NanoC6 Thread Arduino
NanoC6 OpenThread Arduino related example programs.
准备工作
Preparation
编译要求
Build Requirements
- M5Stack board manager version >= 3.2.5
- Development board option = M5NanoC6
基本配置步骤
Basic Configuration Steps
- Open Arduino IDE
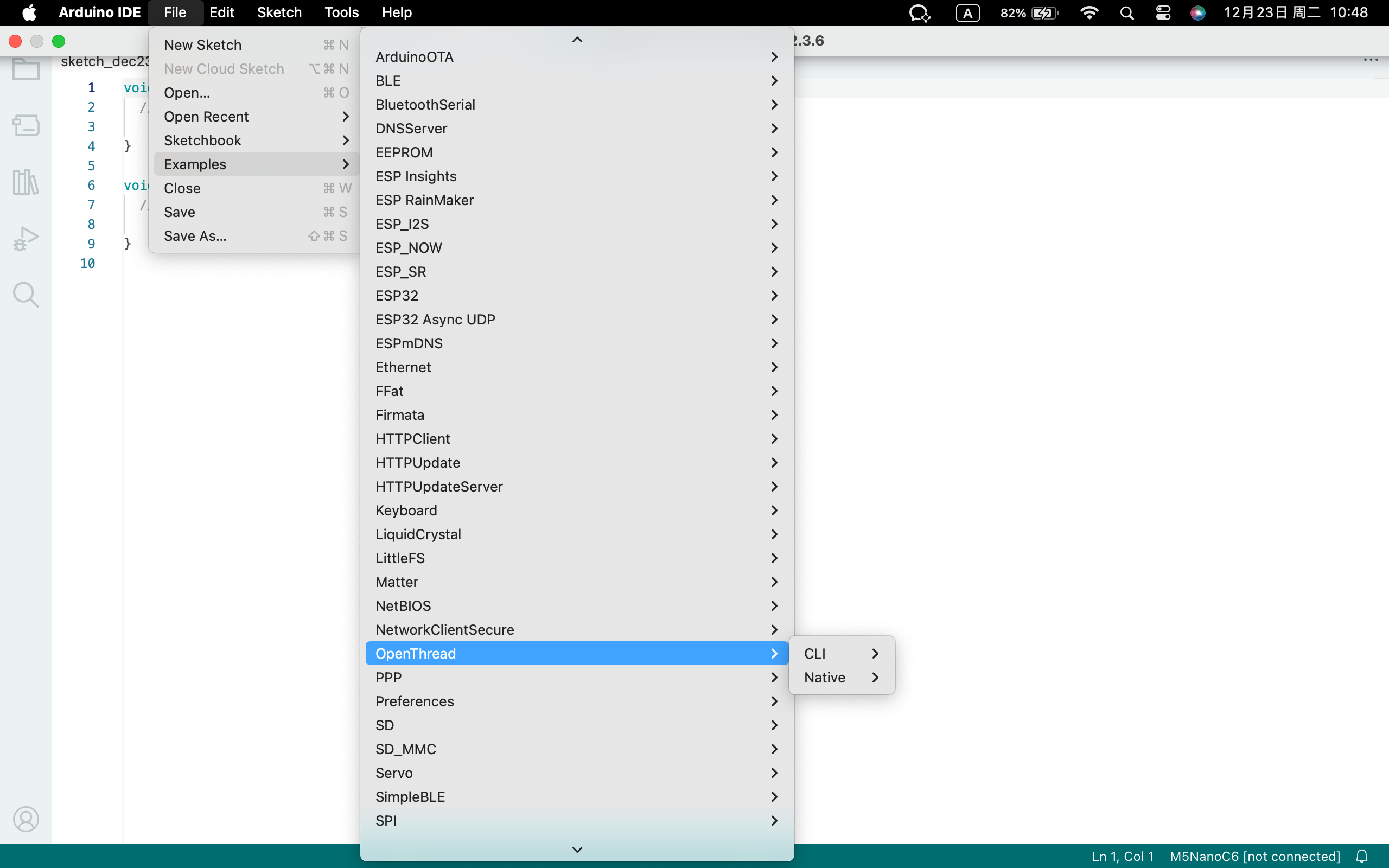
- Click Examples:
File -> Examples -> OpenThread - Select the correct development board:
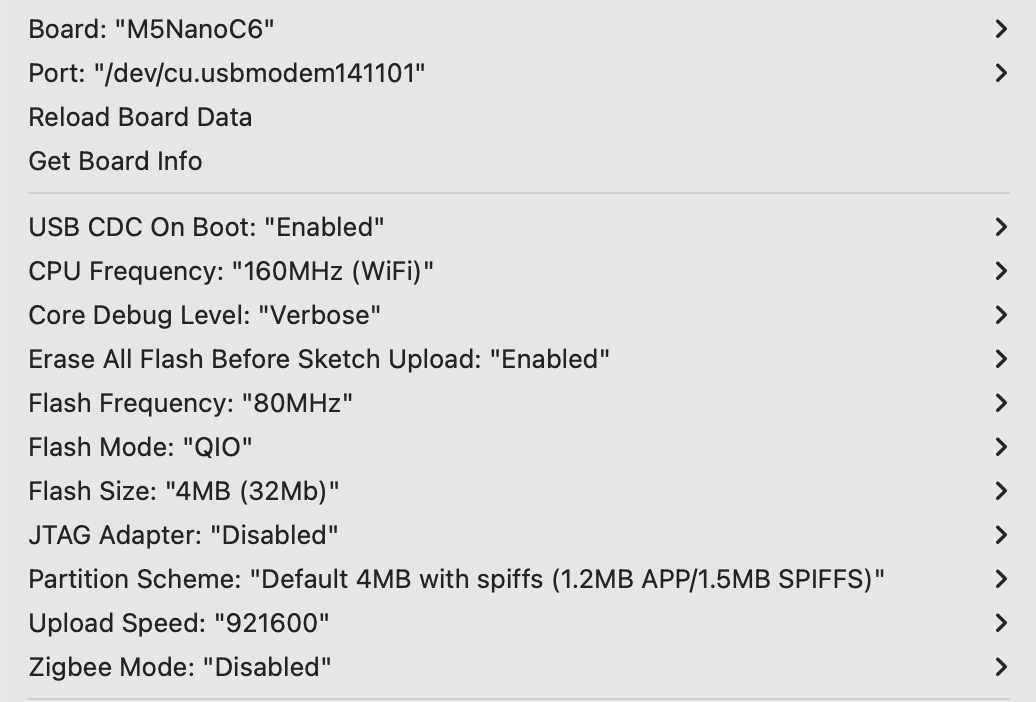
Tools -> Board: M5NanoC6 - Enable USB serial on boot:
Tools -> USB CDC On Boot: Enabled - Select flash size:
Tools -> Flash Size: 4MB - Select partition scheme:
Tools -> Partition Scheme: Default 4MB with spiffs (1.2MB APP/1.5MB SPIFFS) - Select the correct serial port:
Tools -> Port - Upload the firmware to the device
- The device will automatically start and attempt to join the network
- Check the network status via the serial monitor
案例程序
Example Programs
1. Simple Node
This example demonstrates how to create a basic Thread node.
- Automatically starts and joins the Thread network. If no corresponding Thread network exists, it will start as a Leader node.
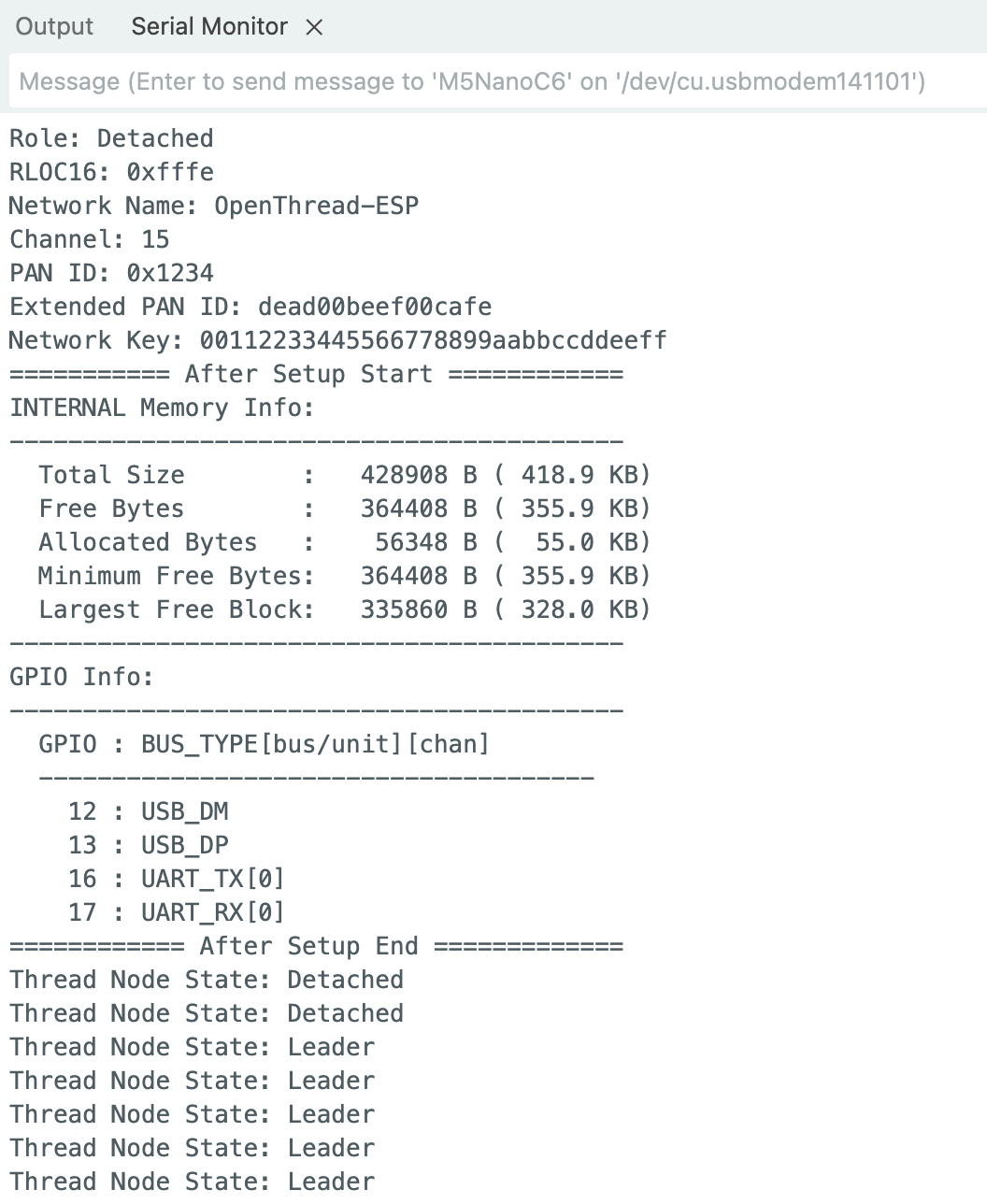
- Uses the default network configuration:
- Network Name: OpenThread-ESP
- Network Prefix: fd00:db8:a0:0::/64
- Network Channel: 15
- PAN ID: 0x1234
- Extended PAN ID: dead00beef00cafe
- Network Key: 00112233445566778899aabbccddeeff
- Displays node status every 5 seconds
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
#include "OThreadCLI.h"
#include "OThreadCLI_Util.h"
// The first device to start Thread will be the Leader
// Next devices will be Router or Child
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
OThread.begin(); // AutoStart using Thread default settings
OThreadCLI.begin();
OThread.otPrintNetworkInformation(Serial); // Print Current Thread Network Information
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Thread Node State: ");
Serial.println(OThread.otGetStringDeviceRole());
delay(5000);
}
2. Thread Network (CLI)
This example demonstrates how to build a complete Thread network with two different types of nodes. The Leader Node will send a "Hello, M5Stack!" message to the Router Node.
2.1 Leader Node
- Creates and manages the Thread network as the first device
- Provides the complete network dataset
- Displays detailed network information:
- Network name
- Channel
- PAN ID
- Extended PAN ID
- Network key
- IP addresses
- Multicast addresses
- Sending prompts
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83
#include "OThreadCLI.h"
#include "OThreadCLI_Util.h"
#define CLI_NETWORK_KEY "dataset networkkey 00112233445566778899aabbccddeeff"
#define CLI_NETWORK_CHANEL "dataset channel 24"
otInstance *aInstance = NULL;
bool udpInitialized = false;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
OThread.begin(false);
OThreadCLI.begin();
Serial.println();
Serial.println("Setting up OpenThread Node as Leader");
aInstance = esp_openthread_get_instance();
OThreadCLI.println("dataset init new");
OThreadCLI.println(CLI_NETWORK_KEY);
OThreadCLI.println(CLI_NETWORK_CHANEL);
OThreadCLI.println("dataset commit active");
OThreadCLI.println("ifconfig up");
OThreadCLI.println("thread start");
}
void loop() {
while (OThreadCLI.available()) {
Serial.write(OThreadCLI.read());
}
Serial.println("=============================================");
Serial.print("Thread Node State: ");
Serial.println(OThread.otGetStringDeviceRole());
if (OThread.otGetDeviceRole() == OT_ROLE_LEADER) {
const char *networkName = otThreadGetNetworkName(aInstance);
Serial.printf("Network Name: %s\r\n", networkName);
uint8_t channel = otLinkGetChannel(aInstance);
Serial.printf("Channel: %d\r\n", channel);
uint16_t panId = otLinkGetPanId(aInstance);
Serial.printf("PanID: 0x%04x\r\n", panId);
const otExtendedPanId *extPanId = otThreadGetExtendedPanId(aInstance);
Serial.printf("Extended PAN ID: ");
for (int i = 0; i < OT_EXT_PAN_ID_SIZE; i++) {
Serial.printf("%02x", extPanId->m8[i]);
}
Serial.println();
otNetworkKey networkKey;
otThreadGetNetworkKey(aInstance, &networkKey);
Serial.printf("Network Key: ");
for (int i = 0; i < OT_NETWORK_KEY_SIZE; i++) {
Serial.printf("%02x", networkKey.m8[i]);
}
Serial.println();
char buf[OT_IP6_ADDRESS_STRING_SIZE];
const otNetifAddress *address = otIp6GetUnicastAddresses(aInstance);
while (address != NULL) {
otIp6AddressToString(&address->mAddress, buf, sizeof(buf));
Serial.printf("IP Address: %s\r\n", buf);
address = address->mNext;
}
const otNetifMulticastAddress *mAddress = otIp6GetMulticastAddresses(aInstance);
while (mAddress != NULL) {
otIp6AddressToString(&mAddress->mAddress, buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("Multicast IP Address: %s\n", buf);
mAddress = mAddress->mNext;
}
if (!udpInitialized) {
Serial.println("\nInitializing UDP sender...");
OThreadCLI.println("udp open");
delay(100);
udpInitialized = true;
Serial.println("UDP initialized");
}
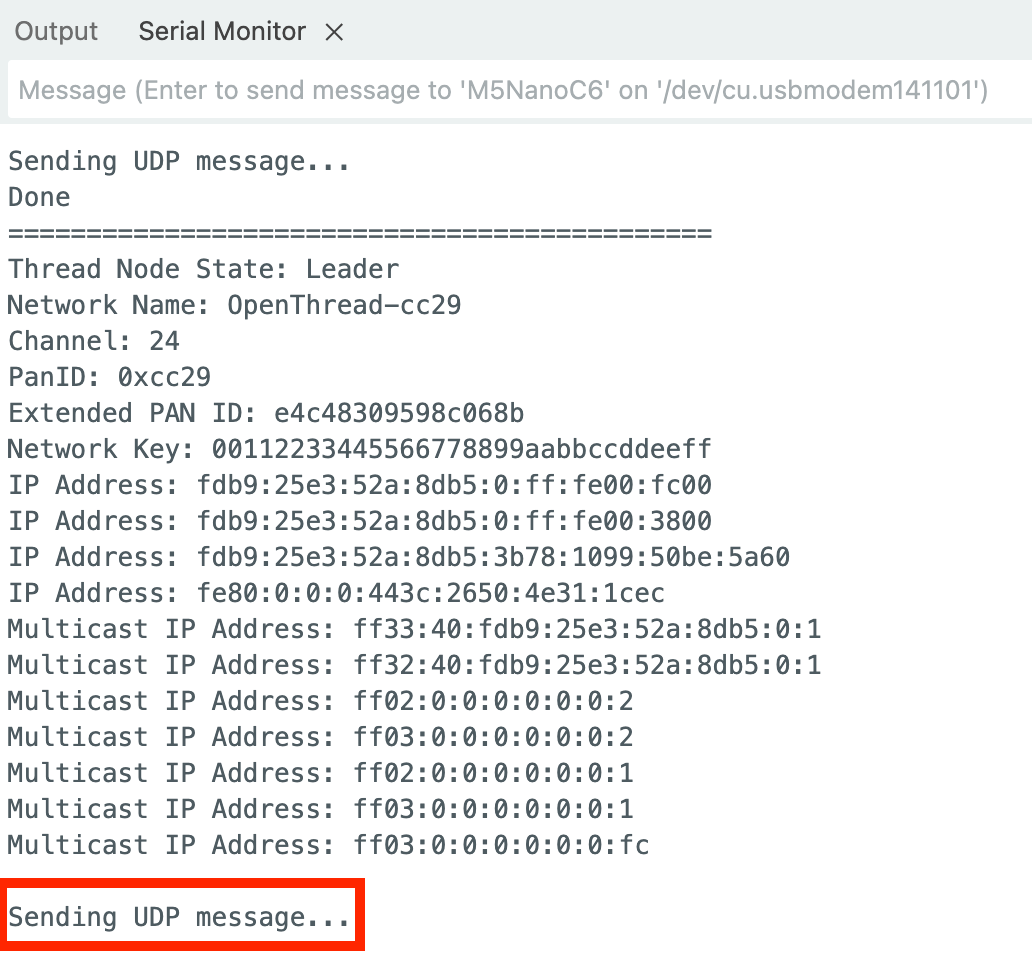
Serial.println("\nSending UDP message...");
OThreadCLI.println("udp send ff03::1 12345 \"Hello,M5Stack\"");
}
delay(5000);
}
2.2 Router Node
- Joins an existing Thread network and forwards network data
- Displays connection status and network information
- Prints received messages via serial output
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84
#include "OThreadCLI.h"
#include "OThreadCLI_Util.h"
#define CLI_NETWORK_KEY "dataset networkkey 00112233445566778899aabbccddeeff"
#define CLI_NETWORK_CHANEL "dataset channel 24"
otInstance *aInstance = NULL;
bool udpInitialized = false;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
OThread.begin(false);
OThreadCLI.begin();
Serial.println();
Serial.println("Setting up OpenThread Node as Router/Child");
Serial.println("Make sure the Leader Node is already running");
aInstance = esp_openthread_get_instance();
OThreadCLI.println("dataset clear");
OThreadCLI.println(CLI_NETWORK_KEY);
OThreadCLI.println(CLI_NETWORK_CHANEL);
OThreadCLI.println("dataset commit active");
OThreadCLI.println("ifconfig up");
OThreadCLI.println("thread start");
}
void loop() {
while (OThreadCLI.available()) {
Serial.write(OThreadCLI.read());
}
Serial.println("=============================================");
Serial.print("Thread Node State: ");
Serial.println(OThread.otGetStringDeviceRole());
if (OThread.otGetDeviceRole() == OT_ROLE_CHILD || OThread.otGetDeviceRole() == OT_ROLE_ROUTER) {
const char *networkName = otThreadGetNetworkName(aInstance);
Serial.printf("Network Name: %s\r\n", networkName);
uint8_t channel = otLinkGetChannel(aInstance);
Serial.printf("Channel: %d\r\n", channel);
uint16_t panId = otLinkGetPanId(aInstance);
Serial.printf("PanID: 0x%04x\r\n", panId);
const otExtendedPanId *extPanId = otThreadGetExtendedPanId(aInstance);
Serial.printf("Extended PAN ID: ");
for (int i = 0; i < OT_EXT_PAN_ID_SIZE; i++) {
Serial.printf("%02x", extPanId->m8[i]);
}
Serial.println();
otNetworkKey networkKey;
otThreadGetNetworkKey(aInstance, &networkKey);
Serial.printf("Network Key: ");
for (int i = 0; i < OT_NETWORK_KEY_SIZE; i++) {
Serial.printf("%02x", networkKey.m8[i]);
}
Serial.println();
char buf[OT_IP6_ADDRESS_STRING_SIZE];
const otNetifAddress *address = otIp6GetUnicastAddresses(aInstance);
while (address != NULL) {
otIp6AddressToString(&address->mAddress, buf, sizeof(buf));
Serial.printf("IP Address: %s\r\n", buf);
address = address->mNext;
}
const otNetifMulticastAddress *mAddress = otIp6GetMulticastAddresses(aInstance);
while (mAddress != NULL) {
otIp6AddressToString(&mAddress->mAddress, buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("Multicast IP Address: %s\n", buf);
mAddress = mAddress->mNext;
}
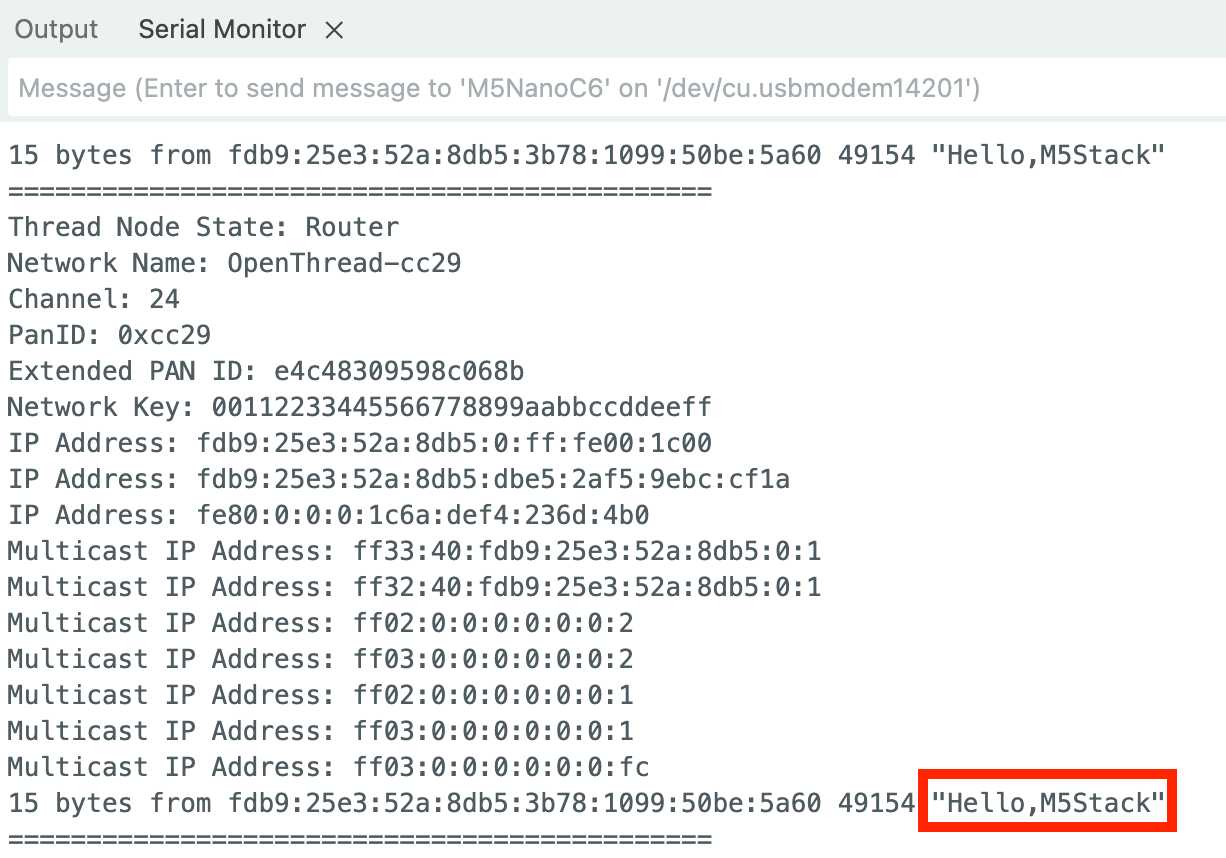
if (!udpInitialized) {
Serial.println("\nInitializing UDP receiver...");
OThreadCLI.println("udp open");
delay(100);
OThreadCLI.println("udp bind :: 12345");
delay(100);
udpInitialized = true;
Serial.println("UDP listening on port 12345");
Serial.println("Waiting for messages...\n");
}
}
delay(5000);
}
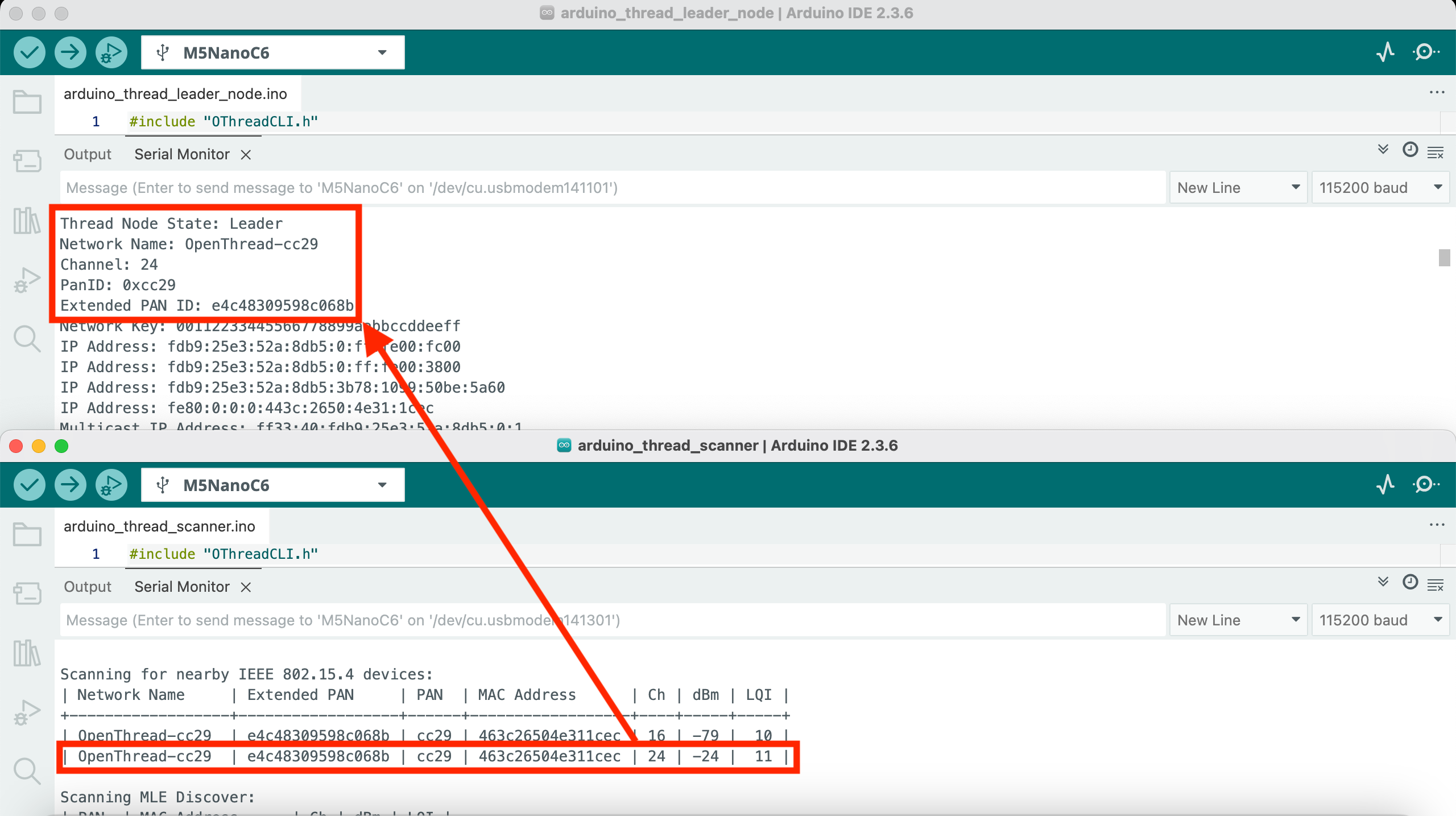
3. Thread Scan
This example demonstrates how to scan nearby Thread networks.
- Scan IEEE 802.15.4 devices
- Display device addresses
- Display signal strength
- Display channel information
- Scan Thread networks (device must be at least in Child state)
- Display network name
- Display extended PAN ID
- Display RLOC16
- Display version information
- Supports continuous scanning mode
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
#include "OThreadCLI.h"
#include "OThreadCLI_Util.h"
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
OThread.begin(true); // For scanning, AutoStart must be active, any setup
OThreadCLI.begin();
OThreadCLI.setTimeout(100); // Set a timeout for the CLI response
Serial.println();
Serial.println("This sketch will continuously scan the Thread Local Network and all devices IEEE 802.15.4 compatible");
}
void loop() {
Serial.println();
Serial.println("Scanning for nearby IEEE 802.15.4 devices:");
// 802.15.4 Scan just needs a previous OThreadCLI.begin()
if (!otPrintRespCLI("scan", Serial, 3000)) {
Serial.println("Scan Failed...");
}
delay(5000);
if (OThread.otGetDeviceRole() < OT_ROLE_CHILD) {
Serial.println();
Serial.println("This device has not started Thread yet, bypassing Discovery Scan");
return;
}
Serial.println();
Serial.println("Scanning MLE Discover:");
if (!otPrintRespCLI("discover", Serial, 3000)) {
Serial.println("Discover Failed...");
}
delay(5000);
}
4. Simple CLI
This example provides a complete OpenThread CLI console.
- Provides a full CLI command interface
- Supports all OpenThread CLI commands:
- Network management commands
- Device configuration commands
- Diagnostic commands
- Security commands
- Real-time command responses
- Supports command history
- Convenient for debugging and configuration
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
#include "OThreadCLI.h"
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
OThread.begin(false); // No AutoStart - fresh start
OThreadCLI.begin();
Serial.println("OpenThread CLI started - type 'help' for a list of commands.");
OThreadCLI.startConsole(Serial);
}
void loop() {}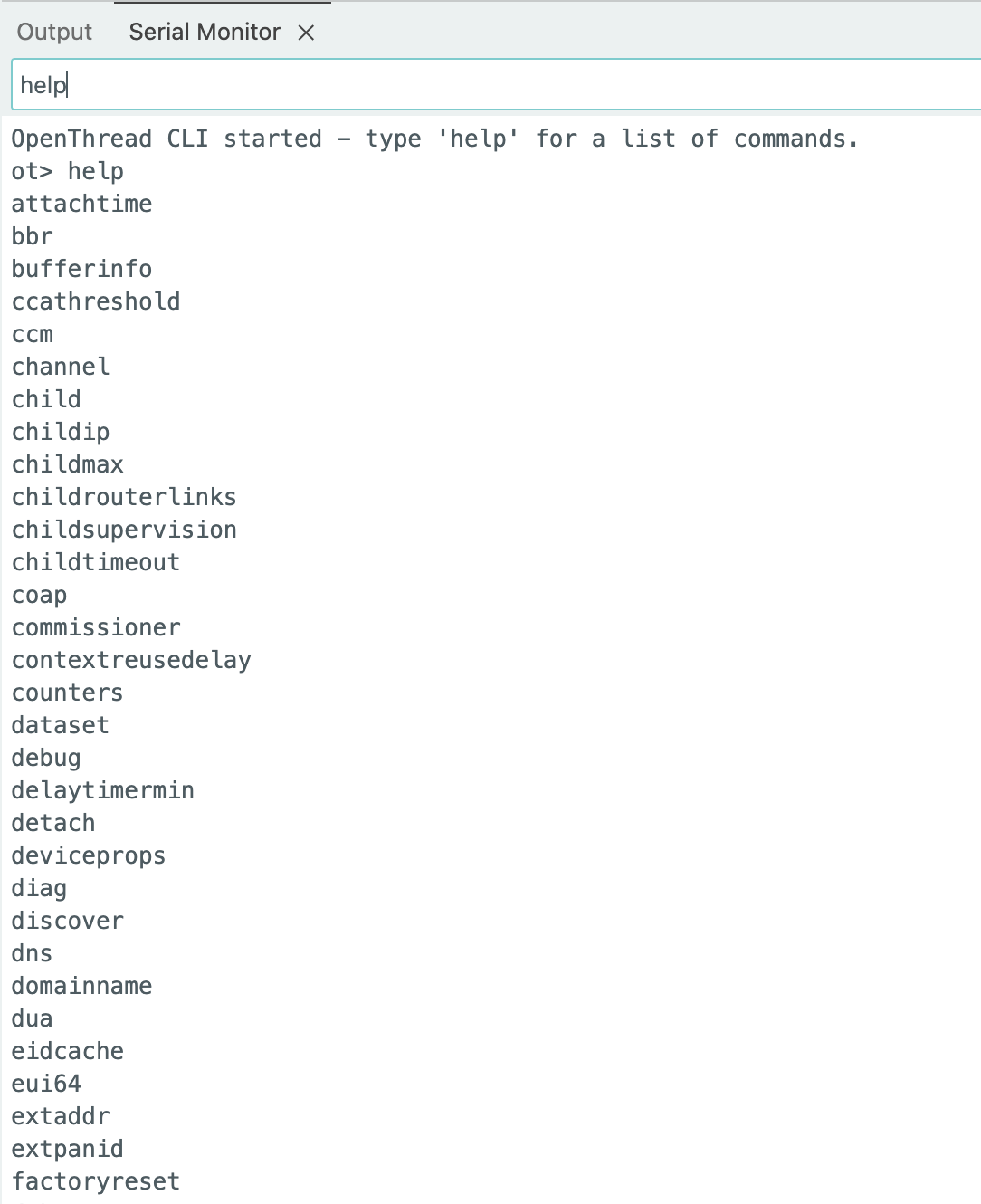
5. 接收回调 (onReceive)
5. Receive Callback (onReceive)
This example demonstrates how to use callback functions to handle CLI responses.
- Capture CLI responses
- Custom response handling
- Status monitoring
- Supports asynchronous processing
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
#include "OThreadCLI.h"
// reads all the lines sent by CLI, one by one
// ignores some lines that are just a sequence of \r\n
void otReceivedLine() {
String line = "";
while (OThreadCLI.available() > 0) {
char ch = OThreadCLI.read();
if (ch != '\r' && ch != '\n') {
line += ch;
}
}
// ignores empty lines, usually EOL sequence
if (line.length() > 0) {
Serial.print("OpenThread CLI RESP===> ");
Serial.println(line.c_str());
}
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
OThread.begin(); // AutoStart
OThreadCLI.begin();
OThreadCLI.onReceive(otReceivedLine);
}
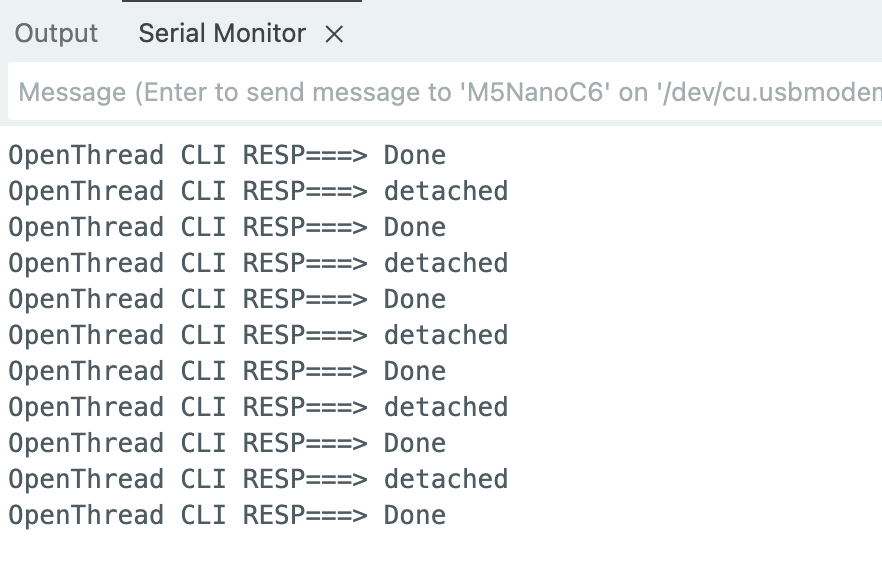
void loop() {
// sends the "state" command to the CLI every second
// the onReceive() Callback Function will read and process the response
OThreadCLI.println("state");
delay(1000);
}