Module13.2 AIN4-20mA Arduino Tutorial
1. Preparation
- Environment Setup: Refer to Arduino IDE Getting Started Guide to complete IDE installation, and install corresponding board management and required driver libraries based on the actual development board used.
- Required Driver Libraries:
Note
You need to download the latest library version from GitHub: M5Module-4-20mA - M5Stack GitHub. Do not download from Arduino Library. (For questions, refer to this tutorial)
- Hardware Products Used:


2. Precautions
Jumper Cap Connection Instructions
The product package includes 12 jumper caps, which can be switched according to the active/passive status of current-type sensors.
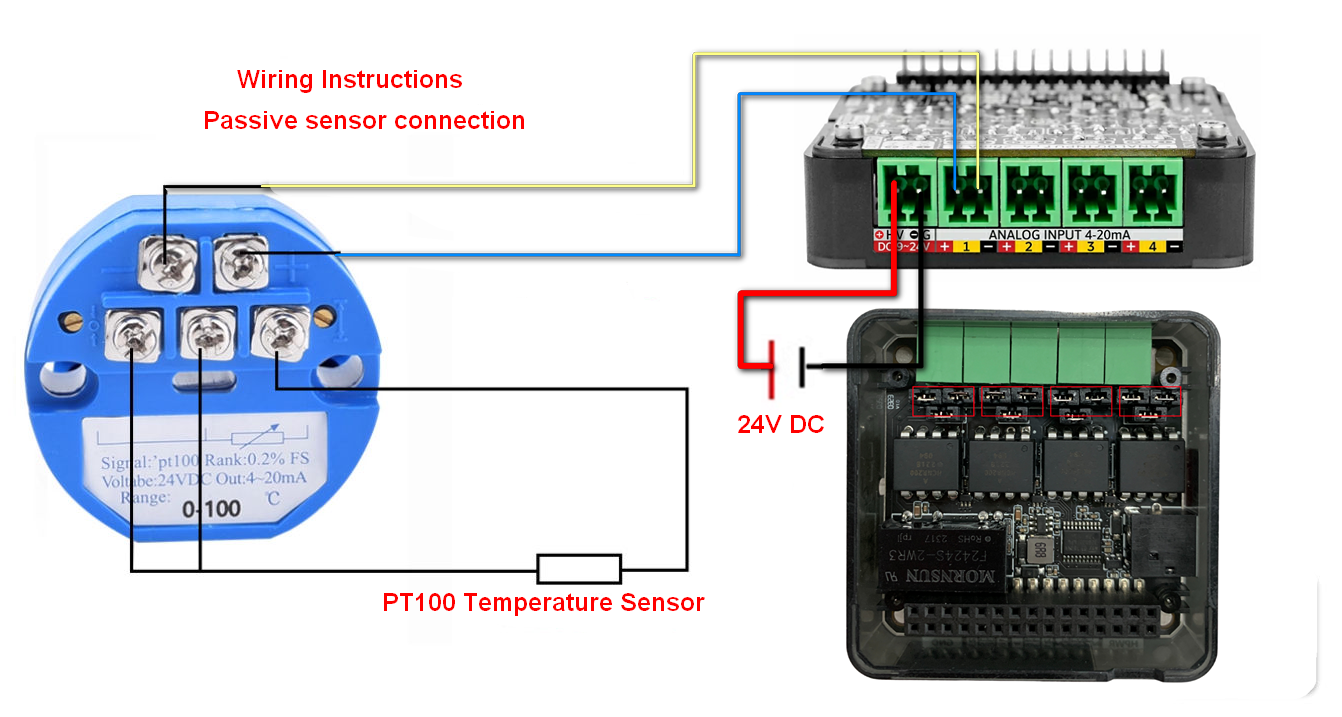
- When using passive current-type sensors, please connect DC 24V power input, connect sensor signals to IN+, IN-, and adjust jumper caps as shown below (note signal polarity):
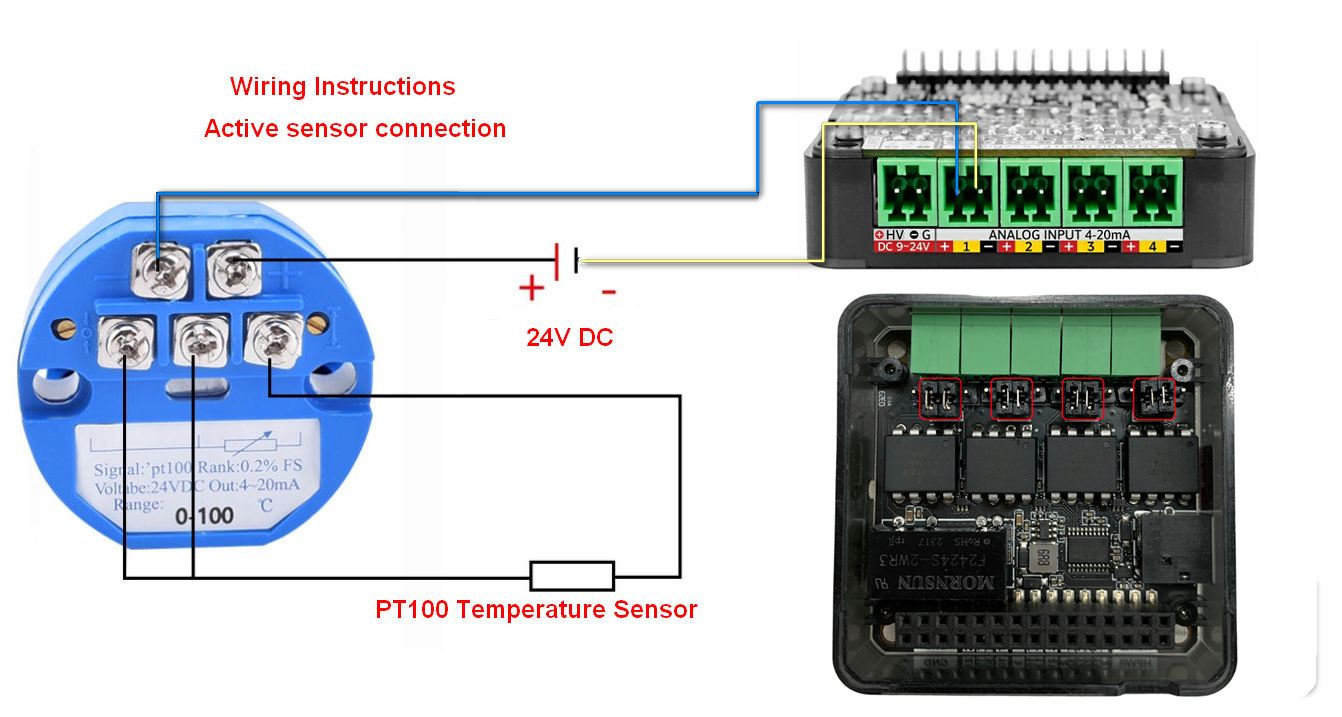
- When using active current-type sensors, please connect sensor signals to IN+, IN-, and adjust jumper caps as shown below (note signal polarity):
Pin Compatibility
Due to different pin configurations for each host device, please refer to the Pin Compatibility Table in the product documentation before use, and modify the example program according to actual pin connections.
3. Example Program
- The main controller used in this tutorial is CoreS3 paired with Module13.2 AIN4-20mA. This current-type analog input module communicates via I2C. Modify pin definitions in the program according to actual circuit connections. After device connection, the corresponding serial IO pins are
G11 (SCL),G12 (SDA).
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44
#include <M5Unified.h>
#include <M5GFX.h>
#include "MODULE_4_20MA.h"
#define channel 3
M5GFX display;
MODULE_4_20MA meter;
void show_current_value(void) {
M5.Display.fillScreen(WHITE);
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 0);
M5.Display.println("Module 4-20mA Demo");
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 50);
M5.Display.printf("CH%d Current:%.2fmA\r\n", channel,
(float)(meter.getCurrentValue(channel - 1)) / 100.0);
Serial.printf("CH%d ADC_12Bits_Value:%d\r\n", channel, meter.getADC12BitsValue(channel - 1));
M5.Display.printf("CH%d ADC_12Bits_Value:%d\r\n", channel, meter.getADC12BitsValue(channel - 1));
M5.Display.printf("CH%d Cal_Current:%d\r\n", channel, meter.getCurrentValue(channel - 1));
}
void setup() {
M5.begin();
Serial.begin(115200);
M5.Display.fillScreen(WHITE);
M5.Display.setTextColor(BLACK);
M5.Display.setFont(&fonts::FreeMonoBold9pt7b);
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 0);
M5.Display.println("Module 4-20mA Demo");
while (!(meter.begin(&Wire, MODULE_4_20MA_ADDR, 12, 11, 100000UL))) {
M5.Display.fillScreen(WHITE);
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 0);
M5.Display.println("No Module!");
}
Serial.printf("Firmware Version:%d.%d.%d\r\n", meter.getFirmwareVersion(),
meter.getI2CAddress(), meter.getFirmwareVersion());
Serial.printf("I2C Address:%02X\r\n", meter.getI2CAddress());
delay(500);
}
void loop() {
show_current_value();
delay(1000);
}4. Compile and Upload
Download Mode: Different devices need to enter download mode before program burning, and this step may vary for different main control devices. For details, please refer to the device program download tutorial list at the bottom of the Arduino IDE Getting Started Guide page to view specific operation methods.
For CoreS3, press and hold the reset button (about 2 seconds) until the internal green LED lights up, then release. The device will now enter download mode and wait for burning.
.gif)
- Select the device port and click the compile and upload button in the upper left corner of Arduino IDE. Wait for the program to complete compilation and upload to the device.
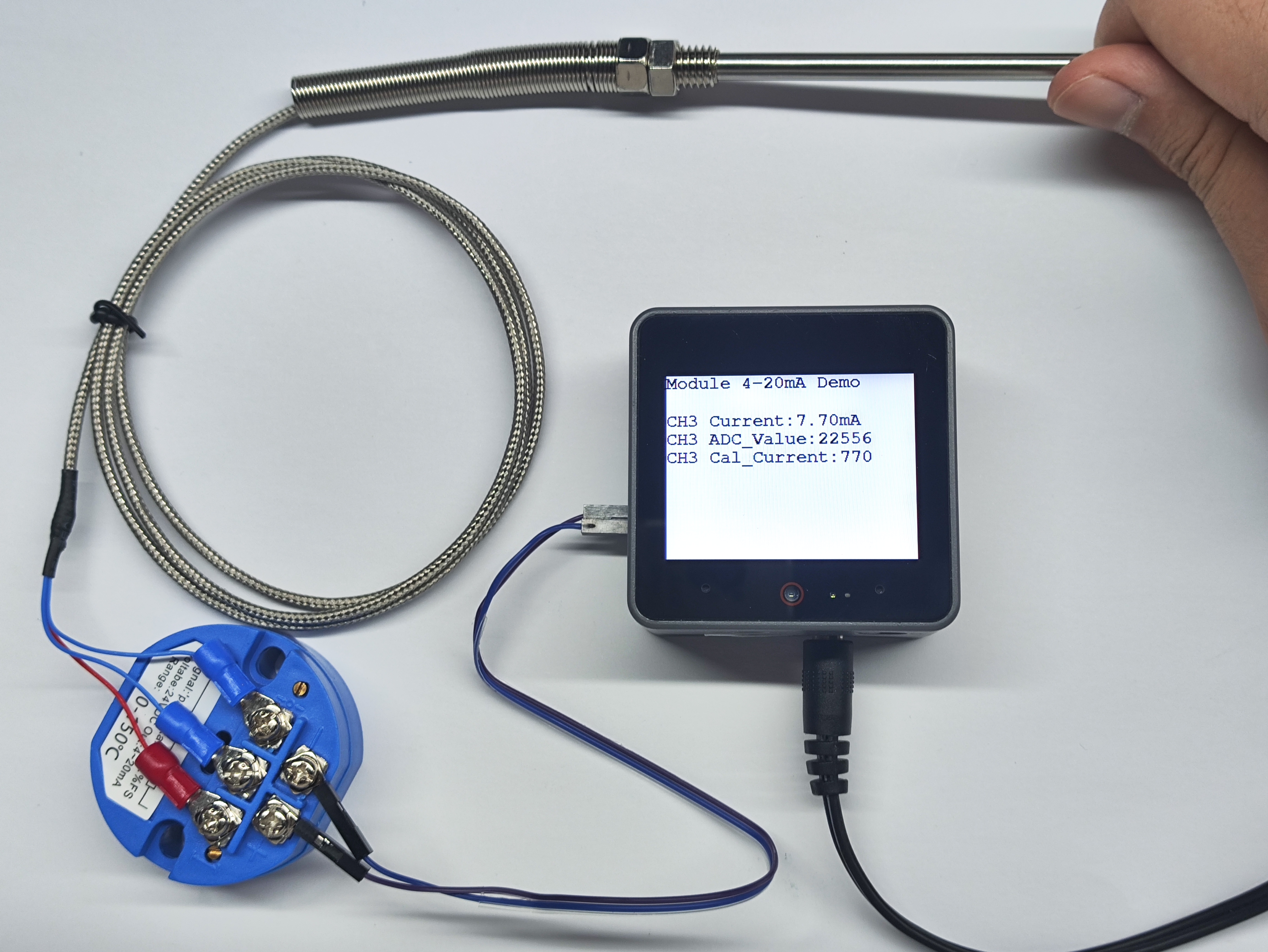
5. Current Measurement
- This experiment uses a PT100 thermocouple temperature sensor paired with a passive current-type sensor, with signal lines connected to 3 channels. After completing the hardware wiring, burn the code to see the collected current analog data.
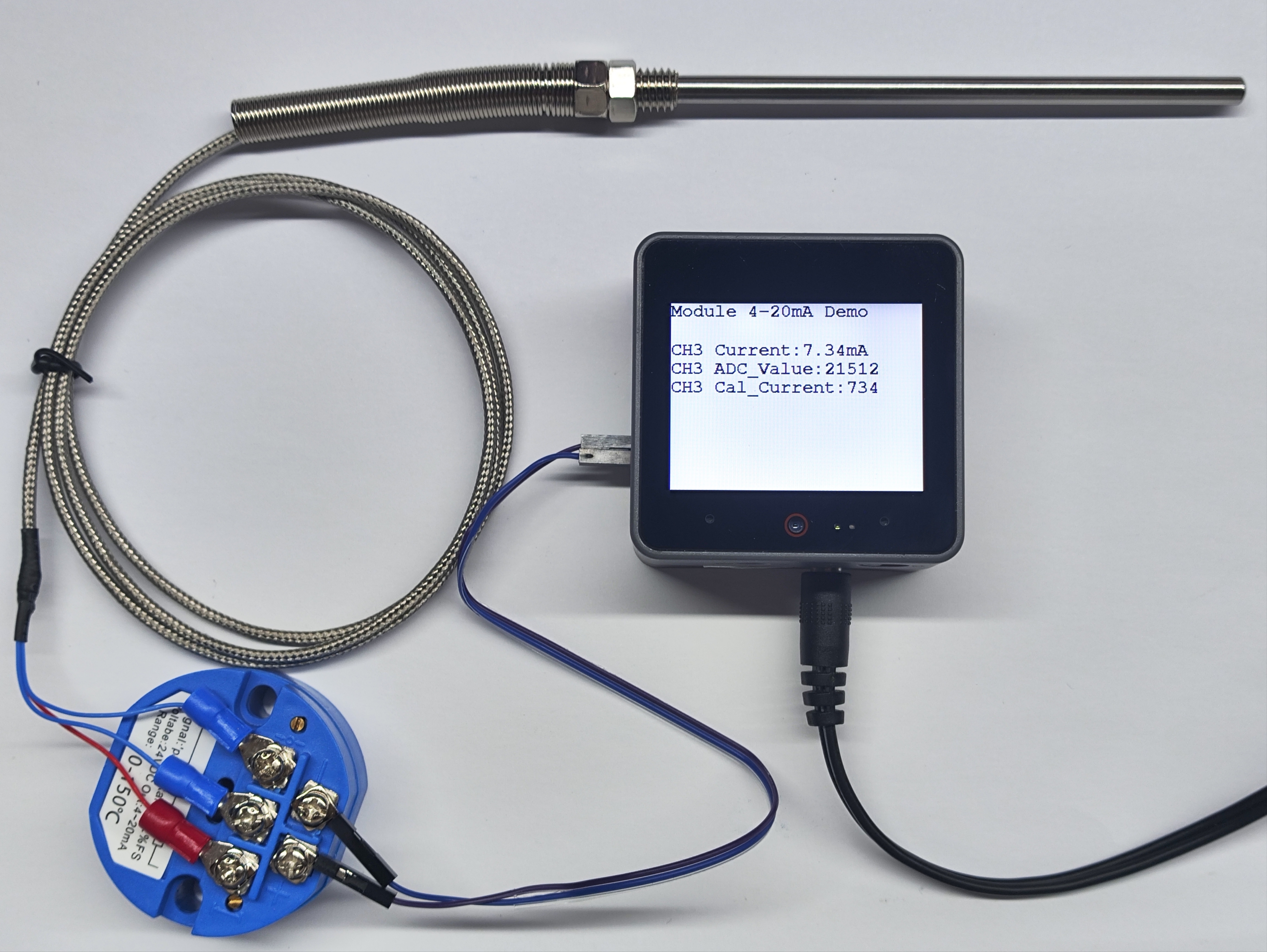
- When the sensor temperature rises, the current value obtained by the current sensor also increases.