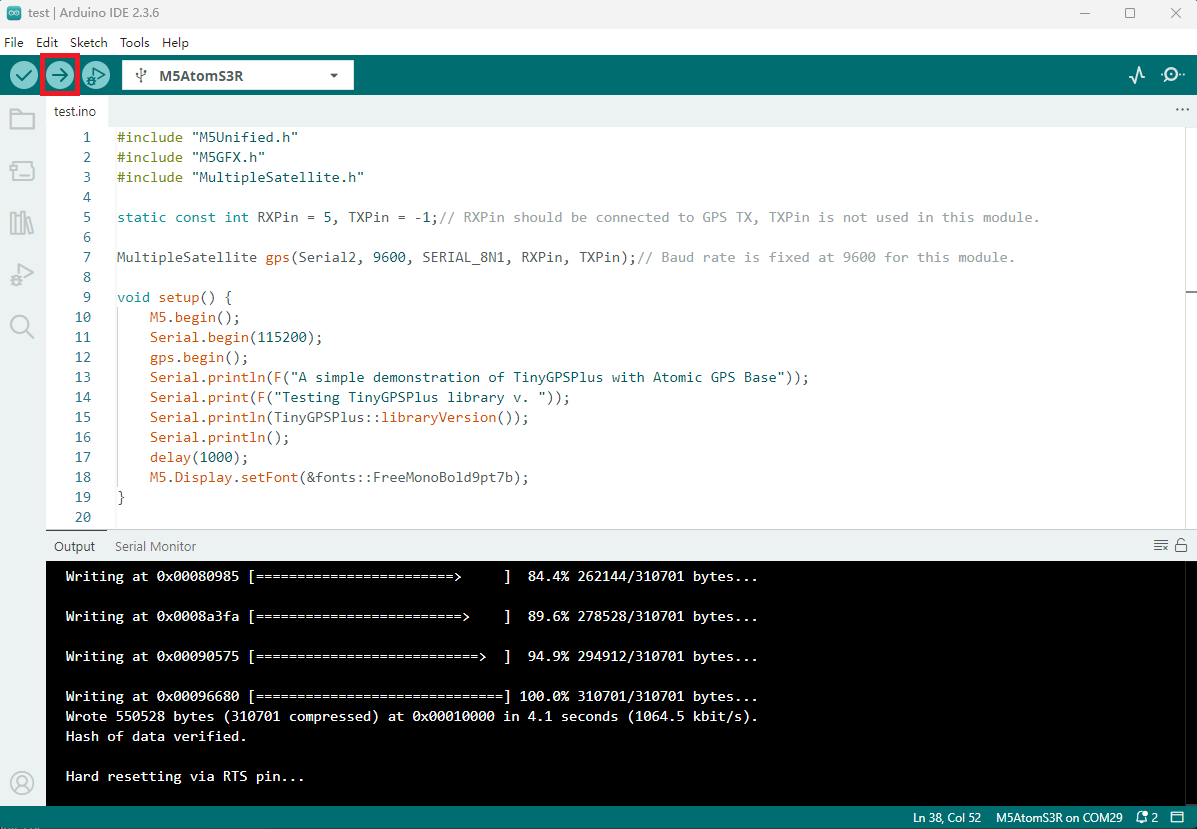
4. Example Output
- Satellite Positioning:
This product uses a built-in antenna without an external one, so use outdoors in open areas like playgrounds or rooftops. First-time satellite acquisition is slow, taking several minutes. Please be patient while the device searches for satellites and obtains coordinates.

- SD Card Read/Write:
After powering on, the screen displays as shown below. Operations such as creating, reading, and deleting folders/files on the card are printed to the serial monitor.
Note
1. Ensure a microSD card formatted as
2. In this demonstration, the microSD card is blank. The "System Volume Information" folder appearing in the serial output is an automatically generated hidden folder by the OS when connected to a computer and can be ignored. To delete it, enable hidden file display on your computer and remove it.
FAT32 is correctly inserted before running this example.2. In this demonstration, the microSD card is blank. The "System Volume Information" folder appearing in the serial output is an automatically generated hidden folder by the OS when connected to a computer and can be ignored. To delete it, enable hidden file display on your computer and remove it.

Serial output:
<-------microSD Example------->
SD Init...
SD Ready
SD Card Type: SDHC
SD Card Size: 15185MB
SD Card Uesd Size: 0MB
Listing directory: /
DIR : System Volume Information
Creating Dir: /mydir
Dir created
Listing directory: /
DIR : System Volume Information
DIR : mydir
Removing Dir: /mydir
Dir removed
Listing directory: /
DIR : System Volume Information
Listing directory: System Volume Information
Failed to open directory
Writing file: /hello.txt
File written
Appending to file: /hello.txt
Message appended
Reading file: /hello.txt
Read from file: Hello World!
Renaming file /hello.txt to /test.txt
File renamed
Reading file: /test.txt
Read from file: Hello World!
13 bytes read for 1 ms
1048576 bytes written for 866 ms
Total space: 15185MB
Used space: 1MB
Deleting file: /test.txt
File deleted