Atomic SPK Base Arduino 使用チュートリアル
1. 準備
環境構築: Arduino IDE 入門チュートリアル を参考に IDE をインストールし、使用する開発ボードに応じたボードマネージャーおよび必要なライブラリをインストールしてください。
使用するライブラリ:
使用するハードウェア製品:


2. サンプルプログラム
- このチュートリアルでは、AtomS3R と Atomic SPK Base を組み合わせて使用します。本拡張モジュールのスピーカーは I2S による通信方式、SD カードは SPI 制御方式を採用しています。実際の回路接続に応じてプログラム内のピン定義を変更してください。接続後、対応する I2S ピンは
G5 (BCLK)、G38 (DATA)、G39 (LRCK)に、SPI ピンはG7 (SCK)、G8 (MISO)、G6 (MOSI)になります。
説明
以下に示す 2 つの API ベースのサンプルは、機能はほぼ同じですが I2S の設定方法が異なります。必要に応じて選択してください。
2.1 基本使用
M5Unified Speaker API ベース
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41
#include <M5Unified.h>
#include <M5GFX.h>
// Define I2S audio pins connected to the speaker
#define PIN_DATA 38 // Data output pin for audio signal
#define PIN_BCLK 5 // Bit clock pin for I2S communication
#define PIN_LRCK 39 // Left/Right clock pin for channel selection
// Set audio output sample rate (44.1kHz is standard for audio)
static constexpr const size_t output_samplerate = 44100;
void setup() {
M5.begin();
M5.Display.setFont(&fonts::FreeMonoBold9pt7b);
M5.Display.setTextDatum(middle_center);
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SPK Example", 64, 60);
// Configure speaker settings using I2S protocol
m5::speaker_config_t spk_cfg = {
.pin_data_out = PIN_DATA, // Assign data pin
.pin_bck = PIN_BCLK, // Assign bit clock pin
.pin_ws = PIN_LRCK, // Assign left/right clock pin
.sample_rate = output_samplerate, // Set audio sample rate
.dma_buf_len = 256, // DMA buffer length (for smooth audio)
.dma_buf_count = 6, // Number of DMA buffers (double buffering)
.i2s_port = i2s_port_t::I2S_NUM_0 // Specify I2S hardware port
};
M5.Speaker.config(spk_cfg); // Apply the speaker configuration
M5.Speaker.begin(); // Initialize the speaker hardware
M5.Speaker.setVolume(128);
}
void loop() {
// Play 6000Hz tone for 100ms
M5.Speaker.tone(6000, 100);
delay(1000);
// Play 2000Hz tone for 20ms
M5.Speaker.tone(2000, 20);
delay(1000);
}ESP32 I2S API ベース
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126
#include <driver/i2s_std.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <atomic>
#include <M5Unified.h>
#include <M5GFX.h>
// Define I2S audio pins connected to the speaker
#define PIN_DATA GPIO_NUM_38 // Data output pin for audio signal transmission
#define PIN_BCLK GPIO_NUM_5 // Bit clock pin for I2S timing synchronization
#define PIN_LRCK GPIO_NUM_39 // Left/Right clock pin for channel selection
// Audio configuration parameters
static constexpr const size_t output_samplerate = 44100; // Audio sampling rate (Hz)
static constexpr const int amplitude = 32767; // Max amplitude for 16-bit audio (-32768 ~ 32767)
static constexpr const int channels = 1; // MONO
static std::atomic<bool> isPlaying(false); // Atomic flag for playback status
static std::atomic<uint8_t> volume(50); // Volume level (0-100%)
// I2S hardware handle for ESP32
i2s_chan_handle_t tx_handle = nullptr;
#define I2S_PORT I2S_NUM_0
/**
* @brief Set audio volume level
* @param vol Volume level (0-100), 0 = mute, 100 = maximum
*/
void setVolume(uint8_t vol) {
volume = constrain(vol, 0, 100); // Constrain volume within valid range
}
void setup() {
M5.begin();
M5.Display.setFont(&fonts::FreeMonoBold9pt7b);
M5.Display.setTextDatum(middle_center);
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SPK Example", 64, 60);
// Configure I2S channel parameters
i2s_chan_config_t chan_cfg = {
.id = I2S_NUM_AUTO, // Automatically assign I2S peripheral
.role = I2S_ROLE_MASTER, // Operate as I2S master
.dma_desc_num = 6, // Number of DMA descriptors
.dma_frame_num = 256, // Number of frames per DMA descriptor
.auto_clear = true, // Automatically clear DMA buffers
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(i2s_new_channel(&chan_cfg, &tx_handle, NULL)); // Create I2S channel
// Configure standard I2S parameters - modified for mono
i2s_std_config_t std_tx_cfg = {
.clk_cfg = I2S_STD_CLK_DEFAULT_CONFIG(output_samplerate), // Clock configuration
.slot_cfg = I2S_STD_MSB_SLOT_DEFAULT_CONFIG(I2S_DATA_BIT_WIDTH_16BIT, I2S_SLOT_MODE_MONO),
.gpio_cfg = {
.mclk = I2S_GPIO_UNUSED, // MCLK not used
.bclk = PIN_BCLK, // Bit clock pin
.ws = PIN_LRCK, // Word select pin
.dout = PIN_DATA, // Data output pin
.din = I2S_GPIO_UNUSED, // No input needed
.invert_flags = {
.bclk_inv = false, // Do not invert BCLK
.ws_inv = false // Do not invert WS
},
}
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(i2s_channel_init_std_mode(tx_handle, &std_tx_cfg)); // Initialize I2S mode
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(i2s_channel_enable(tx_handle)); // Enable I2S channel
}
void playTone(float frequency, uint32_t duration);
void loop() {
playTone(6000, 100); // 6000Hz for 100ms
delay(1000); // Pause 1 second
playTone(2000, 20); // 2000Hz for 20ms
delay(1000); // Pause 1 second
}
/**
* @brief Generate sine wave tone and play through I2S (mono version)
* @param frequency Tone frequency in Hz
* @param duration Playback duration in milliseconds (0 = infinite)
*/
void playTone(float frequency, uint32_t duration) {
if (tx_handle == NULL || frequency <= 0) return; // Validate input
isPlaying = true;
const size_t samples_per_cycle = output_samplerate / frequency; // Samples per sine wave cycle
const size_t total_samples = (duration > 0) ?
(output_samplerate * duration) / 1000 : UINT32_MAX; // Total samples to generate
// Audio buffer - mono 16-bit (modified from stereo)
int16_t buffer[1024 * channels]; // 1024 samples
size_t samples_written = 0;
size_t bytes_written;
float gain = volume / 100.0f; // Calculate volume gain factor
while (isPlaying && samples_written < total_samples) {
// Calculate number of samples to write in this iteration
size_t samples_to_write = std::min(1024, (int)(total_samples - samples_written));
// Fill buffer with sine wave samples
for (size_t i = 0; i < samples_to_write; i++) {
// Calculate phase for continuous sine wave
float phase = 2 * M_PI * (samples_written + i) / samples_per_cycle;
int16_t sample = (int16_t)(amplitude * sin(phase)); // Generate raw sample
sample = (int16_t)(sample * gain); // Apply volume adjustment
// Single channel output
buffer[i] = sample; // Only one channel needed
}
// Transmit audio data via I2S
i2s_channel_write(tx_handle, buffer,
samples_to_write * channels * sizeof(int16_t),
&bytes_written, 100 / portTICK_PERIOD_MS); // 100ms timeout
// Update counter with actual written samples
samples_written += bytes_written / (channels * sizeof(int16_t));
}
// Send silence after playback to prevent noise
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer)); // Clear buffer with 0
i2s_channel_write(tx_handle, buffer, sizeof(buffer), &bytes_written, portMAX_DELAY);
isPlaying = false;
}2.2 SD カード内のオーディオファイル(wav 形式)を再生
M5Unified Speaker API ベース
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
#include <M5Unified.h>
#include <M5GFX.h>
// ------------------- Pin Definitions -------------------
// SPI pins for microSD card in speaker
#define SD_SPI_CS_PIN -1 // CS pin not connected (hardware-enabled permanently)
#define SD_SPI_SCK_PIN 7 // SPI Clock pin
#define SD_SPI_MISO_PIN 8 // SPI MISO pin
#define SD_SPI_MOSI_PIN 6 // SPI MOSI pin
// I2S pins for speaker (audio output protocol)
#define SPK_I2S_PIN_DATA 38 // I2S audio data output pin
#define SPK_I2S_PIN_BCLK 5 // I2S bit clock pin
#define SPK_I2S_PIN_LRCK 39 // I2S LR clock pin
// ------------------- Audio Configuration -------------------
static constexpr const size_t output_samplerate = 44100; // Standard audio sample rate (44.1kHz)
static bool isPlaying = false; // Flag to track audio play state (playing/stopped)
// ------------------- Global File/Buffer Variables -------------------
File wavFile; // File object for WAV audio file
uint8_t* wavBuffer = nullptr; // Buffer to store entire WAV file (header + audio data)
size_t wavBufferLen = 0; // Total length of WAV data in buffer
void setup() {
M5.begin();
M5.Display.setFont(&fonts::FreeMonoBold9pt7b);
M5.Display.setTextDatum(middle_center);
Serial.begin(115200);
// ------------------- SD Card Initialization -------------------
SPI.begin(SD_SPI_SCK_PIN, SD_SPI_MISO_PIN, SD_SPI_MOSI_PIN, SD_SPI_CS_PIN);
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SD Init...", 64, 0);
Serial.println("SD Init...");
// Attempt SD card init (25MHz SPI speed); halt on failure
if (!SD.begin(SD_SPI_CS_PIN, SPI, 25000000)) {
M5.Display.clear();
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SD Error!", 64, 50);
Serial.println("SD Error!");
while (1); // Infinite loop = halt if SD card fails
} else {
M5.Display.clear();
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SD Ready", 64, 0);
Serial.println("SD Ready");
}
// ------------------- Speaker Configuration (I2S) -------------------
m5::speaker_config_t spk_cfg = {
.pin_data_out = SPK_I2S_PIN_DATA,
.pin_bck = SPK_I2S_PIN_BCLK,
.pin_ws = SPK_I2S_PIN_LRCK,
.sample_rate = output_samplerate,
.dma_buf_len = 256, // DMA buffer size (larger = smoother audio)
.dma_buf_count = 6, // Number of DMA buffers (double-buffering for stability)
.i2s_port = i2s_port_t::I2S_NUM_0 // Use I2S hardware port 0
};
M5.Speaker.config(spk_cfg); // Apply speaker settings
// Initialize speaker; halt on failure
if(!M5.Speaker.begin()){
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SPK Error!", 64, 50);
Serial.println("SPK Error!");
while (1);
} else {
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SPK Ready", 64, 15);
Serial.println("SPK Ready\n");
}
M5.Speaker.setVolume(128);
delay(1000);
// ------------------- Display Initial Instructions -------------------
M5.Display.clear();
M5.Display.setTextColor(TFT_YELLOW);
M5.Display.drawCenterString("Press Screen", 64, 0);
M5.Display.drawCenterString("to Play/Stop", 64, 15);
M5.Display.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE);
// ------------------- Load WAV File from SD Card -------------------
wavFile = SD.open("/twinkle_twinkle.wav", FILE_READ); // Open WAV file
// Halt if WAV file not found
if (!wavFile) {
M5.Display.drawCenterString("Find wav Error!", 64, 40);
Serial.println("Find wav Error!");
while (1);
} else {
M5.Display.drawCenterString("Find wav", 64, 40);
Serial.println("Find wav");
}
// Allocate buffer to store entire WAV file (avoids repeated SD reads)
wavBufferLen = wavFile.size(); // Get total file size
wavBuffer = (uint8_t*)malloc(wavBufferLen); // Allocate memory
// Halt if memory allocation fails
if (wavBuffer == nullptr) {
Serial.println("Memory Error!");
wavFile.close();
while (1);
} else {
wavFile.read(wavBuffer, wavBufferLen); // Read entire file into buffer
wavFile.close(); // Close file (buffer has all data now)
// Display WAV file size (convert bytes to KB)
String str_buf = String("Size:") + wavBufferLen/1024 + "KB";
M5.Display.drawCenterString(str_buf, 64, 55);
Serial.printf("Size: %d KB\n", wavBufferLen/1024);
}
M5.Display.drawCenterString("Stopped", 64, 80); // Show initial state (stopped)
}
void loop() {
M5.update(); // Update M5 hardware state (detect button presses, etc.)
if (M5.BtnA.wasClicked())
{
isPlaying = !isPlaying; // Flip play state (playing ↔ stopped)
M5.Display.fillRect(0, 80, 128, 48, TFT_BLACK);
if (isPlaying) {
M5.Display.drawCenterString("Playing", 64, 80);
M5.Speaker.playWav(wavBuffer, wavBufferLen, -1, -1, false);// Infinite loop
} else {
M5.Display.drawCenterString("Stopped", 64, 80);
M5.Speaker.stop();
}
}
}ESP32 I2S API ベース
cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442
#include <driver/i2s_std.h>
#include <endian.h> // For byte-order conversion (handles WAV's little-endian format)
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
#include <M5Unified.h>
#include <M5GFX.h>
// -------------------- Pin Definitions --------------------
// SPI pins for microSD card (connected to speaker module)
#define SD_SPI_CS_PIN -1 // CS pin not connected (hardware-enabled permanently)
#define SD_SPI_SCK_PIN GPIO_NUM_7 // SPI Clock pin
#define SD_SPI_MISO_PIN GPIO_NUM_8 // SPI MISO pin
#define SD_SPI_MOSI_PIN GPIO_NUM_6 // SPI MOSI pin
// I2S pins for speaker (audio output protocol)
#define SPK_I2S_PIN_DATA GPIO_NUM_38 // I2S audio data output pin
#define SPK_I2S_PIN_BCLK GPIO_NUM_5 // I2S bit clock pin
#define SPK_I2S_PIN_LRCK GPIO_NUM_39 // I2S LR clock pin
// ------------------- Audio Configuration -------------------
static constexpr const size_t output_samplerate = 44100; // Fixed audio sample rate (44.1kHz, standard for audio)
static bool isPlaying = false; // Flag to track play state (playing/stopped)
static std::atomic<uint8_t> volume(50); // Volume level (0-100%, atomic for thread safety)
static std::atomic<bool> isI2SEnabled(false); // Tracks I2S channel state (enabled/disabled, thread-safe)
// -------------------- Global Variables --------------------
File wavFile; // File object for the target WAV audio file
uint8_t* wavBuffer = nullptr; // Buffer to store entire WAV file (header + raw audio data)
size_t wavBufferLen = 0; // Total length of data in wavBuffer (bytes)
TaskHandle_t playTaskHandle = nullptr; // Task handle for audio playback (manages playback thread)
std::atomic<bool> stopPlay(false); // Playback stop flag (atomic to ensure thread safety)
// I2S hardware handle (ESP32-specific) for audio transmission
i2s_chan_handle_t tx_handle = nullptr;
#define I2S_PORT I2S_NUM_0 // I2S peripheral port (uses port 0)
// ------------------- Structure Definitions -------------------
// Playback parameters struct (passed to playback task, avoids scope issues)
typedef struct {
const uint8_t* data; // Start address of raw audio data
size_t data_len; // Total length of audio data (bytes)
uint16_t channel; // Number of channels (1 = mono, 2 = stereo)
uint16_t bit_per_sample; // Audio bit depth (8 or 16 bits)
uint32_t repeat; // Playback repeat count (0xFFFFFFFF = infinite loop)
} PlayParams;
// WAV file header struct (for parsing WAV format metadata, packed to avoid memory alignment gaps)
typedef struct __attribute__((packed)) {
char RIFF[4]; // File identifier ("RIFF" for WAV)
uint32_t chunk_size; // Total file size - 8 bytes (RIFF header size)
char WAVEfmt[8]; // Format identifier ("WAVEfmt " with trailing space)
uint32_t fmt_chunk_size; // Size of the format sub-chunk (16 for PCM format)
uint16_t audiofmt; // Audio format (1 = uncompressed PCM)
uint16_t channel; // Number of audio channels (1 = mono, 2 = stereo)
uint32_t sample_rate; // Audio sample rate (Hz)
uint32_t byte_per_sec;// Byte rate = sample_rate * channel * (bit_per_sample/8)
uint16_t block_size; // Block alignment = channel * (bit_per_sample/8)
uint16_t bit_per_sample;// Audio bit depth (8 or 16 bits)
} WavHeader;
// WAV data chunk struct (stores raw audio data, packed for alignment)
typedef struct __attribute__((packed)) {
char identifier[4]; // Chunk identifier ("data" for audio content)
uint32_t chunk_size; // Length of raw audio data (bytes)
uint8_t data[1]; // Flexible array: start of raw audio data
} WavDataChunk;
// Function declarations
bool playWav(const uint8_t* wav_data, size_t data_len, uint32_t repeat = 1, int channel = -1, bool stop_current_sound = false);
void stop();
static void playTask(void* params);
/**
* @brief Set audio volume level
* @param vol Target volume (0-100, 0 = mute, 100 = maximum). Constrained to valid range automatically.
*/
void setVolume(uint8_t vol) {
volume = constrain(vol, 0, 100); // Ensure volume stays within 0-100 (prevents clipping or invalid values)
}
void setup() {
M5.begin();
M5.Display.setFont(&fonts::FreeMonoBold9pt7b);
M5.Display.setTextDatum(middle_center);
Serial.begin(115200);
// ------------------- SD Card Initialization -------------------
SPI.begin(SD_SPI_SCK_PIN, SD_SPI_MISO_PIN, SD_SPI_MOSI_PIN, SD_SPI_CS_PIN);
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SD Init...", 64, 0);
Serial.println("SD Init...");
// Attempt SD card initialization (25MHz SPI speed for fast reads); halt on failure
if (!SD.begin(SD_SPI_CS_PIN, SPI, 25000000)) {
M5.Display.clear();
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SD Error!", 64, 50);
Serial.println("SD Error!");
while (1); // Infinite loop = halt system (SD card is critical for audio file access)
} else {
M5.Display.clear();
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SD Ready", 64, 0);
Serial.println("SD Ready");
}
// ------------------- I2S Speaker Configuration -------------------
// Step 1: Configure I2S channel (master role, DMA settings)
i2s_chan_config_t chan_cfg = {
.id = I2S_NUM_AUTO, // Auto-assign I2S peripheral (avoids port conflicts)
.role = I2S_ROLE_MASTER, // Act as I2S master (generates clock signals for speaker)
.dma_desc_num = 6, // Number of DMA descriptors (reduces underruns)
.dma_frame_num = 256, // Frames per DMA descriptor (balances latency and stability)
.auto_clear = true, // Auto-clear DMA buffers after transmission (cleaner)
};
// Create I2S transmit channel (tx_handle = send channel, NULL = no receive channel)
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(i2s_new_channel(&chan_cfg, &tx_handle, NULL));
// Step 2: Configure standard I2S parameters (clock, slots, GPIO mapping)
i2s_std_config_t std_tx_cfg = {
.clk_cfg = I2S_STD_CLK_DEFAULT_CONFIG(output_samplerate), // Auto-generate clock for 44.1kHz
.slot_cfg = I2S_STD_MSB_SLOT_DEFAULT_CONFIG(I2S_DATA_BIT_WIDTH_16BIT, I2S_SLOT_MODE_MONO),
// Use 16-bit data width, mono output (matches speaker hardware)
.gpio_cfg = {
.mclk = I2S_GPIO_UNUSED, // MCLK not used (speaker doesn't require master clock)
.bclk = SPK_I2S_PIN_BCLK, // Map BCLK to configured GPIO
.ws = SPK_I2S_PIN_LRCK, // Map LRCK to configured GPIO
.dout = SPK_I2S_PIN_DATA, // Map data output to configured GPIO
.din = I2S_GPIO_UNUSED, // No audio input needed (playback-only)
.invert_flags = {
.bclk_inv = false, // Do not invert BCLK (standard polarity)
.ws_inv = false // Do not invert LRCK (standard polarity)
},
}
};
// Initialize I2S channel with standard mode settings
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(i2s_channel_init_std_mode(tx_handle, &std_tx_cfg));
M5.Display.drawCenterString("SPK Ready", 64, 15);
delay(1000); // Short delay to stabilize hardware
// ------------------- Display Initial Instructions -------------------
M5.Display.clear();
M5.Display.setTextColor(TFT_YELLOW); // Highlight instructions in yellow
M5.Display.drawCenterString("Press Screen", 64, 0);
M5.Display.drawCenterString("to Play/Stop", 64, 15);
M5.Display.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE); // Reset text color to white for status
// ------------------- Load WAV File from SD Card -------------------
wavFile = SD.open("/twinkle_twinkle.wav", FILE_READ); // Open WAV file in read-only mode
// Halt if WAV file is not found (critical error)
if (!wavFile) {
M5.Display.drawCenterString("Find wav Error!", 64, 40);
Serial.println("Find wav Error!");
while (1);
} else {
M5.Display.drawCenterString("Find wav", 64, 40);
Serial.println("Find wav");
}
// Allocate buffer to store entire WAV file (avoids repeated SD card reads during playback)
wavBufferLen = wavFile.size(); // Get total file size (bytes)
wavBuffer = (uint8_t*)malloc(wavBufferLen); // Allocate memory for buffer
// Halt if memory allocation fails (not enough RAM for audio data)
if (wavBuffer == nullptr) {
Serial.println("Memory Error!");
wavFile.close();
while (1);
} else {
wavFile.read(wavBuffer, wavBufferLen); // Read entire file into buffer
wavFile.close(); // Close file (buffer now holds all data)
// Display WAV file size (convert bytes to KB for readability)
String str_buf = String("Size:") + wavBufferLen/1024 + "KB";
M5.Display.drawCenterString(str_buf, 64, 55);
Serial.printf("Size: %d KB\n", wavBufferLen/1024);
}
M5.Display.drawCenterString("Stopped", 64, 80); // Show initial state (stopped)
}
void loop() {
M5.update(); // Update M5 hardware state (detect button presses, touch, etc.)
// Toggle play/stop when Button A is clicked
if (M5.BtnA.wasClicked())
{
isPlaying = !isPlaying; // Flip play state (playing ↔ stopped)
M5.Display.fillRect(0, 80, 128, 48, TFT_BLACK); // Clear previous status text
if (isPlaying) {
M5.Display.drawCenterString("Playing", 64, 80);
playWav(wavBuffer, wavBufferLen, -1, -1, true);// Infinite loop
} else {
M5.Display.drawCenterString("Stopped", 64, 80);
stop(); // Stop ongoing playback
}
}
}
// ------------------- Playback Task Function -------------------
// Core audio playback task: Parses audio data, applies volume, and sends to I2S hardware
static void playTask(void* params) {
// Unpack playback parameters (passed from playWav() function)
PlayParams* p = (PlayParams*)params;
// Calculate base audio parameters
const size_t sample_byte = p->bit_per_sample / 8; // Bytes per single sample (1 for 8-bit, 2 for 16-bit)
const size_t total_samples = p->data_len / (sample_byte * p->channel); // Total mono-equivalent samples
size_t data_idx = 0; // Current position in raw audio data (bytes)
uint32_t repeat_cnt = 0; // Number of completed playback loops
// I2S output buffer (16-bit mono, 256 samples per buffer = reduces I2S call frequency)
const size_t I2S_BUF_SAMPLES = 256;
int16_t i2s_buf[I2S_BUF_SAMPLES] = {0};
// Enable I2S channel (starts clock signals and prepares for data transmission)
esp_err_t err = i2s_channel_enable(tx_handle);
if (err == ESP_OK) {
isI2SEnabled = true; // Mark I2S as active (for thread-safe state checks)
} else {
Serial.printf("I2S Enable Failed: %s\n", esp_err_to_name(err));
goto task_cleanup; // Jump to resource cleanup if I2S enable fails
}
// Main playback loop (runs until stop flag is set or repeat count is reached)
do {
size_t buf_idx = 0; // Current position in I2S output buffer
// Fill I2S buffer with processed audio data (until buffer is full or stop is triggered)
while (buf_idx < I2S_BUF_SAMPLES && !stopPlay) {
// Check if end of audio data is reached; handle loop logic
if (data_idx >= p->data_len) {
// Exit loop if repeat count is exhausted (skip for infinite loop)
if (p->repeat != 0xFFFFFFFF && repeat_cnt >= p->repeat - 1) {
break;
}
data_idx = 0; // Reset data index to start of audio (loop)
repeat_cnt++; // Increment loop counter
}
// Step 1: Read raw sample and convert to 16-bit (uniform processing)
int16_t sample = 0;
if (p->bit_per_sample == 8) {
// 8-bit WAV: Unsigned (0-255) → signed (-128-127) → scale to 16-bit (-32768-32767)
uint8_t raw = p->data[data_idx];
sample = (int16_t)(raw - 128) << 8;
} else if (p->bit_per_sample == 16) {
// 16-bit WAV: Little-endian → host byte-order (ESP32 is little-endian, but ensures compatibility)
int16_t raw = le16toh(*(const int16_t*)(p->data + data_idx));
sample = raw;
}
// Step 2: Convert stereo to mono (if needed)
if (p->channel == 2) {
int16_t sample_right = 0;
// Read right channel sample (same conversion as left channel)
if (p->bit_per_sample == 8) {
uint8_t raw_r = p->data[data_idx + 1];
sample_right = (int16_t)(raw_r - 128) << 8;
} else if (p->bit_per_sample == 16) {
int16_t raw_r = le16toh(*(const int16_t*)(p->data + data_idx + 2));
sample_right = raw_r;
}
// Average left/right channels (avoids clipping, maintains volume)
sample = (sample + sample_right) / 2;
data_idx += sample_byte; // Skip right channel data (already processed)
}
// Step 3: Apply volume control (0-100% → 0.0-1.0 gain factor)
float vol = volume.load() / 100.0f;
sample = (int16_t)(sample * vol);
// Step 4: Store processed sample in I2S buffer
i2s_buf[buf_idx] = sample;
buf_idx++;
data_idx += sample_byte; // Move to next sample in raw data
}
// Send buffer to I2S hardware (only if buffer has data and stop is not triggered)
if (buf_idx > 0 && !stopPlay) {
size_t bytes_written = 0;
err = i2s_channel_write(
tx_handle,
i2s_buf,
buf_idx * sizeof(int16_t), // Total bytes to write (samples × 2 bytes/sample)
&bytes_written,
pdMS_TO_TICKS(100) // Timeout (100ms, prevents permanent blocking)
);
if (err != ESP_OK) {
Serial.printf("I2S Write Failed: %s\n", esp_err_to_name(err));
break; // Exit playback on write failure
}
} else {
break; // Exit if no data or stop flag is set
}
} while (!stopPlay);
// ------------------- Task Resource Cleanup -------------------
// Ensure no memory leaks or hardware resource locks
task_cleanup:
// Disable I2S only if it was previously enabled
if (isI2SEnabled) {
i2s_channel_disable(tx_handle);
isI2SEnabled = false; // Reset I2S state flag
}
vPortFree(p); // Free memory allocated for playback parameters
playTaskHandle = nullptr; // Reset task handle (indicates task is done)
isPlaying = false; // Reset global play state
// Update display to show "Stopped" (matches user expectation)
M5.Display.fillRect(0, 80, 128, 48, TFT_BLACK);
M5.Display.drawCenterString("Stopped", 64, 80);
vTaskDelete(nullptr); // Delete the current task (frees task stack)
}
// ------------------- Public Interface: Play WAV File -------------------
/**
* @brief Starts playback of a WAV file from a buffer
* @param wav_data Pointer to WAV file data (header + audio)
* @param data_len Total length of wav_data (bytes)
* @param repeat Number of playback loops ( -1 = infinite, 1 = single play)
* @param channel Force channel mode (unused here, retained for compatibility)
* @param stop_current_sound Stop ongoing playback before starting new
* @return true if playback starts successfully, false otherwise
*/
bool playWav(const uint8_t* wav_data, size_t data_len, uint32_t repeat, int channel, bool stop_current_sound) {
// Step 1: Stop current playback if required (prevents audio overlap)
if (stop_current_sound && playTaskHandle != nullptr) {
stop();
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(10)); // Short delay to ensure task cleanup completes
}
// Step 2: Validate input parameters (prevent invalid data access)
if (wav_data == nullptr || data_len < sizeof(WavHeader)) {
Serial.println("Invalid WAV Data (null or too short)");
return false;
}
// Step 3: Parse WAV header and validate format compatibility
WavHeader* wav_hdr = (WavHeader*)wav_data;
// Check if file is a valid WAV (RIFF and WAVEfmt identifiers)
if (memcmp(wav_hdr->RIFF, "RIFF", 4) != 0 || memcmp(wav_hdr->WAVEfmt, "WAVEfmt ", 8) != 0) {
Serial.println("Not a Standard WAV File");
return false;
}
// Only support uncompressed PCM format (most common WAV type)
if (wav_hdr->audiofmt != 1) {
Serial.println("Only PCM Format WAV Supported");
return false;
}
// Only support 8/16-bit depth (matches I2S configuration)
if (wav_hdr->bit_per_sample != 8 && wav_hdr->bit_per_sample != 16) {
Serial.println("Only 8/16-bit WAV Supported");
return false;
}
// Ensure WAV sample rate matches I2S configuration (prevents pitch distortion)
if (wav_hdr->sample_rate != output_samplerate) {
Serial.printf("WAV Sample Rate Mismatch: WAV=%d, I2S=%d\n", wav_hdr->sample_rate, output_samplerate);
return false;
}
// Step 4: Locate the "data" chunk (skip non-audio chunks like "LIST" or "INFO")
WavDataChunk* data_chunk = (WavDataChunk*)(wav_data + sizeof(WavHeader));
while (memcmp(data_chunk->identifier, "data", 4) != 0) {
// Calculate offset to next chunk (account for chunk header + data)
size_t next_offset = sizeof(WavDataChunk) - 1 + data_chunk->chunk_size;
data_chunk = (WavDataChunk*)((uint8_t*)data_chunk + next_offset);
// Prevent out-of-bounds access (stop if chunk exceeds input data length)
if ((uint8_t*)data_chunk - wav_data >= data_len) {
Serial.println("WAV Data Chunk Not Found");
return false;
}
}
// Step 5: Calculate actual usable audio data length (prevent buffer overflow)
size_t actual_data_len = data_chunk->chunk_size;
if ((uint8_t*)data_chunk + sizeof(WavDataChunk) - 1 + actual_data_len > wav_data + data_len) {
actual_data_len = data_len - ((uint8_t*)data_chunk - wav_data + sizeof(WavDataChunk) - 1);
Serial.printf("WAV Data Truncated to %d Bytes\n", actual_data_len);
}
if (actual_data_len == 0) {
Serial.println("Empty WAV Data Chunk");
return false;
}
// Step 6: Allocate memory for playback parameters (passed to task)
PlayParams* params = (PlayParams*)pvPortMalloc(sizeof(PlayParams));
if (params == nullptr) {
Serial.println("Failed to Allocate Playback Params");
return false;
}
// Populate playback parameters
params->data = data_chunk->data;
params->data_len = actual_data_len;
params->channel = wav_hdr->channel;
params->bit_per_sample = wav_hdr->bit_per_sample;
params->repeat = (repeat == (uint32_t)-1) ? 0xFFFFFFFF : repeat; // Map -1 to infinite loop
// Step 7: Create playback task (runs on core 0, high priority for smooth audio)
stopPlay = false; // Reset stop flag before starting new task
if (xTaskCreatePinnedToCore(
playTask, // Task function to execute
"WavPlayTask", // Task name (for debug)
4096, // Task stack size (4KB = enough for audio processing)
params, // Parameters passed to task
5, // Task priority (higher than loop() to avoid underruns)
&playTaskHandle, // Task handle (tracks task state)
0 // Pin to core 0 (ESP32 core division for stability)
) != pdPASS) {
Serial.println("Failed to Create Playback Task");
vPortFree(params); // Free params if task creation fails
return false;
}
// Step 8: Update global state to indicate playback is active
isPlaying = true;
return true;
}
// ------------------- Public Interface: Stop Playback -------------------
/**
* @brief Stops ongoing audio playback and cleans up resources
*/
void stop() {
// Step 1: Trigger stop flag (playTask() will detect this and exit)
stopPlay = true;
// Step 2: Accelerate stop by disabling I2S (if active) and waiting for task cleanup
if (playTaskHandle != nullptr) {
if (isI2SEnabled) {
i2s_channel_disable(tx_handle);
isI2SEnabled = false; // Reset I2S state to prevent re-enable
}
// Wait up to 100ms for task to delete (avoids blocking main loop)
for (int i = 0; i < 10 && playTaskHandle != nullptr; i++) {
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(10));
}
}
// Step 3: Reset global state and update display
isPlaying = false;
M5.Display.fillRect(0, 80, 128, 48, TFT_BLACK); // Clear previous status
M5.Display.drawCenterString("Stopped", 64, 80); // Show stopped state
}3. コンパイルとアップロード
- 1. ダウンロードモード:デバイスごとにプログラム書き込み前にはダウンロードモードにする必要があります。使用する主制御デバイスによって手順が異なる場合があります。詳細は Arduino IDE 入門チュートリアル ページ下部のデバイス別プログラム書き込みチュートリアル一覧を参照し、具体的な操作方法を確認してください。
- AtomS3R の場合、リセットボタンを長押し(約 2 秒)し、内部の緑色 LED が点灯したらボタンを離します。この時点でデバイスはダウンロードモードに入り、書き込み待機状態になります。

- 2. デバイスポートを選択し、Arduino IDE 左上のコンパイル&アップロードボタンをクリックして、プログラムがコンパイルされデバイスにアップロードされるまで待ちます。
4. スピーカー機能の動作例
- 1. 基本使用
このサンプルでは、スピーカーから一定間隔でビープ音が繰り返し鳴ります。\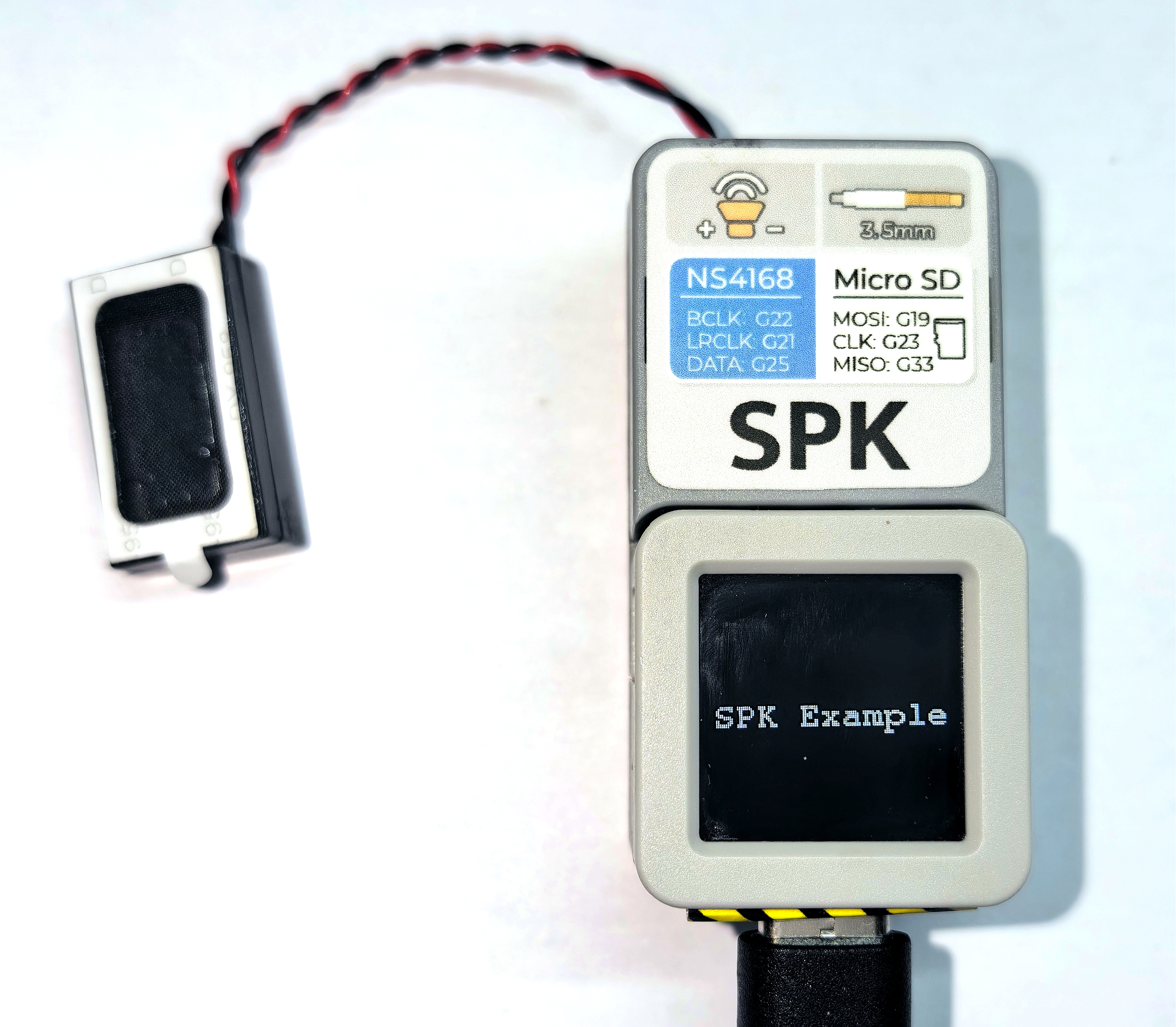 
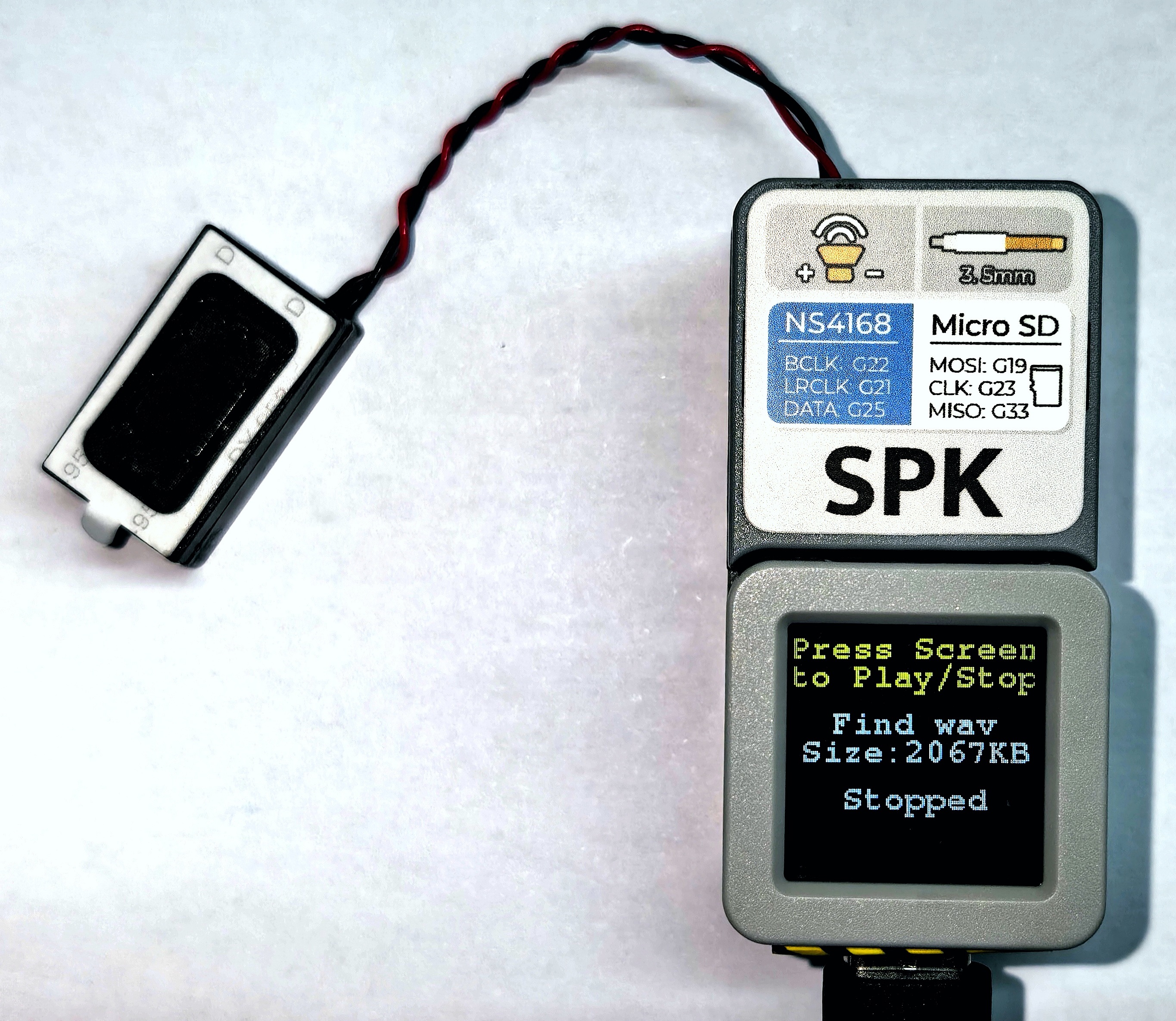
- 2.SD カード内のオーディオファイルを再生
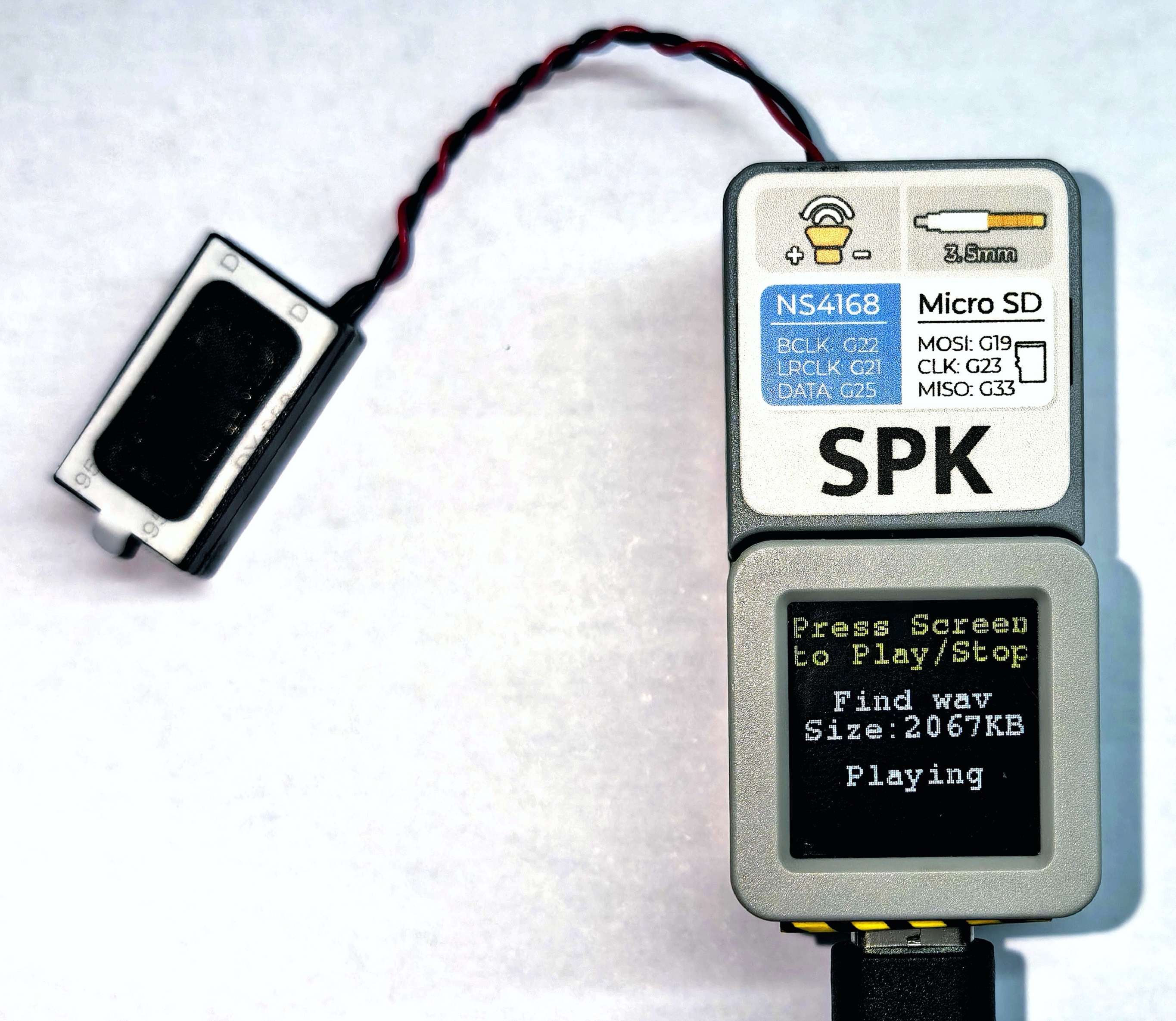
メインデバイスの画面をタップすることで、オーディオの再生と停止を切り替えることができます。再生 / 停止状態ではスクリーンに以下のように表示されます。
(このサンプルでは、SD カード内の twinkle_twinkle.wav という名前の wav ファイルを再生します。こちらからダウンロードでき、ダウンロード後に拡張子を .wav に変更してください)

5. API
このチュートリアルでは M5Unified ライブラリの Speaker_Class を使用しています。その他の関連 API については以下のドキュメントを参照してください:
